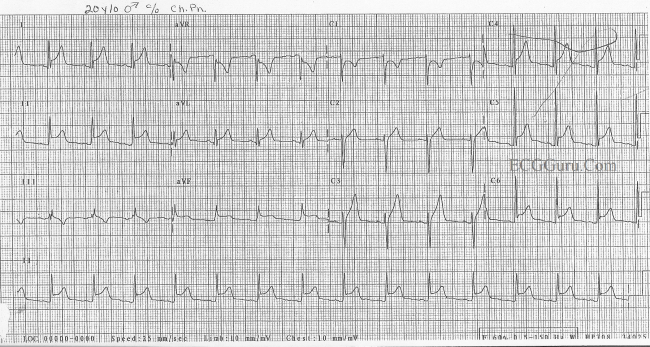
In pericarditis four stages can be distinguished on the ECG:
- stage I: ST elevation in all leads. PTa depression (depression between the end of the P-wave and the beginning of the QRS- complex)
- stage II: pseudonormalisation (transition)
- stage III: inverted T-waves
- stage IV: normalisation
How do you diagnose pericarditis?
· Can you see pericarditis on ECG? The electrocardiogram (ECG) is very useful in the diagnosis of acute pericarditis. Characteristic manifestations of acute pericarditis on ECG most commonly include diffuse ST-segment elevation. However, other conditions may have ECG features similar to those of acute pericarditis. Click to see full answer.
How to diagnose pericarditis?
· This article has been cited by other articles in PMC. Acute pericarditis is an inflammation of the pericardium that can result in chest pain, pericardial friction rub, and serial electrocardiogram (ECG) changes.
What are the signs and symptoms of acute pericarditis?
Pericarditis, or inflammation of the pericardium, has typical ECG findings. These findings occur in progressive stages, all of which are seen in about 50% of cases of pericarditis.
Can you have pericarditis without ECG changes?
· In patients with cardiac tamponade, the EKG may show signs of pericarditis, with especially low QRS voltages and electrical alternans 3. Constrictive pericarditis. Constrictive …
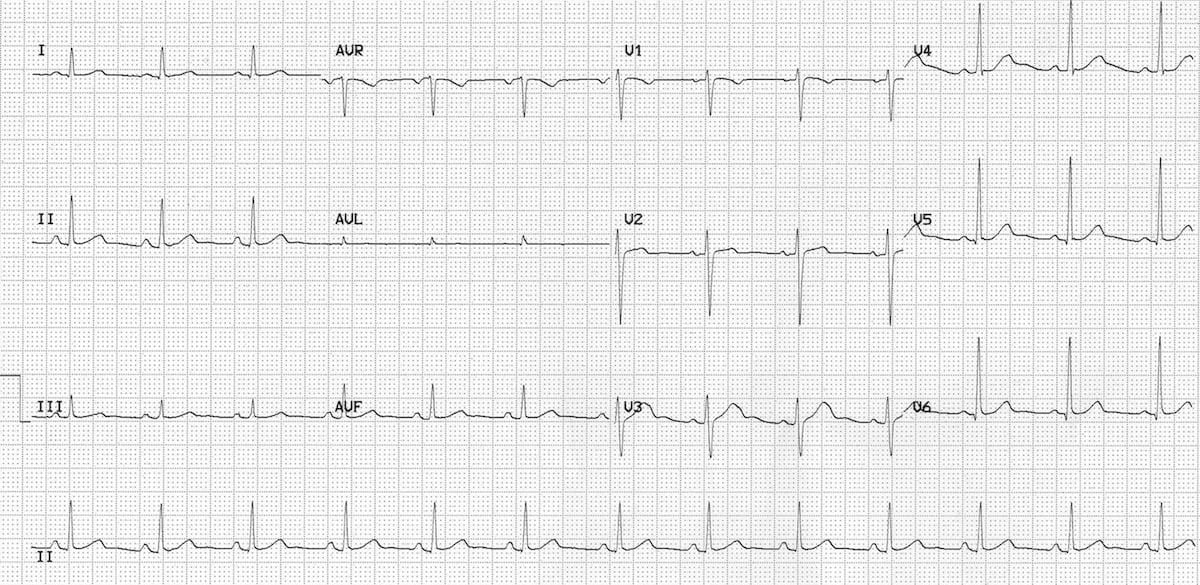
Can you have pericarditis with normal ECG?
In pericarditis, there are hallmark changes that are seen and can help make the diagnosis. While an abnormal EKG is helpful in making the diagnosis, in the early stages of inflammation, the EKG may be normal. In most cases of uncomplicated pericarditis, a chest X-ray is usually normal.
Can pericarditis be missed on ECG?
