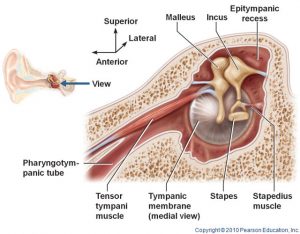
What is tensor tympani syndrome?
Tensor tympani syndrome, also known as the tensor tympani myoclonus, is a rare form of objective pulsatile tinnitus, which includes tensor tympani-associated tinnitus caused by the contraction of the tensor tympani (TT) muscle.
Where is the tensor tympani muscle located?
1 Tensor Tympani Muscle. This is a muscle in the ear, which is located above the osseous portion of the auditory tube in the body canal. 2 Impact Of Tonic Tensor Tympani Syndrome. Tensor tympani muscle protecting the inner ear from loud sounds. ... 3 Symptoms of Tonic Tensor Tympani Syndrome 4 Causes of Tonic Tensor Tympani Syndrome. ...
What is tonic tensor tympani and what does it do?
With a combination of the stapedius muscle, the tensor tympani muscle provides you function like Speaking, Chewing, and it also protects your ears from damaging sounds level. What Is Tonic Tensor Tympani Syndrome?
What is the difference between the stapedius and the tensor tympani?
They both contract to noise, the stapedius muscle more so than the tensor tympani, giving the acoustic reflex its nick name "stapedius reflex". The involvment of the tensor tympani muscle in the reflex is not well understood. When exposed to excessively loud noise, the stapedius muscle has the primary protective role.

Does tensor tympani cause hearing loss?
As markers for tensor tympani contraction, all investigations indicate that tensor tympani hypercontraction should result in a low-frequency hearing loss, predominantly conductive, with a decrease in middle ear compliance.
What does muscular tinnitus sound like?
In muscular tinnitus, the sound is often described as a “clicking” noise and is usually associated with myoclonus affecting muscles near – or in – the ear. Myoclonus is an involuntary spasm or jerking of a muscle or group of muscles caused by abnormal muscular contractions and relaxations.
What does tensor tympani syndrome sound like?
Disorders of the tensor tympani It sometimes results in visible contractions of the ear drum, and sometimes even produces sounds audible to the examiner. Patients usually indicate that it makes a "thumping" noise -- like a tympani drum !
Can tensor tympani syndrome go away?
Placing a membrane on the eardrum allows the tensor tympani to relax so that some of the symptoms can be reduced or disappeared.
How do you treat tensor tympani syndrome?
The most common procedure for TT syndrome as well as stapedius myoclonus is tympanotomy with TT or stapedius tenotomy. It is believed that by releasing the muscle's attachment site, it can reduce or eliminate tinnitus. A limited number of case series evaluating the role of tenotomy in MEM has been described.
Is tinnitus in the ear or brain?
Although we hear tinnitus in our ears, its source is really in the networks of brain cells (what scientists call neural circuits) that make sense of the sounds our ears hear. A way to think about tinnitus is that it often begins in the ear, but it continues in the brain.
How many people have tensor tympani?
Only about 10-20% of the population can do this, it seems to be genetic, and scientists think this may be a vestigial trait left over from when moving your ears to detect which direction predators were coming from could help you not get eaten.
Can tensor tympani cause vertigo?
Data collected: Symptoms consistent with TTTS (pain/numbness/burning in and around the ear; aural "blockage"; mild vertigo/nausea; "muffled" hearing; tympanic flutter; headache); onset or exacerbation from exposure to loud/intolerable sounds; tinnitus/hyperacusis severity.
What percent of people can ear rumble?
Since the tweet, a survey has now also been conducted, with the findings reporting that “16% of people report they can voluntary ear rumble in isolation (& after reading a description 75% report ear rumbling with other movements such as yawning – 62% were already aware).”
How do you relax your inner ear?
Reach over the head with your right hand to the left ear and bring the head into a stretching position. You will feel the stretch at the side of your neck. Stay in this position for two to three minutes and breathe evenly. Change sides to release tension and muscle stiffness on the right side as well.
Why is my inner ear fluttering?
