What is enamel hypoplasia reasons, causes?
Hereditary causes of enamel hypoplasia include:
- Primary abnormalities in enamel development, such as amelogenesis imperfecta
- Certain dermatological conditions, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- Other complex hereditary conditions such as Usher syndrome, Seckel syndrome, Treacher-Collins syndrome, Heimler syndrome & Ellis-Van Creveld syndrome
What are the signs of enamel dysplasia?
These are the symptoms of enamel hypoplasia to look out for:
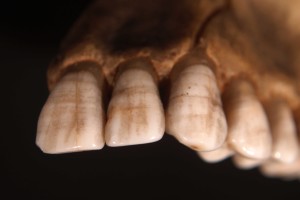
- Pits, tiny groves, depressions, and fissures in teeth
- White spots
- Yellowish-brown stains
- Sensitivity to heat and cold
- Lack of tooth contact or irregular bite
- Susceptibility to acids in food and drink
- Increased vulnerability to tooth decay and cavities
Do you have enamel hypoplasia?
If so, you may have enamel hypoplasia. This lifelong dental condition means that the enamel of your teeth isn’t developed enough. Since enamel is the hardest substance in your body, it’s crucial to monitor your teeth and symptoms to catch any problem before they become severe.
What causes pitting in teeth?
The Top 5 Causes of Pitting Corrosion
- Physical Damage. Damage to a structure interrupts protective layers and provides corrosive materials access. ...
- Uneven Stress or Fluid Flow. Unbalanced wear on a protective coating places more burden on specific areas. ...
- Impure Materials. Low-quality or defective metals are far more prone to pitting corrosion. ...
- Uneven Protective Coating. ...
- Chemical Exposure. ...
How do you fix dental hypoplasia?
Enamel Hypoplasia Treatment The most common treatment options include: Resin-bonded sealant – this treatment makes teeth less sensitive. Resin-based composite fillings – this is the best way to match the color of the sick tooth with the color of healthy teeth. Dental amalgam fillings – they are made of various metals.
How much does it cost to fix enamel hypoplasia?
Here are the average costs of the most common enamel hypoplasia treatments: Sealant: $30-$40 per tooth. Bonding: $200-$600 per tooth. Fillings: $150-$550 per tooth.
What causes hypoplastic enamel?
Hypoplastic teeth, also known as enamel hypoplasia, is when your enamel has not formed properly or has formed incorrectly. There are many reasons why this might happen, including diseases, prenatal issues, and environmental conditions.
Can enamel hypoplasia be whitened?
Treating Enamel Hypoplasia varies by the patient and severity of the disorder. For cases where there is only mild discolouration, your dentist may suggest tooth whitening for the affected tooth so that it looks more natural, like its healthy counterparts.
How common is hypoplastic teeth?
Defective enamel development can be the result of an inherited condition called amelogenesis imperfecta, or congenital enamel hypoplasia, which is estimated to affect about 1 in 14,000 people in the United States.
What causes enamel hypoplasia in kids?
Current research suggests that environmental factors that may increase the risk of enamel hypoplasia in children include the following: Premature birth. Low birth weight. Malnutrition, including vitamin D deficiency rickets.
Can hypoplasia be cured?
The treatment options for hypoplasia will depend on the specific condition it is present with. In many cases, there is no cure for these conditions. So, treatment usually aims to reduce the symptoms and provide support to people with the conditions.
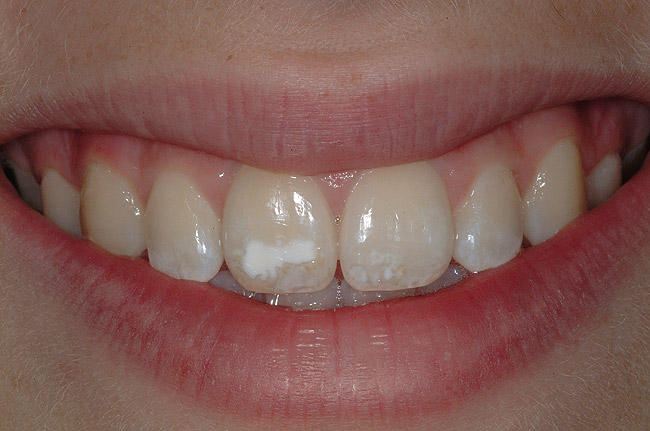
What does enamel hypoplasia look like?
You could be noticing enamel hypoplasia. This condition is a defect that causes a lesser quantity of enamel than normal. It can appear as a white spot, yellow to brown staining, pits, grooves or even thin, chipped or missing parts of enamel. In severe cases, the enamel doesn't develop at all.
Does enamel hypoplasia affect all teeth?
