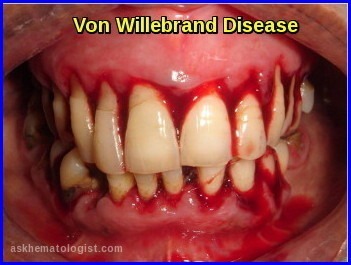
Symptoms
Causes
Prevention
Complications
What is von Willebrand disease?
Why don't people know about von Willebrand disease?
What are the complications of von Willebrand disease?
How much chance of passing von Willebrand disease to children?
Can you pass von Willebrand disease on to your offspring?
Can Von Willebrand be cured?
Does von Willebrand cause bleeding?
See more
About this website

Is von Willebrand disease life threatening?
Complications. Rarely, von Willebrand disease can cause uncontrollable bleeding, which can be life-threatening. Other complications of von Willebrand disease can include: Anemia.
What is the life expectancy of someone with von Willebrand disease?
The life expectancy for people with VWD is normal. What's more, some researchers are finding that mild VWD could be a health benefit. They explain it this way. Von Willebrand disease makes it more difficult for platelets to stick together.
Can von Willebrand disease get worse?
The disease can range from mild to severe. It is mild in most people. It can stay the same or get better or worse as you get older.
Can von Willebrand disease get worse with age?
VWF levels increase with age and elevated levels are associated with an increased risk of venous thromboembolism and cardiovascular disease (CVD). Patients with von Willebrand disease (VWD) due to a deficiency or dysfunction of VWF may have symptoms that ameliorate with aging or may have exacerbation of their disease.
Does von Willebrand make you tired?
The weakening, fatigue and other disruptive effects of VWD can be stopped. Even childbirth can be made safe for a mother and baby. If you have unexplained bleeding symptoms, remember to ask your doctor, “Could I have von Willebrand disease?”
Is von Willebrand disease considered a rare disease?
VWD is the most common bleeding disorder, found in up to 1% of the U.S. population. This means that 3.2 million (or about 1 in every 100) people in the United States have the disease.
How do you live with von Willebrand disease?
If you have von Willebrand disease (VWD), you can take steps to prevent bleeding and stay healthy. For example, avoid over-the-counter medicines that can affect blood clotting, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Always check with your doctor before taking any medicines.
Can you have surgery with von Willebrand?
The results from this retrospective study indicate that surgery can be safely performed by providing adequate and timely hemostasis during and after the procedure in patients with vWD. Perioperative and postoperative bleeding complications are rare when patients are closely and carefully monitored.
Does von Willebrand disease make you dizzy?
Call your doctor or nurse call line now or seek immediate medical care if: You are dizzy or light-headed, or you feel like you may faint. You have abnormal bleeding, such as: Your stools are black and look like tar, or they have streaks of blood.
Can you get the Covid vaccine if you have von Willebrand?
Patients with von Willebrand disease or a rare bleeding disorder should consult with their hematologist regarding special precautions prior to receiving the vaccination. All rare bleeding disorder patients (including those with thrombocytopenia and/or platelet function disorders) should be vaccinated.
Does alcohol affect von Willebrand disease?
Light-to-moderate alcohol consumption was associated with lower levels of fibrinogen, plasma viscosity, von Willebrand factor, and factor VII. This association was most pronounced for consumers of 3 to 7 drinks weekly for viscosity and 7 to 21 drinks weekly for the other hemostatic measures.
What foods should be avoided with von Willebrand disease?
Food and supplements to avoidlarge glasses of juice.soft drinks, energy drinks, and sweetened tea.heavy gravies and sauces.butter, shortening, or lard.full-fat dairy products.candy.foods containing trans fats, including fried. foods and baked goods (pastries, pizza, pie, cookies, and crackers)
Von Willebrand Disease: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments
Von Willebrand disease is an inherited bleeding disorder. People with von Willebrand disease can have heavier-than-normal bleeding after an injury, surgery, menstrual flow and childbirth.
Von Willebrand Disease: Types, Causes, and Symptoms
Three main types of von Willebrand disease exist: Type 1. Type 1 is the most common type of von Willebrand disease. It causes lower-than-normal levels of VWF to occur in your body.
Von Willebrand disease - Wikipedia
Von Willebrand disease (VWD) is the most common hereditary blood-clotting disorder in humans. An acquired form can sometimes result from other medical conditions. It arises from a deficiency in the quality or quantity of von Willebrand factor (VWF), a multimeric protein that is required for platelet adhesion.It is known to affect several breeds of dogs as well as humans.