Doctors suggest that fluttering in the ear is a type of tinnitus called MEM, which is caused by jerky movements of the muscles in the middle ear. Doctors need to individualize treatments and follow up with people who experience fluttering in the ear, since responses to treatments vary greatly from person to person.
What is pulsatile tinnitus?
What Is Pulsatile Tinnitus? People with pulsatile tinnitus often hear rhythmic thumping, whooshing or throbbing in one or both ears. Some patients report the sounds as annoying. But for others, the sounds are intense and debilitating, making it difficult to concentrate or sleep.
What sounds do you hear with tinnitus?
The noises of tinnitus may vary in pitch from a low roar to a high squeal, and you may hear it in one or both ears. In some cases, the sound can be so loud it interferes with your ability to concentrate or hear external sound. Tinnitus may be present all the time, or it may come and go.
What are the 4 types of tinnitus?
Tinnitus sounds different to everyone, so it makes sense that there are four different types: subjective, objective, neurological, and somatic.
What does TMJ tinnitus sound like?
So, what does TMJ tinnitus sound like? It sounds like a high pitched ringing sound or even a hissing, roaring, clicking, or buzzing sound. The ringing might change as you open or close your jaw.
Can tight neck muscles cause tinnitus?
Can tinnitus and ringing in ears be caused by neck problems? The answer is yes. Clinically speaking it is called cervical tinnitus. In practice, these are whistles and ringing perceived in the ear in conjunction with the emergence of cervical pain and neck problems.
Why do tensor tympani and veli palatini open the Eustachian?
The tensor tympani and tensor veli palatini open the Eustachian tube to allow your ear pressure to equalize with outside pressure.
Why do my ear muscles clench?
Since these ear muscles are controlled by the same nerves as our jaw muscles , it’s likely that they might be affected by some of the stimuli that can cause TMJ. When bruxism forces your jaw muscles to clen ch, these ear muscles might also clench. A similar situation might occur when your jaw is out of balance and your muscles are fighting hard against your jawbone and teeth to try to find a comfortable, relaxed position. This may cause your tensor tympani and/or tensor veli palatini to contract at inappropriate times.
What are the three muscles that help us hear?
The three tiny muscles are the tensor tympani, tensor veli palatini, and stapedius may be small, but they still have important roles to play when it comes to hearing. The tensor tympani, for example, is connected to your eardrum, and when you hear a loud noise, it begins to contract involuntarily. Exactly why isn’t known, but there are two prevailing theories: it may protect the delicate hearing components from damage, or it may be intended to improve the transmission of these sounds. The tensor tympani and tensor veli palatini open the Eustachian tube to allow your ear pressure to equalize with outside pressure. The stapedius is the smallest skeletal muscle and it works to stabilize the stapes, the body’s smallest bone to help our hearing.
How many tensor tympani muscles are there?
When everything is working properly, you aren’t even aware you have two tensor tympani muscles working for you. Their actions are totally automatic. However, when something disturbs their normal functions, you may become painfully aware of their existence.
How to tell if you have tonic tympani syndrome?
Classic Tonic Tensor Tympani Syndrome symptoms include: Pain: You may experience a sharp pain in your ear when the tensor tympani muscle tightens and stretches your eardrum, or you may experience a dull ache in your ear.
What muscle is affected by hyperacusis?
In numbers of people who have hyperacusis (where normal sounds are now abnormally loud), and who also typically have misophonia (where you have negative emotional reactions to certain specific sounds) increased (abnormal) activity develops in the tensor tympani muscle as part of the startle response to some sounds. This is called Tonic Tensor Tympani Syndrome.
What is the name of the muscle in the middle of your ear?
Tonic Tensor Tympani Syndrome (TTTS) is probably not a familiar condition to most people. In fact, few people have ever heard of it. The tensor tympani muscle, from which Tonic Tensor Tympani Syndrome gets its name, is one of the two tiny muscles in your middle ears. (The other is the stapedius muscle.) The tensor tympani muscle reacts ...
What muscle is used to protect the inner ear from noise?
The tensor tympani muscle also has other functions. For example, it also contracts (tenses) immediately before you begin talking.
What causes TTTS?
