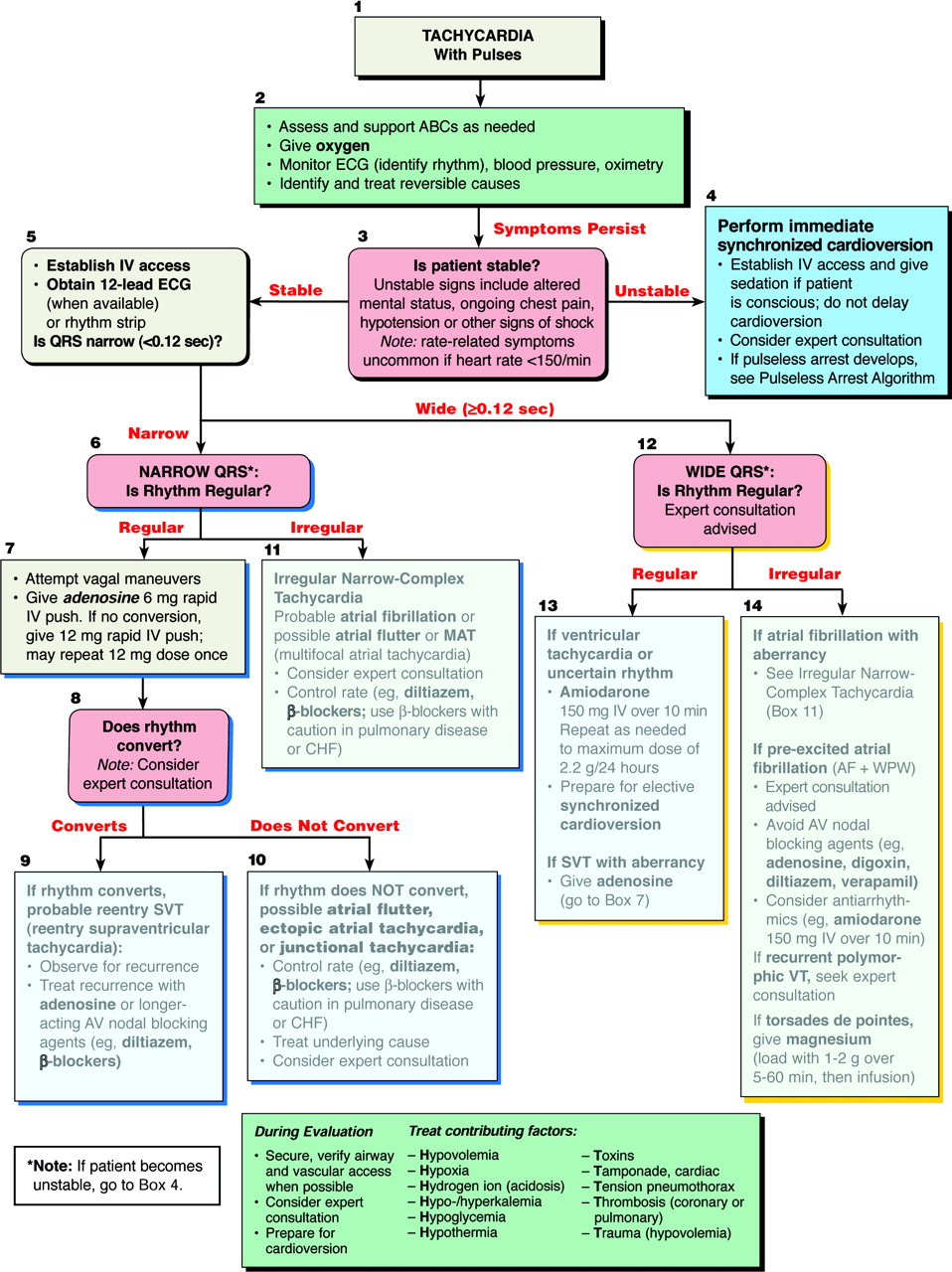
Common Causes
Use motherwort to control tachycardia. Motherwort is used in traditional Chinese medicine to combat different heart problems, including tachycardia. This herb contain alkaloid leonurine, a natural chemical that acts as a vasodilator. It has an antispasmodic property that can help to relax your heart muscles.