Signs, Symptoms, and Complications of Von Willebrand Disease
The signs and symptoms of von Willebrand disease (VWD) depend on which type of the disorder you have. They also depend on how serious the disorder is. Many people have such mild symptoms that they don't know they have VWD. If you have type 1 or type 2 VWD, you may have the following mild-to-moderate bleeding symptoms:
IN BRIEF YOUR GUIDE TO von Willebrand Disease
IN BRIEF von Willebrand Disease YOUR GUIDE TO If you often have large, lumpy bruises; frequent or difficult-to-stop nosebleeds; bleed a lot after a fairly minor cut; or are
What is von Willebrand disease?
Overview. Von Willebrand disease is a lifelong bleeding disorder in which your blood doesn't clot well. People with the disease have low levels of von Willebrand factor, a protein that helps blood clot, or the protein doesn't perform as it should. Most people with the disease are born with it, having inherited it from one or both parents.
Why don't people know about von Willebrand disease?
Many people with von Willebrand disease don't know it because the signs are mild or absent. The most common sign of the condition is abnormal bleeding.
What are the complications of von Willebrand disease?
Rarely, von Willebrand disease can cause uncontrollable bleeding, which can be life-threatening. Other complications of von Willebrand disease can include: 1 Anemia. Women who have heavy menstrual bleeding can develop iron deficiency anemia. 2 Swelling and pain. This can be a result of abnormal bleeding in the joints or soft tissue.
How much chance of passing von Willebrand disease to children?
If you have the gene for von Willebrand disease, you have a 50% chance of transmitting this gene to your children. The most severe form of the condition is "autosomal recessive," which means both of your parents have to pass an abnormal gene to you.
Can you pass von Willebrand disease on to your offspring?
Because von Willebrand disease is usually an inherited disorder, consider having genetic counseling if you have a family history of this condition and you're planning to have children. If you carry the defective gene for von Willebrand disease, you can pass it on to your offspring, even if you don't have symptoms.
Can Von Willebrand be cured?
Von Willebrand disease can't be cured. But with treatment and self-care, most people with this disease can lead active lives.
Does von Willebrand cause bleeding?
This interferes with the clotting process and can sometimes cause uncontrolled bleeding. Many people with von Willebrand disease also have low levels of factor VIII, another protein that helps in clotting. Factor VIII is involved in another inherited clotting disorder called hemophilia. But unlike hemophilia, which mainly affects males, ...
What is von Willebrand disease?
Von Willebrand disease (VWD) is a bleeding disorder in which your blood has trouble clotting. It is inherited, meaning it is passed down from parents to their children. People with von Willebrand disease sometimes experience heavier-than-normal bleeding from injury, surgery, and, in women, menstrual flow and childbirth.
How to make sure von Willebrand disease does not interfere with enjoying a healthy life?
Receiving treatment when necessary and visiting your doctor regularly are the best ways to make sure von Willebrand disease does not interfere with enjoying a healthy life.
What is VWF type 2?
Type 2: In this type, the VWF has a defect that makes it unable to work properly. Bleeding symptoms can be mild or moderate.
What is the name of the protein that causes von Willebrand disease?
Problems with a protein in the blood cause von Willebrand disease. This protein, known as von Willebrand factor (VWF), helps the blood clot.
Does von Willebrand disease have symptoms?
Many people with von Willebrand disease have mild cases and no symptoms. Symptoms in more severe cases include:
Is von Willebrand disease preventable?
Because von Willebrand disease is usually inherited, it is not preventable.
Can a mutation cause a reduced VWF?
In both of these scenarios the ability of the blood to clot properly is impaired. A variety of gene mutations cause either a reduced production of VWF or production of an abnormally functioning VWF. Although the cause of these mutations is unknown, the abnormal gene is passed from one generation to another.
What is von Willebrand disease?
Related Pages. Von Willebrand disease (VWD) is a blood disorder in which the blood does not clot properly. Blood contains many proteins that help the blood clot when needed. One of these proteins is called von Willebrand factor (VWF). People with VWD either have a low level of VWF in their blood or the VWF protein doesn’t work the way it should.
How long does VWD bleeding last?
This bleeding may be characterized in the following ways: After a cut to the skin, the bleeding lasts more than 5 minutes.
Who is Affected?
population. This means that 3.2 million (or about 1 in every 100) people in the United States have the disease. Although VWD occurs among men and women equally, women are more likely to notice the symptoms because of heavy or abnormal bleeding during their menstrual periods and after childbirth. There are 3 major types of VWD: Type 1, Type 2, and Type 3.
