
Were You diagnosed with PCOS by ultrasound?
The polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is an important cause of both menstrual irregularity and androgen excess in women. PCOS can be readily diagnosed when women present with the classic features of hirsutism, irregular menstrual cycles, and polycystic ovarian morphology on transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS).
How to confirm PCOS diagnosis?
- you have irregular periods or infrequent periods – this indicates that your ovaries do not regularly release eggs (ovulate)
- blood tests showing you have high levels of "male hormones", such as testosterone (or sometimes just the signs of excess male hormones, even if the blood test is normal)
- scans showing you have polycystic ovaries
Can PCOS be diagnosed with a transvaginal ultrasound?
Transvaginal ultrasound is one of the main tools a physician has when it comes to diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). The images found on the ultrasound, in conjunction with the results of blood tests and a thorough patient history and physical, are used to diagnose this syndrome.
Does PCOS increase the risk of cancer?
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have a 2.7-fold increased risk for developing endometrial cancer. A major factor for this increased malignancy risk is prolonged exposure of the endometrium to unopposed estrogen that results from anovulation.
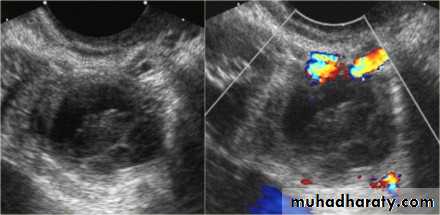
Does PCOS always show up on an ultrasound?
As only 2 of these need to be present to diagnose PCOS, you will not necessarily need to have an ultrasound scan before the condition can be confirmed.
How do doctors know you have PCOS through an ultrasound?
Transvaginal ultrasound On an ultrasound image (inset), a polycystic ovary shows many follicles. Each dark circle on the ultrasound image represents a fluid-filled follicle in the ovary. Your doctor may suspect PCOS if you have 20 or more follicles in each ovary.
Can PCOS be detected by abdominal ultrasound?
NEW YORK — Ovarian volume assessed by transabdominal ultrasound correlated strongly with serum testosterone levels in a study of 39 adolescent girls undergoing evaluation for polycystic ovary syndrome.
What can mimic PCOS?
Other disorders that mimic the clinical features of PCOS should be excluded: thyroid disease, high prolactin levels, and non-classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Large ovaries with many small follicles (which look like cysts, hence the name "polycystic"). These follicles are not cancerous.
How do you rule out PCOS?
There's no single test for it, but a physical exam, ultrasound, and blood tests can help diagnose PCOS. You need to meet 2 of these 3 "official" criteria to be diagnosed: Irregular, heavy, or missed periods due to missed ovulation—the release of an egg from your ovaries.
Can ultrasound detect hormonal imbalance?
Transvaginal ultrasound is one of the main tools a healthcare provider has when it comes to diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). The images found on the ultrasound, in conjunction with the results of blood tests and a thorough patient history and physical, are used to diagnose this syndrome.
Is it possible to be misdiagnosed with PCOS?
Even though PCOS is fairly common, it is often misdiagnosed. Women may experience PCOS symptoms for years before discovering what's causing their problems.
Can you see ovarian cysts on ultrasound?
A doctor may feel a cyst during a pelvic exam. Ultrasound. An ultrasound can pinpoint the location, size, and makeup of ovarian cysts. Abdominal ultrasound and vaginal ultrasound can evaluate ovarian cysts.
What hormones indicate PCOS?
The hormones that play a role in PCOS are: Androgens (like testosterone and androstenedione). Luteinizing hormone (LH). Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
What blood tests are done to diagnose PCOS?
Blood tests for testosterone and free androgen index (FAI) are the best tests for diagnosing whether you have hyperandrogenism (high androgen levels). Other blood tests that can be useful in identifying high androgen levels include: sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate (DHEAS)
Can you have PCOS with normal hormone levels?
It is also important to mention that since the “normal” ranges vary greatly for some hormones (especially since each lab sets its own “normal” values for these hormones), some women with PCOS have hormone levels that appear within the “normal” range, but still suffer from symptoms and still might have PCOS.
Should I see a gynecologist or endocrinologist for PCOS?
A reproductive endocrinologist can manage your PCOS treatment and often do ultrasounds in the office. Since many women with PCOS have difficulty conceiving, this is a good specialist to consider.
When is ultrasound done for PCOS?
You should go on 6 that day of periods.
What tests are done to diagnose PCOS?
Blood and Imaging tests: Your doctor may recommend blood tests to measure hormone levels and a pelvic ultrasound to get a closer look at your ovaries. Since PCOS still remains a diagnosis of exclusion, your doctor will ask you questions to rule out or rule in conditions that may mimic polycystic ovary syndrome.
Can you see ovarian cysts on ultrasound?
A doctor may feel a cyst during a pelvic exam. Ultrasound. An ultrasound can pinpoint the location, size, and makeup of ovarian cysts. Abdominal ultrasound and vaginal ultrasound can evaluate ovarian cysts.