Related Conditions
Can anxiety cause abnormal EKG? Premature ventricular contractions is one of the manifestations of sympathetic over activity due to anxiety . However, anxiety might induce electrocardiographic ( ECG ) changes in normal person with normal heart, as in this documented case.
Can ventricular tachycardia be cured naturally?
Emotional states such as shock, fright or stress can also cause irregular heart rhythms. Arrhythmias that are recurrent or related to an underlying heart condition are more concerning and should always be evaluated by a doctor. In most cases, treating the underlying condition will take care of the arrhythmia.
Can stress cause EKG changes?
This can happen with heart disease but stress may also trigger chest pain for other reasons. However, when chest pain occurs with dizziness, difficulty breathing and/or confusion then it should be investigated immediately. The term stress is often used loosely but it is a growing problem in modern societies.
Can stress cause irregular heart rhythm?
Can stress cause mild chest pain?

What is the most common cause of ventricular tachycardia?
What causes it? Sometimes it is not known what causes ventricular tachycardia, especially when it occurs in young people. But in most cases ventricular tachycardia is caused by heart disease, such as a previous heart attack, a congenital heart defect, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, or myocarditis.
Can extreme stress cause tachycardia?
There are many different types of tachycardia. Sinus tachycardia refers to a typical increase in the heart rate often caused by exercise or stress.
What causes sudden ventricular tachycardia?
This irregular rhythm happens most often in people with heart disease or a prior heart attack. It may also occur in those with electrolyte imbalances (such as high or low potassium levels). Ventricular fibrillation may cause sudden cardiac arrest and lead to death if not treated immediately.
Can emotional stress cause arrhythmia?
Stress can contribute to heart rhythm disorders (arrhythmias) such as atrial fibrillation. Some studies suggest that stress and mental health issues may cause your atrial fibrillation symptoms to worsen.
How long can tachycardia from anxiety last?
The heart rate may speed up to 200 beats per minute or even faster. A fast heart rate can make you feel lightheaded and short of breath. Or you might feel fluttering or pounding in the chest. Usually, tachycardia that happens in response to emotional stress and only lasts a few minutes is not harmful.
Can panic attacks cause ventricular tachycardia?
A PSVT is often difficult to document on the ECG since it has often ceased before the patient comes to medical attention. Besides, a tachycardia may still be present and even be documented but interpreted as a phenomenon secondary to the panic attack.
Does ventricular tachycardia go away?
Ventricular tachycardia may go away on its own within 30 seconds (nonsustained V-tach ) or last more than 30 seconds (sustained V-tach or VT ). Brief episodes may not cause any symptoms. But sustained VT can cause serious problems, including: Fainting.
How often is ventricular tachycardia fatal?
Procedure mortality is approximately 3%, with most deaths due to failure of the procedure to control frequent, life-threatening VT. Ablation is also useful for controlling recurrent VT in the setting of dilated cardiomyopathy, infiltrative heart disease such as cardiac sarcoidosis, or ARVD.
What is life expectancy with ventricular tachycardia?
In patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy and nonsustained VT, sudden-death mortality approaches 30% in 2 years. In patients with idiopathic VT, the prognosis is excellent, with the major risk being injury incurred during syncopal spells.
Can Vtach be benign?
Although considered a benign arrhythmia, about 10% of the time, outflow tract tachycardias manifest with syncope. In addition, patients can present with symptomatic heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction, presumably due to tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy.
Can a Holter monitor detect anxiety?
To diagnose anxiety palpitations, a doctor will begin with a screening questionnaire. This will help them identify people who are likely to have palpitations from anxiety. A doctor will refer anyone who passes a certain score for monitoring. A doctor may use a Holter monitor or a transtelephonic event monitor.
What does emotional stress do to the heart?
Stress may lead to high blood pressure, which can pose a risk for heart attack and stroke. Stress also may contribute to such cardiovascular disease risks as smoking, overeating and lack of physical activity. "Chronic stress has been shown to be associated with increased cardiovascular events," Schiffrin said.
Why does anxiety cause tachycardia?