What happens when VWF is attached to platelets?
The body removes the platelets attached to VWF, causing a reduced amount of both platelets and VWF in the blood when needed to form a clot.
How does VWF work?
Normally, when a person is injured and starts to bleed, the VWF in the blood attaches to small blood cells called platelets. This helps the platelets stick together, like glue, to form a clot at the site of injury and stop the bleeding. When a person has VWD, because the VWF doesn’t work the way it should, the clot might take longer to form or form incorrectly and bleeding might take longer to stop. This can lead to heavy, hard-to-stop bleeding. Although rare, the bleeding can be serious enough to damage joints or internal organs, or even be life-threatening.
Why is VWF important?
Because the treatment is different for each type, it’s important that a person know which subtype he or she has. In Type 2A, the VWF is not the right size and doesn’t help the platelets attach together in order to form a clot. In Type 2B, the VWF attaches to platelets at the wrong time (when there is no injury).
How often do you have to use a tampon for VWD?
Women with VWD might have heavy menstrual periods during which they experience. Soaking through a pad or tampon every 1-2 hours (or more often) on the heaviest day (s) Menstrual bleeding that lasts longer than 7 days from the time bleeding starts until the time it ends.
What happens if you have von Willebrand disease?
If you have von Willebrand disease, a cut, accident, or surgery can result in bleeding that’s hard to stop. VWD is the most common inherited bleeding disorder. That means you get it from your parents. It affects an estimated 1 in 100 to 1 in 1,000 people.
What is the chance of having a VWD?
Typically, you have 20% to 50% of normal levels. Symptoms of Type 1 VWD are mild. Type 2: This is the second most common form of inherited VWD. It’s caused by your own VWD factor not working well. If you have VWD, there’s a 15% to 30% chance you have Type 2. Symptoms range from mild to moderate.
What is the most common form of inherited VWD?
There are three types of inherited VWD and one type of the disorder that isn’t hereditary. Type 1: This is the most common form of inherited VWD. About 60% to 80% of people with VWD have this type. With Type 1, you don’t have enough von Willebrand factor in your blood. Typically, you have 20% to 50% of normal levels.
Why does VWF go up and down?
This shows how much VWF you have in your blood plasma. Levels of VWF go up and down because of things like stress and exercise. For this reason, you might have to have these tests more than once to confirm the results.
What is the rarest form of VWD?
Symptoms range from mild to moderate. Type 3: This is the rarest form of inherited VWD. It’s found in 5% to 10% of cases. If you have this type, you typically have no von Willebrand factor and very low levels of another protein needed for clotting. Type 3 has the most severe symptoms.
Can von Willebrand factor be increased?
These can increase the amount of von Willebrand factor in your blood. Another possible treatment is a levonorgestrel intrauterine device. This is a type of birth control that contains the hormone progestin. If you’re done having children or don’t want any, you can also have an endometrial ablation.
Does von Willebrand factor cause water retention?
It causes the release of von Willebrand factor from your cells. A side effect of this hormone is that it causes your body to retain water. As a result, you will need to be on fluid restrictions if you’re taking the medication. Your doctor might also recommend that you get clotting factor concentrates through an IV.
How to evaluate for von Willebrand disease?
To evaluate you for von Willebrand disease, your doctor will likely ask you detailed questions about your medical history and check for bruises or other signs of recent bleeding.
What is the Von Willebrand factor?
Von Willebrand factor antigen. This determines the level of von Willebrand factor in your blood by measuring a particular protein. Von Willebrand factor activity. There are a variety of tests to measure how well the von Willebrand factor works in your clotting process. Factor VIII clotting activity.
What is the first treatment for von Willebrand disease?
Many doctors consider DDAVP the first treatment for managing von Willebrand disease. It can be used before minor surgical procedures to help control bleeding. You might be given a trial of desmopressin to make sure it's effective for you.
Why do von Willebrand tests fluctuate?
The results of these tests can fluctuate in the same person over time due to factors such as stress, exercise, infection, pregnancy and medications. So you might need to repeat some tests. If you have von Willebrand disease, your doctor might suggest ...
Can von Willebrand disease be diagnosed?
Diagnosis. Mild forms of von Willebrand disease can be difficult to diagnose because bleeding is common, and, for most people, doesn't indicate a disease. However, if your doctor suspects you have a bleeding disorder, he or she might refer you to a blood disorders specialist (hematologist). To evaluate you for von Willebrand disease, your doctor ...
Does von Willebrand disease cure?
