
Can sepsis and SIRS
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome is an inflammatory state affecting the whole body. It is the body's response to an infectious or noninfectious insult. Although the definition of SIRS refers to it as an "inflammatory" response, it actually has pro- and anti-inflammatory components.
Full Answer
How do you Code Sepsis and SIRS due to infection?
The guidelines also state that “sepsis generally refers to SIRS due to infection.” For example, if the physician documented sepsis or SIRS due to a virus, code 038.8 should be sequenced first followed by code 995.91 and a code for the specific viral infection (such as 487.1 for influenza).
What is the difference between SIRS and sepsis/septic shock?
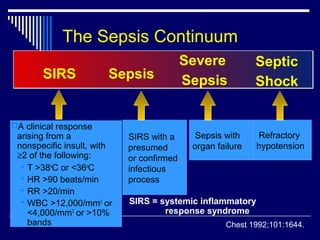
• SIRS is a systemic response to infection, trauma or burns, or other insult (such as cancer), with symptoms including fever, tachycardia, tachypnea, and leukocytosis. • Sepsis is SIRS due to infection. • Severe sepsis is sepsis with associated acute organ dysfunction. • Septic shock refers to circulatory failure associated with severe sepsis.
What is the CPT code for sepsis?
Coding tips: When sepsis is due to a procedural complication, sequence the complication code first, followed by the code for the specific infection. If the patient has severe sepsis, code R65.2- along with the codes for each organ dysfunction. If the exact causative organism is known, code for the infectious agent (guidelines I.C.1.5.b-c).
Can SIRS be linked to an infection?
Look in the ICD-9-CM alphabetic index under SIRS, which states the following: There is no an automatic linkage between SIRS and infections like we have with diabetes with osteomyelitis or gangrene. The physician must explicitly state what condition causes the SIRS.
Can you code both SIRS and sepsis together?
According to AHA Coding Clinic® (Vol. 1, No. 3, p. 4), when a patient has SIRS and a localized infection, sepsis can no longer be coded and an ICD-10-CM code for sepsis cannot be assigned unless the physician specifically documents sepsis.
Can you code SIRS without sepsis?
ICD-9-CM Coding However, there are many noninfectious conditions in which SIRS can develop. According to coding guidelines, the code for SIRS (995.90 to 995.94) should never be sequenced as a principal diagnosis. If SIRS is caused by an infection, coding rules require septicemia (038.
Is sepsis and SIRS the same thing?
Sepsis is a systemic response to infection. It is identical to SIRS, except that it must result specifically from infection rather than from any of the noninfectious insults that may also cause SIRS (see the image below).
Can you code sepsis and severe sepsis?
The coding of severe sepsis requires a minimum of two codes: first a code for the underlying systemic infection, followed by a code from subcategory R65. 2, Severe sepsis. If the causal organism is not documented, assign code A41. 9, Sepsis, unspecified organism, for the infection.
Does sepsis always have to be the principal diagnosis?
Sepsis as Principal Diagnosis Is sepsis always sequenced as the principal diagnosis when it is present on admission? Some may say yes, because after all, that's what is stated in the official coding guidelines. However, my answer to this question is no, not always.
When coding for SIRS in a patient WHO has not developed an infection you would code in which sequence?
If the patient is admitted for the localized infection and the sepsis/severe sepsis/SIRS does not develop until after admission, the localized infection should be sequenced first, followed by the code for the systemic infection and then by 995.91 or 995.92 as secondary diagnoses.
How does SIRS turn into sepsis?
When SIRS occurs as a result of infection, it is termed sepsis. Severe sepsis occurs when there is evidence of organ hypoperfusion or dysfunction including decreased urine output, altered mental status, and disseminated intravascular coagulation.
What is the SIRS criteria for sepsis?
Four SIRS criteria were defined, namely tachycardia (heart rate >90 beats/min), tachypnea (respiratory rate >20 breaths/min), fever or hypothermia (temperature >38 or <36 °C), and leukocytosis, leukopenia, or bandemia (white blood cells >1,200/mm3, <4,000/mm3 or bandemia ≥10%).
What are the key differences between systemic inflammatory response syndrome SIRS and sepsis?
Background. Sepsis is an infection which has evoked a systemic inflammatory response. Clinically, the Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) is identified by two or more symptoms including fever or hypothermia, tachycardia, tachypnoea and change in blood leucocyte count.
What are two coding principles?
10 Basic Programming Principles Every Programmer Must KnowKeep It Simple, Stupid (KISS) ... Write DRY Code. ... Open/Closed. ... Composition Over Inheritance. ... Single Responsibility. ... Separation of Concerns. ... You Aren't Going to Need It (YAGNI) ... Document Your Code.More items...•
When do you code severe sepsis?
Severe sepsis requires at least 2 ICD-10-CM codes; a code for the underlying systemic infection and a code from category R65. 2 Severe Sepsis; you should also assign a code(s) for the acute organ dysfunction if documented; Codes R65. 20 and R65.
How do you code sepsis severe sepsis and septic shock?