A: Enamel hypoplasia is a condition where teeth have less enamel (the outer, white part of the tooth) then they should. It can affect only a single tooth or multiple teeth, and it can range from looking like a small dent to affecting the entire size/shape of the teeth.
What can a dentist do for enamel loss?
Treatment of tooth enamel loss depends on the problem. Sometimes tooth bonding is used to protect the tooth and increase cosmetic appearance. If the enamel loss is significant, the dentist may recommend covering the tooth with a crown or veneer. The crown may protect the tooth from further decay.
Can teeth grow without enamel?
Teeth can come in without enamel as a result of inherited issues or because of exposure to certain substances while the teeth are erupting. Baby teeth and permanent teeth can both emerge with enamel that is weak, improperly formed or missing altogether.
How can I restore my teeth. Enamel naturally?
Demineralization and remineralization are interrelated and in constant flux.Brush your teeth. ... Use fluoride toothpaste. ... Cut out sugar. ... Chew sugarless gum. ... Consume fruit and fruit juices in moderation. ... Get more calcium and vitamins. ... Consider probiotics. ... Address your dry mouth.More items...
How much does it cost to replace enamel?
Enameloplasty is one of the least expensive and invasive cosmetic dentistry procedures, ranging from around $50 to $300 per tooth on average. This cost can vary based on how extensive the reshaping needs to be, the location of the tooth or teeth being contoured, your geographical location, and your overall oral health.
Can a dentist rebuild enamel?
One treatment option is repairing tooth enamel with dental bonding. Dental bonding involves applying a dental resin to the tooth surface to protect damaged areas and restore the intact surface. Enamel damage is usually experienced on the front of your teeth.
Can a dentist fix enamel loss?
Treatment of tooth enamel loss depends on the problem. Sometimes tooth bonding is used to protect the tooth and increase cosmetic appearance. If the enamel loss is significant, the dentist may recommend covering the tooth with a crown or veneer. The crown may protect the tooth from further decay.
Can I get my teeth re enameled?
Tooth enamel is the hardest tissue in the body. Problem is, it's not living tissue, so it can't be naturally regenerated. Unfortunately, you can't regrow it artificially, either -- not even with those special toothpastes.
What is the condition where teeth develop with very little enamel?
In amelogenesis imperfecta , the genes that control enamel formation and development don’t function properly in the ameloblasts, cells that create the teeth. Teeth often develop with very little enamel. Thankfully, there is a very low prevalence of this condition.
Why do pediatric dentists treat enamel defects?
Pediatric dentists are trained to look for enamel defects that can cause problems later in life. Because enamel hypoplasia can cause so many major dental issues, treatment is an essential part of an affected child’s oral health.
What causes hypoplastic enamel?
What causes hypoplastic enamel? Enamel hypoplasia is caused by genetics, environment, or sometimes a combination of both. During tooth development, something goes wrong with the matrix formation of enamel. The enamel is very thin and weak or is deposited unevenly.
What is enamel hypoplasia?
Enamel hypoplasia is one of the less-discussed conditions that can affect children’s teeth as they come in. If you’re interested in prevention or your child has been diagnosed, don’t panic! Here’s what you need to know about the signs, prevention, and treatment of enamel hypoplasia.
How to help a baby with gum disease?
Wipe your baby’s gums: Wiping your baby’s gums with a soft cloth or toothbrush breaks up bacterial colonies that might be growing on the surface. Practicing good oral hygiene with your infant can prevent infections that might lead to enamel hypoplasia later. It also sets the stage for healthy brushing habits once their teeth come in.
How to prevent tooth decay in kids?
Avoid sugary, gummy foods: Certain foods like fruit snacks or crackers can stick to teeth and promote tooth decay. Try to keep processed, high-sugar, and high-carb foods out of your kids’ diet as much as possible, or choose xylitol candy when a sweet tooth strikes.
What happens if you don't have enamel on your teeth?
What happens if you have no enamel on your teeth? If you had absolutely no enamel on your teeth, they would be quite sensitive to hot and cold food and drinks. They would be a brownish-yellow color and have a rough texture.
What is Enamel Hypoplasia?
Enamel hypoplasia is a term that denotes incomplete or underdeveloped tooth enamel. But first, what exactly is enamel? It’s the hard, protective layer covering the outside of your teeth. Essentially, the “white part” of your teeth is your enamel, made up of mostly mineral-based compounds that your body creates to form your teeth.
What are the two types of enamel hypoplasia?
There are two types of enamel hypoplasia: hereditary enamel hypoplasia and environmental enamel hypoplasia, each with their own causes.
Why do teeth have lines?
This can be seen in the form of lines across the surface of one or multiple teeth or can manifest as a discoloration on the teeth. In rarer cases, the entire tooth may have a dark brown discoloration.