Sinus Tachycardia Those with anxiety are thought to have an overactive fight or flight system that is active throughout the day even when there are no immediate dangers. This floods adrenaline into your bloodstream which causes your heart to speed up as a response.
Can you get rid of tachycardia?
The treatment of tachycardia involves taking steps to prevent the heart from beating too fast. This may involve medication, implanted devices, or other surgeries or procedures. Medications. Drugs to control the heart rate and restore a normal heart rhythm are typically prescribed for most people with tachycardia.
How Anxiety Causes Tachycardia
There is more than one type of tachycardia, and more than one cause of tachycardia related to stress and anxiety. The easiest way to understand tac...
Is Tachycardia from Anxiety Dangerous?
It's difficult to say whether tachycardia is dangerous. The reality is that it is not dangerous on its own. The fight or flight system is something...
Tachycardia and Heart Attack Fears
Another issue that many people struggle with is in how they respond to tachycardia. It's not uncommon for those with panic attacks to know that the...
How to Stop Anxiety Tachycardia
Stopping this type of rapid heartbeat is sort of a waiting game. Once your body is flooded with adrenaline (or if you're hyperventilating) your hea...
What causes tachycardia in the heart?
When something goes wrong and signals are sent too quickly, it can cause tachycardia. Most patients with ventricular tachycardia have another heart problem, such as coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, an enlarged heart (cardiomyopathy) or heart valve disease.
How to tell if you have ventricular tachycardia?
The most common test used to diagnose ventricular tachycardia is an electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG). An EKG records your heart’s electrical activity. Electrodes (small sticky patches) are placed on your chest and arms to record the heart’s rhythm, and the pattern prints on graph paper. Your doctor may also want to track your heart rhythm at home. If so, you will wear a Holter monitor at home for 24 to 48 hours.
What is the normal heart rate for tachycardia?
The ventricles are the heart’s two lower chambers. Blood flows from the top chambers of the heart (atria) into the ventricles, then it moves to the lungs and through the aorta to be circulated throughout the body. Tachycardia is a heart rate higher than 100 beats per minute. A normal resting heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute.
What happens if your heart rate is too high?
When the heart rate is extremely high or the ventricular tachycardia persists for more than a few seconds, it can cause fainting, unconsciousness or cardiac arrest and death. If you experience unexplained fainting, dizziness, lightheadedness, shortness of breath or palpitations, you should be evaluated for possible ventricular tachycardia.
Does ablation help with ventricular tachycardia?
Ablation of ventricular tachycardia has a long history of safety and success. For some patients, ablation completely cures the abnormal rhythm, and no other treatment is needed. Ablation can also improve treatment with an implantable cardioverter defibrillator.
Why does my heart tachycardia?
This throws off your body's balance and causes your blood vessels to constrict. When your ventricles constrict, this makes your heart need to work harder to get blood around your body, and that's what triggers the tachycardia. ADVERTISEMENT.
How many beats per minute is tachycardia?
Tachycardia is a heartbeat described as over 100 beats per minute in a healthy adult, and it is often followed by other symptoms due to the way tachycardia affects your body.
Why is my heartbeat slowing down?
Once your body is flooded with adrenaline (or if you're hyperventilating) your heartbeat won't slow until it gets back to its normal balance. Even if your heartbeat was under your control (which it isn’t), you wouldn’t want it to slow right away as it is needed to pass blood through the body.
How fast does the heart beat?
The heart is designed to handle speeds of greater than 100 beats per minute, but that doesn't mean that it isn't any less frightening. If your doctor has ruled out heart health issues, it's very likely you are suffering from anxiety. Stop anxiety related tachycardia today - take this test and find out more.
How to calm your body when you are anxious?
For example, deep breathing is a good way to calm the body when you are struggling with anxiety. By slowing down your breathing, you are able to control your hyperventilation and your anxiety at the same time. Cognitive behavioral therapy and medication can also be useful, as can many self-help techniques.
What is the most common symptom of anxiety?
Last updated October 10, 2020. Many physical symptoms of anxiety can cause further anxiety as mimic serious health problems. One of the most common is tachycardia, also known as "rapid heartbeat.". A healthy heartbeat is generally between 60 and 100 beats a minute.