However, there is a growing body of evidence pointing to another, and totally different, cause of TTTS. Tonic Tensor Tympani Syndrome can also be the result of temporomandibular joint (TMJ) problems and/or upper cervical spine problems—specifically, your C 1 and C 2 vertebrae being out of proper alignment.
What is a tonic muscle?
The word “tonic” in this syndrome name describes the continuous or pulsing action of the tensor tympani muscle. Quite often the word “tonic” is omitted and people just refer to this syndrome as “Tensor Tympani Syndrome”. When everything is working properly, you aren’t even aware you have two tensor tympani muscles working for you.
Why does my ear tens up when I hear loud noises?
Basically, your ear tenses up due to the perception of loud noise, or even sometimes the anticipation of the noise. When you have hyperacusis, everything seems too loud, so your brain is on overdrive trying to protect your hearing, and so the muscles in your ear which normally only are used when things are very loud become overworked, which can lead to pain and other odd sensations.
What causes TTTS and ASD?
Studies show that TTTS and ASD is often caused by TMJ and upper cervical spine disorders. This can involve the C1 and C2 being out of alignment. It can be caused by whiplash, injury, falling down, a history of bad posture with too much forward head bending, dental whiplash causing TMJ. TMJ and misalignment of the upper spine can happen together.
What does TTTS mean?
TTTS can include tinnitus, the ear - clicks, flutter, feeling like ear is block or fullness, muffled or distorted hearing, numbness or burning. Click to expand... That's not my understanding of it. Tinnitus can accompany many of these symptoms, but it's not a sub-type of TTTS.
Which reflex contracts to noise?
The tensor tympani contracts to noise. The stapedius is an acoustic reflex that is triggered by noise. The tympani reflex is a protective reflex.
What does ASD mean in the context of ear problems?
ASD in the context of ear problems stands for Acoustic Shock Disorder. It is the cause, not the effect. It is what triggers abnormal middle ear contractions. Myriam Westcott describes it like this:
How long does it take for TTTS to go away?
I used to have TTTS. It took over 6 months for it to get better, and it was mostly gone after 12 months.
Is subjective tinnitus subjective?
Not many may share my view, but I consider subjective tinnitus to be the only kind of tinnitus. I sometimes come across terms like "objective tinnitus" in research papers. With the risk of being jumped by the so called professionals, I will say that if what you have is objectively measurable, then it's not really tinnitus.
What Is Tonic Tensor Tympani Syndrome?
Tonic tensor tympani syndrome is an abbreviation of TTTS, this is a disease of tensor tympani muscle. It is a condition related to anxiety that can drastically affect a person’s ability to hear.
What is the job of the Tensor Tympani muscle?
The job of the tensor tympani muscle is to pull the tiny malleus (hammer) bone away from the eardrum (tympani), thus tensing the eardrum. Tensor tympani Syndrome is involuntary.
What muscle is responsible for eardrums?
Whenever sound enter the ear the ossicles vibrate and sound increase, the more these bones will vibrate. It’s one major function of the Tensor Tympani Muscle.
What muscle reacts to loud sounds?
This muscle reacts sudden loud sounds, it’s called the startle reflex . If any person suffers from hyperacusis and misophonia increased activity develops in the tensor tympani muscle as a part of the startle response to some sounds, this is called Tonic Tensor Tympani Syndrome.
What is the name of the muscle in the middle of the ear?
Some statistics saying that it occurs in only 1 out of every 100,000 people. The tensor tympani muscle , from which TTTS gets its name, is one of the two tiny muscles in your middle ears and the other is the stapedius muscle. The word “tonic” in this syndrome name describes the pulsing action of the tensor tympani muscle.
What is the abnormal activity of the tensor tympani muscle of the middle ear?
The abnormal activity of the tensor tympani muscle of the middle ear is known as a tonic tensor tympani syndrome. With a combination of the stapedius muscle, the tensor tympani muscle provides you function like Speaking, Chewing, and it also protects your ears from damaging sounds level.
What causes tonic tensor syndrome?
2. Tonic Tensor Treatment Syndrome Magnesium. Low levels of magnesium can cause people to suffer from the problem of anxiety disorder, which is one of the major causes of tonic tensor treatment syndrome. Many people with tensor tympani syndrome had an anxiety disorder.