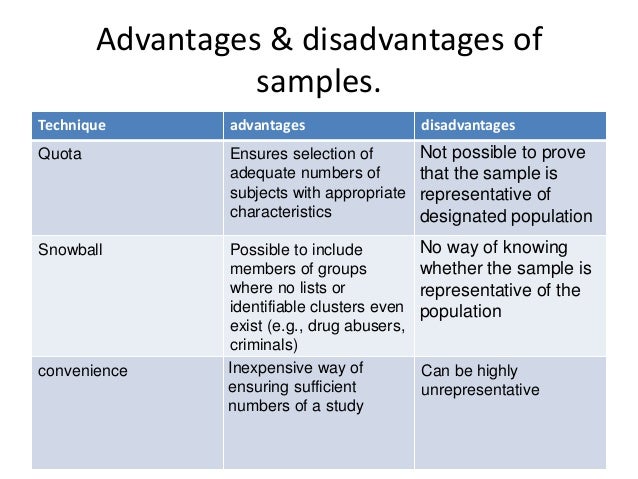
Qualitative researchers can also use snowball sampling techniques to identify study participants. In snowball sampling, a researcher identifies one or two people they would like to include in their study but then relies on those initial participants to help identify additional study participants. When can snowball sampling be possibly used?
What are the disadvantages of snowball sampling?
What are the limitations of snowball sampling?
- The researcher has little control over the sampling method.
- Representativeness of the sample is not guaranteed.
- Sampling bias is also a fear of researchers when using this sampling technique.
What is the purpose of snowball sampling?
There are some advantages to using snowball sampling, including:
- Researchers can reach subjects in a particular population that would otherwise be difficult or impossible to reach.
- Snowball sampling is low-cost and easy to implement.
- Snowball sampling doesn’t require a research team to hire recruiters for the study since the initial subjects act as the recruiters who bring in additional subjects.
What is Snowball methodology?
The snowball method is a common debt repayment strategy. This method focuses on paying down your smallest debt balance before moving onto larger ones. The snowball method is all about building momentum as you pay off debt. It may be a good solution to better manage your finances over time.
What is the ideal sample size in qualitative research?
What is the ideal sample size in qualitative research? We’ll answer it this time. Based on studies that have been done in academia on this very issue, 30 seems to be an ideal sample size for the most comprehensive view, but studies can have as little as 10 total participants and still yield extremely fruitful, and applicable, results.
Is snowball sampling qualitative or quantitative?
qualitative researchSnowball sampling is a commonly employed sampling method in qualitative research, used in medical science and in various social sciences, including sociology, political science, anthropology and human geography [1–3].
What research design uses snowball sampling?
In sociology and statistics research, snowball sampling (or chain sampling, chain-referral sampling, referral sampling) is a nonprobability sampling technique where existing study subjects recruit future subjects from among their acquaintances. Thus the sample group is said to grow like a rolling snowball.
Why is snowball sampling rarely used?
Disadvantages of Snowball Sampling Representativeness of the sample is not guaranteed. The researcher has no idea of the true distribution of the population and of the sample. Sampling bias is also a fear of researchers when using this sampling technique. Initial subjects tend to nominate people that they know well.
Can purposive sampling be used in quantitative research?
You may use purposive sampling for your quantitative research if your objective is to generalize the data to develop a model or module for example if you're doing need analysis before starting your research.
When should snowball sampling be used?
Snowball sampling is used when researchers have difficulty finding participants for their studies. This typically occurs in studies on hidden populations, such as criminals, drug dealers or sex workers, as these individuals tend to be difficult for researchers to access.
What are the limitations of snowball sampling?
Disadvantages of snowball sampling Since snowball sampling does not select units for inclusion in the sample based on random selection, unlike probability sampling techniques, it is impossible to determine the possible sampling error and make statistical inferences from the sample to the population.
Can I use both purposive and snowball sampling?
In sociology, "snowball sampling" refers to a non-probability sampling technique (which includes purposive sampling) in which a researcher begins with a small population of known individuals and expands the sample by asking those initial participants to identify others that should participate in the study.
What are the pros and cons of snowball sampling?
Pros and Cons: Non-random: A snowball sample will likely provide results that are hard to generalize beyond the sample studied. Slow: Because snowball sampling relies on each participant to recommend others, the data collection process is typically slow when compared to other methods.
What is the difference between purposive and snowball sampling?
In purposive sampling, the researcher uses their discretion to select suitable participants for the study, based on their knowledge of the context of the systematic investigation. However, in snowball sampling, the researcher depends on existing research participants to help identify other potential subjects.
Which sampling method is best for quantitative research?
Probability samplingProbability sampling means that every member of the population has a chance of being selected. It is mainly used in quantitative research. If you want to produce results that are representative of the whole population, probability sampling techniques are the most valid choice.
What are quantitative sampling methods?
The quantitative research sampling method is the process of selecting representable units from a large population. Quantitative research refers to the analysis wherein mathematical, statistical, or computational method is used for studying the measurable or quantifiable dataset.
What is sampling strategy in quantitative research?
What are sampling strategies? The strategy is the plan you set forth to be sure that the sample you use in your research study represents the population from which you drew your sample.
What is snowball sampling in qualitative research?
