Two of the carpal bones are commonly dislocated: The capitate (which is the largest bone in the hand, located in the middle of the lower palm) Dislocation of the capitate is called a perilunate dislocation. Perilunate dislocations are more common than lunate dislocations.
What carpal bone is most frequently dislocated?
Two of the carpal bones are commonly dislocated: The capitate (which is the largest bone in the hand, located in the middle of the lower palm) The lunate (which is located between the capitate and the end of the ulna) Dislocation of the capitate is called a perilunate dislocation. Perilunate dislocations are more common than lunate dislocations.
How do you treat a broken carpal?
- Wrist splinting. A splint that holds your wrist still while you sleep can help relieve nighttime symptoms of tingling and numbness. ...
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), may help relieve pain from carpal tunnel syndrome in the short term. ...
- Corticosteroids. ...
Is a dislocation the same thing as a fracture?
Dislocations are usually caused by a sudden impact to the joint following a blow, fall, or other trauma and can be hard to distinguish from a fracture. Dislocations may also have an associated fracture and these can be very dangerous to the long term health and viability of the affected limb (such as the ankle and foot).
Is a carpal an irregular bone?
Irregular bones: Irregular bones are irregular in size and shape and are usually quite compact. They include the bones in the vertebral column, the carpal bones in the hands, tarsal bones in the feet, and the patella (kneecap). Also to know is, what kind of bone is the patella?
Can carpal bones dislocation?
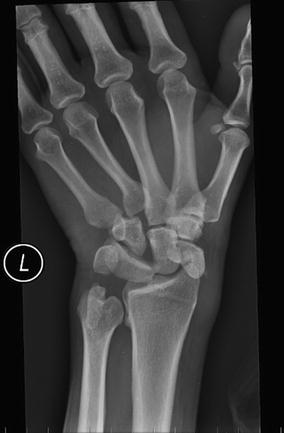
Hand dislocations occur when one of the eight carpal bones (bones located at the base of the hand) fall out of the joint to cause a hand dislocation. The capitate (largest bone in the hand) or lunate bones are the bones that most frequently dislocate.
How do you know if your wrist bone is out of place?
The main symptom of a dislocated wrist is intense pain that's usually worse when you try to move your wrist up and down or side to side. You might also feel pain in your forearm. You may also notice the following around your wrist: swelling.
What is the most common dislocation of the carpal bones?
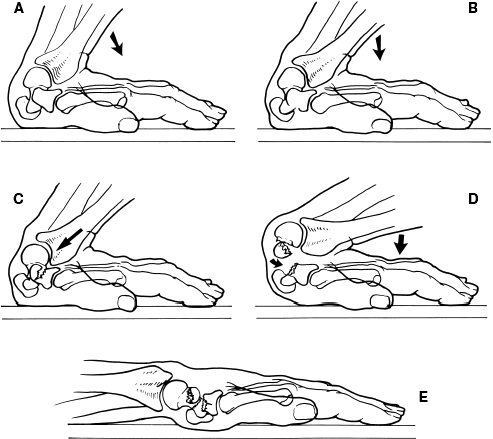
Perilunate dislocation (Fig. 4-19A and B) is the most common type of wrist dislocation. There is a dorsal dislocation of the carpal bones (scaphoid, triquetrum, and other carpal bones) about the lunate, while the lunate itself remains in normal position with respect to the distal radius.
Is it possible to dislocate a bone in your hand?
With 27 bones in each of your hands and wrists, there are plenty of opportunities for hand dislocations. A dislocation occurs when a bone moves out of its normal position, usually at a joint. These painful injuries can lead to permanent disability and deformity if untreated or incorrectly treated.
How do you pop a wrist bone back into place?
2:355:43How to Reset Your Wrist - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd place it down into the towel take the other hand and use the webbing right here to go rightMoreAnd place it down into the towel take the other hand and use the webbing right here to go right outside the bony spot of the wrist you want to grab on there and really just latch onto the wrist.
How do you fix a dislocated wrist bone?
Treatment. In people with a wrist dislocation, doctors manipulate the wrist bones back in place, without making an incision (called closed reduction). Then a splint is applied to immobilize the wrist and elbow. Usually doctors also immediately refer people to an orthopedist.
Why is my wrist bone popping out?
When the tendon in the wrist that connects the joint to the bone is damaged, it begins to rub over the bone or muscles in its way (instead of moving fluidly) and causes the “snapping” or “popping” sensation. The tendon moves in this irregular way because its foundation, the ligaments, have also become damaged or lax.
Can you move your wrist if it's dislocated?
When the wrist is dislocated, one or more of the bones inside the wrist has moved out of alignment, and will need to be moved back into place. This is called reduction. In some cases, reduction can be accomplished externally with sedation.
Can you dislocate a metacarpal?
The trapezoid metacarpal dislocation is a rare event. In the literature, it is found in case reports. This injury is caused by direct or indirect high energy trauma. In most cases, the dislocation is dorsal and is difficult to reproduce because the joint is not very mobile.
Can you dislocate bones in your wrist?
Your wrist can be forced out of its normal position (dislocated) if you fall on it hard. This can happen in a crash or when playing sports. When the wrist is dislocated, bones, ligaments, tendons, and nerves can be damaged. You may need more treatment.
What does a broken carpal feel like?
Severe pain that might worsen when gripping or squeezing or moving your hand or wrist. Swelling. Tenderness. Bruising.
How do you fix a dislocated metacarpal?
Metacarpal fracture or dislocation can be treated non-surgically by aligning the fractured bones and checking the movement of fingers, under local anesthesia. The fractured hand is wrapped with forearm-based splints or a cast to immobilize the bone to promote natural healing.