Septic shock – Code first the underlying systemic infection, such as 038.0 (Streptococcal septicemia), then code 995.92 for severe sepsis, then code 785.52 for septic shock and finally assign the code for the specific type of organ failure inherent to septic shock, such as 584.9 for acute renal failure.
What are SIRS criteria?
Clinically, the Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) is the occurrence of at least two of the following criteria: fever >38.0°C or hypothermia <36.0°C, tachycardia >90 beats/minute, tachypnea >20 breaths/minute, leucocytosis >12*109/l or leucopoenia <4*109/l [1,2].
Is SIRS a medical diagnosis?
A serious condition in which there is inflammation throughout the whole body. It may be caused by a severe bacterial infection (sepsis), trauma, or pancreatitis. It is marked by fast heart rate, low blood pressure, low or high body temperature, and low or high white blood cell count.
Do we still use SIRS criteria?
Although still in use clinically, it is important to note that systemic inflammatory response syndrome(SIRS) as a definition has been abandoned since 2016.
What is the ICD 10 code for SIRS?
There are two codes for SIRS of a non-infectious origin in ICD-10-CM, with assignment depending on the presence or absence of associated organ dysfunction: R65. 10, systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) of non-infectious origin without acute organ dysfunction and R65.
What is the code for streptococcal septicemia?
Provider documentation of streptococcal septicemia is considered a generalized infection caused by a streptococcal organism, and only code 038.0 should be assigned. The coder may also want to query the physician in order to determine if the patient has sepsis.
What is severe sepsis?
Severe sepsis is defined as SIRS due to an infection that progresses to organ dysfunction, such as kidney or heart failure. In order to code a patient with severe sepsis, the documentation within the medical record should clearly indicate that organ failure is related to sepsis. If the documentation is not clear, always query the physician for accurate coding.
What is the definition of sepsis?
Sepsis is defined as SIRS due to an infection. The inclusion term sepsis was added to code 995.91, SIRS due to infectious process without organ dysfunction. Although sepsis and septicemia may be used interchangeably by the provider, from a coding perspective they are not synonymous. Coders should query the physician for clarification when appropriate.
What is urosepsis in medical terms?
Providers often use the term urosepsis to describe both septicemia and a urinary tract infection. For accurate coding, coders should determine if the term urosepsis is being used to describe sepsis or urinary tract infection. However, if a coder finds conflicting documentation within the medical record stating both a diagnosis of urosepsis and septicemia, the physician should be queried to determine which diagnosis is intended.
What is septic shock?
Septic shock generally refers to circulatory failure associated with severe sepsis, and therefore represents a type of acute organ dysfunction. 5 Therefore, septic shock meets the definition for severe sepsis. Cases of septic shock should follow coding and sequencing guidelines for severe sepsis. In addition to codes for severe sepsis, code 785.52, Septic shock, should also be placed as a secondary diagnosis.
What is systemic inflammatory response syndrome?
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) is defined as a clinical response to an insult, infection, or trauma that includes a systemic inflammation as well as elevated or reduced temperature, rapid heart rate, rapid respiration, and elevated white blood count. According to the American College of Chest Physicians and the Society of Critical Care Medicine, the clinical manifestations of SIRS include:
Can coding a chart with sepsis be challenging?
Coding a chart with a sepsis diagnosis can prove challenging for coders . The coding guidelines for sepsis as well as ambiguous provider documentation can often mean an extended length of time reviewing a chart only to place it on hold for a physician query. This column outlines the clinical differences between systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock as well as coding guidelines for each diagnosis.
How many codes are needed for sepsis?
A minimum of two codes are required when coding sepsis: a code for the underlying systemic infection and a code from subcategory 995.9x for SIRS.
What is the cause of severe sepsis?
Severe sepsis is SIRS due to septicemia with organ dysfunction which may be cardiovascular, renal, respiratory, hepatic, central nervous system, or metabolic acidosis.
What is septic shock?
Septic shock is associated with severe sepsis and circulatory failure or acute organ dysfunction. Frequently, a patient is suspected of having septicemia and is treated for the condition even though the blood cultures may not be positive.
What is the systemic response to infection, trauma, burns, or other cause such as cancer?
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) refers to the systemic response to infection, trauma, burns, or other cause such as cancer with symptoms that include fever, tachycardia, tachypnea, and leukocytosis. Sepsis is SIRS due to an infection that can originate anywhere in the body and be triggered by a bacterial, viral, parasitic, ...
Is septicemia the same as sepsis?
Septicemia and Sepsis are often used interchangeably by physicians; however, they are not the same. Septicemia refers to a systemic disease identified by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other organisms in the blood. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) refers to the systemic response to infection, trauma, burns, ...
Can negative blood cultures be used to diagnose septicemia?
Negative or inconclusive blood cultures do not preclude a diagnosis of septicemia in patients with clinical evidences of the condition. Careful review of the medical record, understanding the pathology of the infections in the Septic Continuum, and following the coding guidelines are necessary to ensure accurate code assignment.