How many follicles indicate PCOS?
The ASRM/ESHRE threshold to define polycystic ovaries on ultrasound was the presence of 12 or more follicles measuring 2–9 mm in diameter or an increased ovarian volume (>10 mL) in at least one ovary.
How big are PCOs?
The cysts are found just below the surface of the ovaries and are usually no bigger than 8 mm in diameter. They are egg-containing follicles that have not developed properly due to a hormonal imbalance and do not release at the time of ovulation, instead they remain in a small, immature state appearing like small cysts arranged in a radial pattern just below the surface around the edge of the ovary. Due to the small size of the cysts a transvaginal ultrasound is going to give a clearer indication of PCOS to your doctor than any external ultrasound would.
What is a polycystic ovary?
Polycystic Ovaries: The presence on ultrasound scan of multiple small follicles just below the surface of the ovary.
Why do I need an ultrasound?
Diagnosing PCOS isn’t always straightforward. To be officially classified as having PCOS you have to meet a standard known as the Rotterdam Criteria. The Rotterdam Criteria states that you must have two of the three following conditions to be diagnosed with PCOS.
Does Inofolic Alpha help with PCOs?
Inofolic Alpha has been clinically proven to restore ovulation in 95% of PCOS women after only 3 months and is recommended by UK clinicians. It doesn’t just help with restoring ovulation and regulating periods, it can treat all aspects of PCOS.
Is transvaginal ultrasound more invasive than external ultrasound?
Whilst the transvaginal ultrasound procedure is more invasive than an external ultrasound, this procedure does give you the best possible chance of an accurate diagnosis. The transvaginal ultrasound will give your doctor a better understanding of your reproductive health to better manage your situation.
What is PCOS syndrome?
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), also known as hyperandrogenic anovulation or Stein–Leventhal syndrome, is a multifaceted collection of signs and symptoms. Since this condition is a complex syndrome, no gold standard criteria exist for a quick and easy PCOS diagnosis.
What is the best ultrasound for ovarian cancer?
3D transvaginal ultrasound provides the most detailed view of ovarian tissue. If 3D ultrasound is not available, using 2D transvaginal ultrasound with a cine sweep through both the sagittal and transverse planes of each ovary can provide adequate information on ovarian size and number of follicles. In situations where transvaginal ultrasound is contraindicated (as with non-sexually-active or young patients), transabdominal ultrasound can be used instead.
What is the string of pearls on an ultrasound?
This last symptom commonly presents as an ultrasound marker known as the string of pearls.
How many follicles are there in the ovary?
Presence of 12 or more ovarian follicles (measuring 2–9 mm), arranged peripherally in the ovary like a string of pearls.
Can you get PCOs from an ultrasound?
Keeping this in mind, the educated clinician will know that not every string of pearls glimpsed on ultrasound will lead to a PCOS diagnosis. However, ultrasound exams can be a critical factor in the search for answers for patients with PCOS.
Can a pelvic ultrasound show PCOs?
When PCOS is suspected and a pelvic ultrasound is necessary to evaluate the appearance of the ovaries, it’s helpful to know how to identify the specific ultrasound features of PCOS. Only one ovary has to be polycystic to raise any suspicions.
What is the role of ultrasound in PCOs?
PCOS Diagnosis: The Role of Pelvic Ultrasound. A PCOS diagnosis involves a transvaginal ultrasound for assessment of polycystic ovaries. Learn more today. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) affects 6.6 percent or 4-5 million women in the United States, making it the most common endocrine abnormality in women of reproductive age, ...
How much ovarian volume does PCOs have?
The presence of a dominant follicle (a follicle with diameters greater than 10 mm) or corpus luteum may increase the ovarian volume to more than 10 cm³. In these cases, the physician should perform additional scans during the patient's next menstrual cycle.
What can ultrasound help with?
Ultrasound can help look for patterns to diagnose polycystic ovary syndrome and predict outcomes.
What are the criteria for polycystic ovary?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists acknowledges two criteria on the basis of which a polycystic ovary may be identified: ovarian volume and number of follicles. These criteria are based on a review of literature in RadioGraphics comparing women with PCOS with healthy control subjects.
What should be included in an ovarian imaging report?
The imaging report should specifically include ovarian volumes, follicle counts and any other relevant information, such as the presence of a dominant follicle or corpus luteum.
What percentage of women have polycystic ovaries?
Polycystic ovaries are commonly seen during routine ultrasounds. The Lancet Journal reports that 23 percent of women of reproductive age are likely to have polycystic ovaries. Only 5-10 percent of these women, however, will have classic symptoms of PCOS, such as infertility, amenorrhea, signs of hirsutism or obesity.
Which is more effective for detecting polycystic ovaries?
Compared with transabdominal ultrasound, it is more effective for detecting the appearance of polycystic ovaries in women ...