What is the most active response to anxiety?
Sinus Tachycardia. The vast majority of experts in the anxiety field focus on one type of tachycardia: sinus tachycardia, which is caused by activation of the fight or flight system. This is the response that is most active during anxiety, triggering the nervous system to react. Normally your body rushes with adrenaline during times ...
What Is Ventricular Tachycardia?
Ventricular tachycardia is an unusually fast heartbeat that starts in the lower part of your heart, the ventricles. It’s sometimes called VT or V-tach.
What is the procedure called when you have ventricular tachycardia?
Cardiac ablation. This is also called catheter or radiofrequency ablation. Doctors use heat to destroy unusual heart tissue. This method treats the ventricular tachycardia and can cure it.
What is the normal heart rate for VT?
The pulses coming from your SA node are also affected. Most regular heart rates are in the range of 60 to 100 beats a minute. Ventricular tachycardia can result in rates of 170 beats a minute or even more.
How fast does tachycardia beat?
Ventricular tachycardia can result in rates of 170 beats a minute or even more. When this happens, your heart’s upper chambers don’t have time to refill and send that blood to the ventricles. So your blood doesn’t get pumped throughout your body the way it should.
What are the symptoms of VT?
VT can cause: Feeling lightheaded or dizzy. Chest pain. Heart palpitations. Shortness of breath. Fainting. Tightness in your neck.
What is the first test you can do to check your heart?
Your doctor will review your medical history and symptoms. You’ll also have some tests of your heart. The first one you’ll probably get is called an EKG. It records your heart’s electrical activity. Your doctor may also want you to get electrophysiology testing, which pinpoints problem areas in your heart.
What are the two upper and lower ventricles?
The two upper ones are called the atria. The two lower ones are called the ventricles. They work together to pump blood throughout your body. Every day, a healthy heart beats about 100,000 times. Your heartbeat is controlled by electrical signals. These signals follow a pattern. They start in the sinoatrial (SA) node.
What is ventricular tachycardia?
Ventricular tachycardia is characterized as a wide complex (QRS duration greater than 120 milliseconds) tachyarrhythmia at a heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute. It is classified by duration as non-sustained or sustained. Non-sustained ventricular tachycardia is defined as more than 3 beats of ventricular origin at a rate greater than 100 beats per minute that lasts less than 30 seconds in duration.[1] When the rhythm lasts longer than 30 seconds or hemodynamic instability occurs in less than 30 seconds, it is considered sustained ventricular tachycardia.[1]
What is the mechanism of ventricular tachyarrhythmia?
The mechanism for ventricular tachyarrhythmias includes enhancement of normal automaticity or abnormal automaticity, activity triggered by early or late afterdepolarizations, and reentry.[10] In acute myocardial infarction, the transient ischemia results in an increased concentration of extracellular potassium, which causes partial depolarization of the resting membrane potential.[10] This creates injury currents between the infarcted tissue and healthy myocardium that may trigger spontaneous activity.
What causes the most sudden cardiac death?
Ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation cause most cases of sudden cardiac death with an estimated rate of 300,000 deaths each year in the United States. [5][6] This accounts for approximately half of the deaths related to cardiac causes.[6] Risk factors for ventricular tachycardia are hypertension, previous myocardial infarction, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and ST-segment changes at presentation.[7] Patients presenting with acute myocardial infarction have ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia at a rate of 5% to 10%. [1][8] Ventricular tachycardia 48 hours after hospital presentation is associated with an increased risk of death compared to ventricular tachycardia occurring within the first 48 hours of hospital presentation. [9]
What is the first step in the evaluation of presumed ventricular tachycardia?
The first step in the evaluation of presumed ventricular tachycardia is a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG). [12][13] Patients with ventricular tachycardia symptoms associated with exertion, ischemic heart disease, or catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia should undergo further testing with a treadmill stress test.[14] Patients having syncope, presyncope or palpitations with no arrhythmia detected on a single 12-lead ECG should undergo further evaluation with ambulatory ECG monitoring.[15] In patients with ventricular tachycardia and possible structural heart disease, .an echocardiogram is recommended. [16][17] Patients who undergo an episode of unexplained sudden cardiac arrest secondary to a ventricular tachyarrhythmia, CT, or coronary angiography can be used to confirm the presence or absence of ischemic heart disease. [18][19]
What is the prognosis of VT?