What is the code for sepsis?
Sepsis requires two codes to classify the condition. The first is the systemic infection code and is usually found in category 038. However, it may be found elsewhere depending on the organism. For example, sepsis due to candidiasis is classified to codes 112.5 and 995.91. Infection is not restricted to only bacterial infection as it is relates ...
What is sepsis sequenced?
If sepsis is present on admission, it will be sequenced as the principal diagnosis over the localized infection (eg, pneumonia, cellulitis, urinary tract infection) causing the sepsis. If the documentation is unclear as to whether the sepsis was present on admission, the physician should be queried for clarification.
What is the code for septic shock?
Documentation of septic shock is assumed to be severe sepsis, and coding guidelines indicate that the underlying infection should be listed first (typically a code from category 038) followed by severe sepsis (995.92) and then septic shock (785.52).
What is septicemia in medical terms?
Coding guidelines state, “Septicemia generally refers to a systemic disease associated with the presence of pathological microorganisms or toxins in the blood , which can include bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other organisms.”. The guidelines also state that “sepsis generally refers to SIRS due to infection.”.
How many people with sepsis have a positive blood culture?
Only 30% to 50% of patients with sepsis have positive blood culture results.
What biological markers are used to identify sepsis?
Certain biological markers were identified (eg, interleukin 6, procalcitonin, C-reactive protein) as pointing to the inflammatory response in sepsis patients. However, due to a lack of epidemiological data, there is no recommendation for inclusion of those criteria.
What is the treatment for severe sepsis?
Treatment of sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock is dependent on the organism (s) involved and clinical progression but may include the following: • broad-spectrum IV antibiotics (eg, cefepime, ceftazidime, ciprofloxacin, Levaquin, moxifloxacin, timentin, tobramycin, vancomycin, and Zosyn);
What happens if a physician does not document that a patient is systemically ill?
When the physician does not document that the patient was systemically ill, he or she is losing one of the major clinical indicators that would support him or her during a retrospective review.
Is there an automatic linkage between SIRS and infections?
There is no an automatic linkage between SIRS and infections like we have with diabetes with osteomyelitis or gangrene. The physician must explicitly state what condition causes the SIRS.
Is SIRS a synonym of sepsis?
A: SIRS is not synonymous with sepsis. SIRS is sepsis only when the physician documents it as being due to an underlying infection. Report ICD-9 code 995.90 for SIRS alone. Follows the usual coding conventions for sepsis when reporting SIRS due to an infection.
Can SIRS and urinary tract infection be linked?
Note that just because SIRS and a urinary tract infection coexist does not mean that they’re linked. Look in the ICD-9-CM alphabetic index under SIRS, which states the following:
What is the code for sepsis?
When sepsis or severe sepsis develops during the encounter (it was not present on admission), the systemic infection code and code 995.91 or 995.92 should be assigned as secondary diagnoses.
What is the code for streptococcal sepsis?
If the documentation in the record states streptococcal sepsis, codes 038.0, Streptococcal septicemia, and code 995.91 should be used, in that sequence.
What is the secondary code for Pdx?
The sepsis (038.X) will lead your Pdx (and DRG). Then UTI and 995 code will be secondary.
Should the provider be asked about sepsis?
whether the sepsis or severe sepsis was present on admission, the provider should be queried.
Is urosepsis a nonspecific term?
4) Bacterial Sepsis and Septicemia The term urosepsis is a nonspecific term. If that is the only term documented then only code 599.0 should be assigned based on the default for the term in the ICD-9-CM index, in addition to the code for the causal organism if known.
What is the code range for sepsis?
In Chapter 1 the code range A40 – A41.9, classifies several types of bacterial sepsis but also includes “Sepsis, unspecified organism”. When assigning a code for SIRS and Severe Sepsis, Chapter 18 is where the codes are located:
What is the code for sepsis due to E. coli?
If the organism causing the Sepsis is documented, use a code in subcategory A41 (e.g., A41.51 Sepsis due to E. coli);
What is the definition of sepsis 3?
In 2016, researchers and clinical experts published the consensus for a Sepsis -3 definition, stating: Sepsis should be defined as life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection.
What is the SIRS criteria?
A medical consensus on SIRS and Sepsis was published in 1991-1992 (Referred to as Sepsis 1), the SIRS criteria included two or more of the following (keep in mind that each patient is different so the signs/symptoms will vary): Fever/Temperature >38°C or <36°C (some research states >38.3°C) Tachycardia/Heart rate >90/min.
What would happen if SIRS was present?
According to this initial research study, if SIRS was present and there was an infection then a diagnosis of “Sepsis” could be made.
What is the ICD-10 code for severe sepsis?
A code from ICD-10-CM code subcategory R65.2- (severe sepsis) would not be reported unless the physician has documented severe sepsis or an acute organ dysfunction;
Is there clinical research on SIRS?
There continues to be significant clinical research and work to standardize clinical terminology and clinical criteria, so we can expect more attention surrounding SIRS and Sepsis.