What happens to the lunotriquetral ligament after a rupture?
Alternately, a triquetral avulsion fracture may result. After rupture of the lunotriquetral ligament, the extension-supination vector is transmitted to the long radiolunate ligament, resulting in failure of this ligament as well. The short radiolunate and ulnolunate ligaments are left as the sole stabilizing structures of the lunate. These forces produce a dorsal perilunate dislocation.
What ligaments are taut?
The volar radiocarpal ligaments, scapholunate (SL) ligament, and scaphotrapeziotrapezoid ligament are taut in maximum extension. With an injury mechanism of forceful extension, ulnar deviation, and supination, the scaphoid extends, tightening the scapholunate ligament and the scaphotrapeziotrapezoid ligament. The short radiolunate and long radiolunate ligaments are taut, holding the lunate reduced and resisting the torque transferred from the extended scaphoid via the scapholunate ligament. With continued force transmission through an extended scaphoid, one of two things will occur: either the scapholunate ligament will tear in a volar to dorsal direction, or a scaphoid waist fracture will occur. The ligamentous or bony disruption thereby opens the space of Poirier.
How many bones are in the carpus?
The anatomy of the carpus is complex and has been the focus of numerous studies. The carpus consists of eight carpal bones arranged in a proximal and a distal row. Wrist motion occurs simultaneously at the intercarpal and radiocarpal joints. Motion is initiated by the extrinsic musculature as it acts on the distal carpal row. The proximal row is thought to be an “intercalated segment” during wrist motion, which moves in accordance with the vector of the distal carpal row. The stability and intercarpal motions of the wrist depend on muscular balance, articular congruence, and ligamentous integrity.
What are the four groups of injuries to the carpus?
Injuries to the carpus have been classified by Cooney and associates into four groups: lesser arc injuries (perilunate dislocations), greater arc injuries (transcarpal perilunate dislocations), axial dislocations, and isolated carpal bone dislocations. Isolated carpal bone dislocations have been extensively described in the literature and so are not included here.
What bones are involved in dislocated wrist?
This results in a dislocated wrist. While a dislocated wrist can involve all eight carpals, your lunate and scaphoid bones are often affected. These two bones form a bridge between the radius and ulna bones in your forearm and the other, smaller bones in your wrist. There are a few different types of wrist dislocations.
How to tell if your wrist is dislocated?
What are the symptoms? The main symptom of a dislocated wrist is intense pain that’s usually worse when you try to move your wrist up and down or side to side. You might also feel pain in your forearm. You may also notice the following around your wrist: swelling. tenderness. weakness.
What is the name of the bone that holds the wrist in place?
Your wrist contains eight small bones, called carpals. A network of ligaments holds them in place and allows them to move. A tear in any of these ligaments can result in two or more of your carpal bones being pushed out of their usual position. This results in a dislocated wrist.
How long does it take for a dislocated wrist to heal?
The healing time for a dislocated wrist depends on how severe it is. If you only need a reduction procedure, you should recover within two or three months. However, if you need surgery, it may take six months to a year to fully recover.
What to wear when you have a torn ligament in your wrist?
You might also need to wear a sling. For more severe cases, you might need surgery to realign your wrist bones or repair torn ligaments. This is sometimes done using pins or screws to hold everything in place.
Which fracture involves a break in the radius bone and dislocation of the radioulnar joint?
Perilunate dislocation. This type involves the lunate bone and the three ligaments around it. Galeazzi fracture. This type involves a break in your radius bone and dislocation of your radioulnar joint. Monteggia fracture.
How to help a wrist injury?
This can be quite painful, depending on the severity of your injury. To help with the pain, your doctor will use either local or general anesthesia before hand. Following the procedure, you’ll probably need to wear a splint or cast to prevent your wrist from moving while it heals. You might also need to wear a sling.
What is the most common wrist dislocation?
Lunate dislocation is also one of the most common types of wrist dislocation. 2. Perilunate Dislocation. Located near the lunate bone, dislocation of the capitate bone from the lunate bone is one of the most common types of wrist dislocation. 3.
What is the dislocation of the carpal bone?
The truth is, there are a few different types of dislocated wrists. 1. Lunate Dislocation. This is the dislocation of the carpal bone known as the lunate. It’s located towards the center of the wrist. Specifically, it is in the center of the proximal row carpal bones (between the ulna and radius and the hand itself).
How to stretch your wrist and forearm?
For this exercise, you will need a partner to help you out. Lie down, keep your elbow on the ground while your hand is raised up, and extend your fingers to the ceiling. Your partner then fully pronates the hand so the palm faces down. You should feel a mild stretch in the wrist and forearm.
How to do radial deviation?
Resistance Band Radial Deviation. Place a resistance band over your fingers with your thumb facing upwards while keeping your elbow at the side of your body, bent at a right angle with your other hand supporting it. Slowly, curl your wrist upwards with your forearm muscles becoming tight. Repeat for 15 repetitions.
How to get your forearms to go tight?
Keep the elbow at the side of the body, bent at a right angle, supporting it with your other hand. Slowly, curl your wrist and fingers upwards ( you should be able to feel the muscles in your forearms go tight). Repeat for 15 repetitions. 4.
What to do if your wrist hurts?
If the exercise is creating pain beyond what a doctor expects, stop the exercise immediately. 1. Ball Squeeze.
How long do you have to wear a cast on your hand?
In this case, you will have to wear a hard cast on the hand and wrist for approximately six weeks.