The prognosis of VT depends on the cause and cardiac status. Patients who develop VT can suffer from hemodynamic failure and the mortality can exceed 30% if no treatment is provided. In the setting of percutaneous coronary intervention, VT occurring prior to revascularization is associated with very high mortality. The prognosis does not correlate with ejection fraction. Patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, long QT syndrome and right ventricular dysplasia often have normal heart function but yet are a high risk for sudden death.
What does the findings of cannon A waves and variable intensity of the S1 heart sound suggest?
The physical examination findings of cannon A waves and variable intensity of the S1 heart sound suggest AV dissociation, a criterion favoring the diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia. [11]
Can ventricular tachycardia be differentiated from supraventricular tachycardia?
A good history and physical can help you differentiate ventricular tachycardia from supraventricular tachycardia. Patients presenting with ventricular tachycardia are more likely to be older with a history of heart disease. A past medical history of heart failure, recent angina, and prior myocardial infarction all have a greater than 9% positive predictive value for ventricular tachycardia. [11]
What are the effects of emotional stress on the heart?
Acute emotional stress can produce left ventricular contractile dysfunction, myocardial ischemia, or disturbances of cardiac rhythm.
What is the role of cerebral lateralization in stress?
Lateralization of cerebral activity during emotional stress may stimulate the heart asymmetrically and produce areas of inhomogeneous repolarization that create electrical instability and facilitate the development of cardiac arrhythmias.
Can emotional stress affect the heart?
Episodes of acute emotional stress can have significant adverse effects on the heart. Acute emotional stress can produce left ventricular contractile dysfunction, myocardial ischemia, or disturbances of cardiac rhythm. Although these abnormalities are often only transient, their consequences can be ….
Can emotional stress cause contractile dysfunction?
Acute emotional stress can produce left ventricular contractile dysfunction, myocardial ischemia, or disturbances of cardiac rhythm. Although these abnormalities are often only transient, their consequences can be gravely damaging and sometimes fatal.
What is the term for an abnormally fast heartbeat caused by irregular electrical impulses that originate in the heart's?
Ventricular tachycardia is an abnormally fast heartbeat caused by irregular electrical impulses that originate in the heart's lower chambers. Non-sustained ventricular tachycardia is a type that stops by itself within 30 seconds.
What is it called when your heart beats fast?
Causes. Diagnosis. Treatment. Ventricular tachycardia is an abnormally fast heartbeat caused by irregular electrical impulses that originate in the lower chambers of the heart (the ventricles). Ventricular tachycardia that stops by itself within 30 seconds is called non-sustained ventricular tachycardia (NSVT).
What is NSVT diagnosis?
NSVT may arise in healthy people or in those with significant heart disease. Diagnosis involves the use of heart rhythm test or monitoring system. Other tests may be ordered to help figure out the cause of the ventricular tachycardia.
What causes electrical instability?
Electrical Instability. Sometimes, NSVT is caused by cardiac conditions that are not associated with structural heart disease (that is, heart disease that does not alter the anatomy of the heart). The most common of these conditions is repetitive monomorphic ventricular tachycardia (RMVT). This is a congenital disorder involving ...
Does NSVT increase the risk of cardiac arrest?
If no underlying heart disease is found, in general, NSVT does not measurably increase the risk of cardiac arrest.
Does NSVT cause heart palpitations?
Most often, NSVT does not cause any symptoms at all. If it does, palpitations —when one feels a fast or irregular heartbeat—may be the only one. The palpitations may be associated with trouble breathing or chest pain. 3
Is NSVT dangerous?
Any ventricular tachycardia is considered a potentially dangerous cardiac arrhythmia. 1 However, because NSVT does not persist, it is substantially less dangerous than a sustained ventricular tachycardia (SVT) and may turn out to be completely benign. Still, NSVT can cause potentially worrisome symptoms and may indicate an increased cardiac risk.