Even though von Willebrand disease has no cure, treatment can help prevent or stop bleeding episodes. Your treatment depends on:
How many bleeding symptoms are there for VWD?
Women reported an average of 6 bleeding symptoms before a diagnosis of VWD was made. Common symptoms included menorrhagia, bruising, nosebleeds, and bleeding from surgery, injury, and delivery. Menorrhagia was the most commonly reported symptom.
How many women with VWD have bleeding?
74% of women with VWD reported excessive bleeding from several sites (e.g. nose, gum and uterus) or following several procedures or injuries (e.g. dental, surgical, childbirth and minor injury) compared to 6% of controls.
What are the symptoms of VWD?
In studies of 42 men and 38 women with Type 1 VWD (the most common form): 1 The most common bleeding symptoms were heavy menstrual bleeding in women (93%) and nosebleeds in men (53%). 2 45% of women and 50% of men with VWD reported excessive bruising. 3 40% of women and 47% of men with VWD reported excessive bleeding with surgery. 4 34% of women and 29% of men with VWD reported dental bleeding. 5 21% of women and 26% of men with VWD had received a blood transfusion. 6 76% of men with VWD had been diagnosed by age 10, but 50% of women with VWD were not diagnosed until after age 12.
How many people with VWD have received blood transfusions?
21% of women and 26% of men with VWD had received a blood transfusion. 76% of men with VWD had been diagnosed by age 10, but 50% of women with VWD were not diagnosed until after age 12.
How many people with VWD have bruising?
45% of women and 50% of men with VWD reported excessive bruising.
How many times does VWD test?
To obtain the diagnosis of VWD, tests were carried out on average twice (range 1–20 times).
What is von Willebrand syndrome?
Acquired von Willebrand syndrome (AVWS) is a bleeding disorder that can occur due to a variety of conditions, but is not caused by a VWF gene mutation. It is most often seen in persons over age 40 years with no prior bleeding history. This condition may result from lymphoproliferative disorders, autoimmune disorders (including systemic lupus erythrematosus, scleroderma, and antiphospholipid antibody syndrome ), heart conditions such as aortic valvular stenosis, increased blood platelet count such as essential thrombocythemia, and certain drugs. [1] About 300 cases of this condition have been reported in the medical literature thus far. Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the condition. [2]
What is the name of the database that lists articles that discuss acquired Von Willebrand syndrome?
PubMed is a searchable database of medical literature and lists journal articles that discuss Acquired Von Willebrand syndrome. Click on the link to view a sample search on this topic.
How long does a VWD last?
The main symptoms of VWD are: Frequent (more than 5 a year) nosebleeds that last longer than 10 minutes. Bleeding from cuts or injuries that lasts longer than 10 minutes. Bruising easily, with bruises that are raised and larger than a quarter. Being told you are “low in iron” or have been treated for anemia.
How is VWD Diagnosed?
A combination of blood tests are used to diagnose VWD, including a VWF antigen test, which measures the amount of VWF in the blood, tests that measure clotting time and ability to form a clot, and tests measuring platelet function. Some of these tests may have to be repeated, because the levels of VWF can change due to stress, exercise, the use of birth control pills, pregnancy, and hyperthyroidism. People with VWD usually have less than 50% of normal VWF in their blood. After a diagnosis of VWD is discovered, an additional is given to determine the type. The best place for patients with bleeding disorders to be diagnosed and treated is at one of the federally funded hemophilia treatment centers (HTCs) that are spread throughout the country. HTCs provide comprehensive care from skilled hematologists and other professional staff, including nurses, physical therapists, social workers and sometimes dentists, dieticians and other healthcare providers. In addition, HTCs often have specialized labs that can run more accurate VWD testing.
What percentage of people have type 3 VWD?
Type 3 VWD is found in 5%-10% of patients. People with type 3 VWD have a very low levels or no VWF in their blood.. Some people with this type of VWD may also be low in factor VIII (factor eight). Symptoms are typically severe, and include spontaneous bleeding episodes, often into their joints and muscles.
How common is VWD?
VWD is the most common bleeding disorder, affecting up to 1% of the US population – or approximately 1 in every 100 people. It occurs equally in men and women. However, women may be more symptomatic due to heavy menstrual bleeding (periods). VWD occurs equally across all races and ethnicities.
What is the difference between type 1C and type 2 VWD?
There is one subtype called Type 1C where the VFW has increase clearance leading to prolonged bleeding. Type 2 VWD is found in 15%-30% of patients. People with type 2 VWD have a normal levels of VWF, but the factor doesn’t function as it should.