How to prevent hereditary enamel hypoplasia?
Although nothing can be done to prevent hereditary enamel hypoplasia, there are a few simple ways to reduce or reverse the environmental causes of enamel hypoplasia. Adding supplements of Vitamin A or D to your diet can help to strengthen developing teeth. Green, leafy vegetables and increased consumption of milk can also help .
What Causes Enamel Hypoplasia?
There are three main reasons why enamel hypoplasia happens during your teeth’s development.
How to restore enamel?
Drinking more milk and orange juice, and eating more leafy green vegetables can effectively resto re your body’s needs for Vitamins. If you have enamel hypoplasia, it may be useful to visit the dentist often for dental cleanings. The dents in your teeth are especially comfortable for harmful bacteria.
What does enamel hypoplasia look like?
Depending on the severity, enamel hypoplasia can look like a small dent in the tooth, or take up several teeth throughout the mouth. It often takes the form of grooves, pits, or lines within teeth, either across the surface or in certain spots.
What is it called when your teeth don't develop?
Enamel hypoplasia is a condition of your tooth enamel. When your baby teeth and adult teeth grow, sometimes the enamel doesn’t fully develop. While this condition is more common among children, adults can also be affected.
What does it mean when your teeth are not developed enough?
If so, you may have enamel hypoplasia. This lifelong dental condition means that the enamel of your teeth isn’t developed enough. Since enamel is the hardest substance in your body, it’s crucial to monitor your teeth and symptoms to catch any problem before they become severe. Discover what hypoplasia is, what symptoms to look out for, ...
How much does a Carefree Dental Card save?
If you treat enamel hypoplasia at participating dentists, the Carefree Dental Card can save you between 15%-50%* per visit in most instances.
Why is enamel worn out?
It’s incapable of repairing itself if it gets injured or eroded. Enamel wears away when it comes in contact with acids. That’s why you need to stay away from sugar and acidic foods. Good dental hygiene is crucial to keep your tooth’s enamel healthy.
How to treat EH?
Treatment for these conditions depends on the symptoms. For instance, if you or your child has EH or hypomineralization but are not experiencing pain or sensitivity, your dental professional may monitor the tooth during routine visits and likely recommend a fluoride toothpaste. However, some children and adults with EH or hypomineralization might experience cosmetic issues, tooth sensitivity, and an increased risk of decay. That’s why an early dental evaluation by your dental professional is critical. If they find either condition, they will likely recommend fluoride applications and remineralizing paste to decrease tooth decay. Teeth may also require repair with bonding, filling materials or crowns, and in some extreme cases, extraction. If your child grinds their teeth, your dental professional might recommend a nighttime mouthguard to prevent excessive tooth wear.
What is the difference between enamel hypoplasia and enamel hypoplasia?
On the other hand, enamel hypoplasia is a condition where teeth have pits, grooves, and missing enamel. It can also result in smaller teeth. Hypoplasia appears as brown or yellow stains and exposed dentin. While the enamel is still hard, it’s weak. It’s a type of amelogenesis imperfecta, where the enamel on teeth is missing or severely thin ...
What is enamel hypoplasia?
Enamel hypoplasia (EH) and hypomineralization are two teeth defects that can sometimes get confused. That’s because they’re both defects, often caused by genetic predispositions, that affect the development and enamel of your teeth. Here, we’ll look into the differences, causes, and treatments.
What does it mean when your teeth are discolored?
It can appear as discolored patches of soft or decaying, bumpy enamel that usually affect the molars and incisors as they grow in . The teeth with hypomineralization are sensitive and can cause children pain when eating, and these teeth typically start to deteriorate once they grow in.
What is the best treatment for tooth decay?
If they find either condition, they will likely recommend fluoride applications and remineralizing paste to decrease tooth decay. Teeth may also require repair with bonding, filling materials or crowns, and in some extreme cases, extraction.
Why does enamel break down?
Enamel hypomineralization happens when the mineralization process is not fully achieved, resulting in discolored enamel. This condition also weakens the teeth, which means that teeth can break down. The Australian Academy of Pediatric Dentistry also explains that hypomineralization is prevalent in a fifth of all children. It can appear as discolored patches of soft or decaying, bumpy enamel that usually affect the molars and incisors as they grow in. The teeth with hypomineralization are sensitive and can cause children pain when eating, and these teeth typically start to deteriorate once they grow in.
What are the stages of enamel formation?
These cells form in six stages: morphogenetic, organizing, formative, maturative, protective, and desmolytic. Enamel hypoplasia happens in the formation stage, resulting in the pitting, grooving, or even total absence of enamel. Hypomineralization happens in the maturative stage and can appear as “chalky” areas on your tooth’s enamel.