Snowball sampling is a sampling method used by researchers to generate a pool of participants for a research study through referrals made by individuals who share a particular characteristic of research interest with the target population. It is also referred to as chain sampling or chain referral sampling.
How would you classify this kind of sampling snowball sampling?
Snowball sampling is a non-probability sampling method. It doesn't have the probability involved, with say, simple random sampling (where the odds are the same for any particular participant being chosen). Rather, the researchers used their own judgment to choose participants.
Can you use purposive and snowball sampling?
In sociology, "snowball sampling" refers to a non-probability sampling technique (which includes purposive sampling) in which a researcher begins with a small population of known individuals and expands the sample by asking those initial participants to identify others that should participate in the study.
Which of the method is generally used in qualitative research?
What are some qualitative research methods? The three most common qualitative methods, explained in detail in their respective modules, are participant observation, in-depth interviews, and focus groups. Each method is particularly suited for obtaining a specific type of data.
What is snowball sampling?
Snowball sampling (also known as chain-referral sampling) is a non-probability (non-random) sampling method used when characteristics to be possessed by samples are rare and difficult to find.
What is the most difficult stage of sampling?
Establish a contact with one or two initial cases from the sampling frame. This stage is usually the most difficult one.
Is there a guarantee about the representativeness of a sample?
There is no guarantee about the representativeness of samples. It is not possible to determine the actual pattern of distribution of population. It is not possible to determine the sampling error and make statistical inferences from the sample to the population due to the absence of random selection of samples.
Can you use a questionnaire as a snowball sampling method?
If using questionnaire as primary data collection method, you can effectively apply snowball sampling with the use of emails. Specifically, body of the email requesting sample group members to participate in the survey can include a sentence along the following lines:
Why do researchers use convenience sampling?
Researchers use convenience sampling not just because it is easy to use, but because it also has other research advantages . In pilot studies, convenience sample is usually used because it allows the researcher to obtain basic data and trends regarding his study without the complications of using a randomized sample.
What is probability sampling?
In probability Samples, each member of the population has a known non-zero probability of being selected. Probability methods include random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified sampling. Probability sampling includes simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling and disproportional sampling The advantage of probability sampling is that sampling error can be calculated.
What is the most important type of sampling?
This may be the most important type of sample. A random sample allows a known probability that each elementary unit will be chosen. This is the type of sampling that is used in lotteries and raffles.
How is systematic sampling calculated?
This interval, called the sampling interval, is calculated by dividing the population size by the desired sample size. Despite the sample population being selected in advance, systematic sampling is still thought of as being random if the periodic interval is determined beforehand and the starting point is random.
How to get cluster sample?
- A cluster sample is obtained by selecting clusters from the population on the basis of simple random sampling. The sample comprises a census of each random cluster selected. Cluster sampling is a method used to enable random sampling to occur while limiting the time and costs that would otherwise be required to sample from either a very large population or one that is geographically diverse. Using this method, a one- or two-level randomization process is used the important element in this process is that each one of the criteria have an equal opportunity to be chosen, with no researcher or facility bias.
What are the two groups of sampling techniques?
Broadly speaking, there are two groups of sampling technique: probability sampling techniques and non-probability sampling techniques.
Why are samples chosen randomly?
Rather they are chosen in a systematically random way so that chance or the operation of probability is utilized. Where random selection is not possible, other systematic means are used. Randomization is a sampling method used in scientific experiments.
How to find the sample size of a sample?
The Slovin's Formula is given as follows: n = N/ (1+Ne 2 ), where n is the sample size, N is the population size and e is the margin of error to be decided by the researcher. However, its misuse is now also a popular subject of research here in my country and students are usually discourage to use the formula even though the reasons behind are not clear enough to them. Perhaps it will helpful if we could know who really is Slovin and what were the bases of his formula.
Why is it not statistically justified to use probability statistical measurements?
confidence level) and sample size because the probability of participants' opportunity to participate is unknown.
How to find the minimum and maximum of a Likert scale?
To determine the minimum and the maximum length of the 5-point Likert type scale, the range is calculated by (5 − 1 = 4) then divided by five as it is the greatest value of the scale (4 ÷ 5 = 0.80). Afterwards, number one which is the least value in the scale was added in order to identify the maximum of this cell. The length of the cells is determined below:
Why stratify data into categories?
At any rate, whatever you do, stratification/grouping of your data into categories so as to reduce variance is often useful.
Can you do a quantitative analysis with a non-parametric method?
Yes, you still can do the puposive sampling for quantitative analysis. In quantitaive analysis, you have two techniques such as parametric and non-parametric techniques involved. Basically, probability sampling is suit to parametric tecnique since the this application need normality data for an analysis. Since purposive sampling is one of the non-probability sampling, i prefer non-parametric technique such as mann whitney test, wilcoxon, fisher exact test, kruskal wallis test and etc.
Can you do purposive sampling?
Yes, you can do purposive sampling, but only if you can identify a reasonable 'super-population' model. In that case you consider the values of the population units as random and your actual population as just one possible realization from that model.
Is parametric vs distribution free statistics a separate issue?
Also, parametric vs distribution- free statistics would be a separate issue entirely. I also worked in that area extensively.