When will the new VWD guidelines be released?
NEW VWD Guidelines: What You Need To Know. New VWD Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of von Willebrand disease were released in January 2021. These updated guidelines are the result of a collaborative effort between the American Society of Hematology (ASH), the International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostatsis (ISTH), ...
Is VWD hereditary?
There are three main types of VWD. A fourth type, acquired VWD, is not hereditary. Type 1 VWD is found in 60%-80% of patients. People with type 1 VWD have a low levels of VWF in their blood. Levels of VWF in the blood range from 20%-50% of normal. The symptoms are usually mild.
What is von Willebrand disease?
Overview. Von Willebrand disease is a lifelong bleeding disorder in which your blood doesn't clot well. People with the disease have low levels of von Willebrand factor, a protein that helps blood clot, or the protein doesn't perform as it should. Most people with the disease are born with it, having inherited it from one or both parents.
Why don't people know about von Willebrand disease?
Many people with von Willebrand disease don't know it because the signs are mild or absent. The most common sign of the condition is abnormal bleeding.
What are the complications of von Willebrand disease?
Rarely, von Willebrand disease can cause uncontrollable bleeding, which can be life-threatening. Other complications of von Willebrand disease can include: 1 Anemia. Women who have heavy menstrual bleeding can develop iron deficiency anemia. 2 Swelling and pain. This can be a result of abnormal bleeding in the joints or soft tissue.
How much chance of passing von Willebrand disease to children?
If you have the gene for von Willebrand disease, you have a 50% chance of transmitting this gene to your children. The most severe form of the condition is "autosomal recessive," which means both of your parents have to pass an abnormal gene to you.
Can you pass von Willebrand disease on to your offspring?
Because von Willebrand disease is usually an inherited disorder, consider having genetic counseling if you have a family history of this condition and you're planning to have children. If you carry the defective gene for von Willebrand disease, you can pass it on to your offspring, even if you don't have symptoms.
Can Von Willebrand be cured?
Von Willebrand disease can't be cured. But with treatment and self-care, most people with this disease can lead active lives.
Does von Willebrand cause bleeding?
This interferes with the clotting process and can sometimes cause uncontrolled bleeding. Many people with von Willebrand disease also have low levels of factor VIII, another protein that helps in clotting. Factor VIII is involved in another inherited clotting disorder called hemophilia. But unlike hemophilia, which mainly affects males, ...

Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
- Von Willebrand disease is a lifelong bleeding disorder in which your blood doesn't clot properly. People with the disease have low levels of von Willebrand factor, a protein that helps blood clot, or the protein doesn't perform as it should. Most people with the disease are born with it, having inherited it from one or both parents. However, warning signs, such as heavy bleeding after a de…
Prevention
- Many people with von Willebrand disease don't know it because the signs are mild or absent. The most common sign of the condition is abnormal bleeding. There are three main types of the disease. The amount of bleeding varies from one person to another, depending on the type and severity of the disease. If you have von Willebrand disease, you might have: 1. Excessive bleedin…
Who Is Affected?
- The usual cause of von Willebrand disease is an inherited abnormal gene that controls von Willebrand factor — a protein that plays a key role in blood clotting. When you have low levels of this protein or it doesn't work as it should, small blood cells called platelets cannot stick together properly nor attach themselves normally to the blood vessel walls when an injury has occurred. …
Types of VWD
- The main risk factor for von Willebrand disease is having a family history of it. Parents pass the gene for the disease to their children. Rarely, the disease skips generations. The disease is usually an "autosomal dominant inherited" disorder, which means you need a mutated gene from only one parent to get the disease. If you have the gene for von Willebrand disease, you have a 50% chanc…
Causes
- Rarely, von Willebrand disease can cause uncontrollable bleeding, which can be life-threatening. Other complications of von Willebrand disease can include: 1. Anemia.Heavy menstrual bleeding can cause iron deficiency anemia. 2. Swelling and pain.This can be a result of abnormal bleeding in the joints or soft tissue.
Signs and Symptoms
- If you plan to have children and have a family history of von Willebrand disease, consider genetic counseling. If you carry the gene for von Willebrand disease, you can pass it on to your offspring, even if you don't have symptoms.
Diagnosis
Treatments
- Type 1 This is the most common and mildest form of VWD, in which a person has lower-than-normal levels of VWF. A person with Type 1 VWD also might have low levels of factor VIII (8), another type of blood-clotting protein. About 85% of people treated for VWD have Type 1. Type 2 With this type of VWD, although the body makes normal amounts of the VWF, the factor does no…