] suggested that PR-segment deviation is the earliest ECG change in patients with acute pericarditis. Therefore, PR-segment deviation seen in ECG must be important in terms of acute pericarditis diagnosis. We have called this type of pericarditis as atypical pericarditis, for acute pericarditis diagnosis may be missed.
How is pericarditis diagnosed on ECG?
Pericarditis ECG ReviewStage I (acute phase): Diffuse concave upward ST segment elevation in most leads, PR depression in most leads (may be subtle) and sometimes notching at the end of the QRS complex.Stage II: ST segment elevation and PR depression have resolved and T waves may be normal or flattened.More items...
Is pericarditis seen on echocardiogram?
Pericarditis remains a clinical diagnosis confirmed by ECG and echocardiography. Patients typically have precordial pain that improves with sitting and leaning forward.
What is the best test for pericarditis?
The diagnostic test of choice for large effusions, cardiac tamponade, and constrictive pericarditis is two-dimensional Doppler echocardiography.
How do I know if I have pericarditis or myocarditis?
The main difference between pericarditis, myocarditis, and endocarditis is the layer affected. Pericarditis is inflammation in the pericardium, myocarditis inflames the myocardium, and endocarditis means inflammation in the endocardium.
What does acute pericarditis feel like?
A common symptom of acute pericarditis is a sharp, stabbing chest pain, usually coming on quickly. It's often is in the middle or left side of the chest, and there may be pain in one or both shoulders. Sitting up and leaning forward tends to ease the pain, while lying down and breathing deep worsens it.
Does pericarditis hurt to touch?
If you have pericarditis, you'll notice pain in your chest. This pain is usually constant and may be sharp, stabbing or aching. You may find this gets better if you sit down and lean forward. But the pain may spread to your neck and shoulders (especially your left shoulder), and to your tummy (abdomen).
Does chest xray show pericarditis?
Expert Analysis. The chest radiograph (CXR) is typically the first imaging test performed in patients with potential pericardial disease. Within 10 years of the discovery of x-rays, publications highlighted their value in detecting pericardial disease.
What can mimic pericarditis?
In addition to these conditions, chest pain that can mimic pericarditis is seen in a wide range of conditions including gastric inflammation (gastritis) or ulcers, esophageal inflammation (esophagitis) and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), clots in the arteries of the lung (pulmonary embolism), inflammation of ...
How to distinguish pericarditis from benign early repolarisation?
Pericarditis can be difficult to differentiate from Benign Early Repolarisation (BER) as both conditions are associated with concave ST elevation. One useful trick to distinguish between these two entities is to look at the ST segment / T wave ratio and the Fish Hook Pattern
What is pericardial pain?
Definition. Inflammation of the pericardium secondary to infection, localised injury or systemic disorders producing characteristic chest pain, dyspnoea and serial ECG changes. Chest pain is often retrosternal in nature, pleuritic, and positional (relieved by sitting forward, worse lying flat)
Why is sinus tachycardia common in acute pericarditis?
Sinus tachycardia is also common in acute pericarditis due to pain and/or pericardial effusion
Can BER cause pericarditis?
Remember that it is possible for a patient with BER to get pericarditis!
Can pericarditis cause PR segment depression?
PR segment depression is only reliably seen in viral pericarditis, not by other causes. It is often only an early transient phenomenon (lasting only hours). MI can also cause PR segment depression due to atrial infarction (or PR segment elevation in aVR).
Is tachycardia age appropriate?
This (sadly slightly faded) ECG was taken from a 6-year old child with viral pericarditis, hence the tachycardia is age-appropriate. The child also had evidence of myocardial involvement with elevated cardiac enzymes (i.e. myopericarditis) .
Can pericarditis cause ST elevation?
Pericarditis can cause localised ST elevation but there should be no reciprocal ST depression (except in AVR and V1). STEMI, like pericarditis, can also cause concave up ST elevation. Only STEMI causes convex up or horizontal ST elevation. ST elevation greater in III than II strongly suggests a STEMI.
What is the most common symptom of pericarditis?
Chest pain is the most common symptom of pericarditis, it is most often sharp and pleuritic in nature. Usually it is precordial or retrosternal, with exacerbation by inspiration or coughing, and it decreases in intensity when the patient sits up and leans forward.
What is acute pericarditis?
Acute pericarditis is an inflammation of the pericardium. This inflammation causes EKG changes that have typically evolved sequentially through 4 stages 1. Acute pericarditis can be difficult to distinguish from ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.
Why is serial electrocardiogram important?
Serial electrocardiograms are helpful in patients with acute pericarditis because it causes characteristic 12-lead EKG changes that have typically evolved sequentially through 4 stages 1 2.
How long does it take for pericarditis to recur?
Recurrent pericarditis: Recurrent pericarditis is diagnosed with a documented first episode of acute pericarditis, a symptom-free interval of 4 – 6 weeks or longer and evidence of subsequent recurrence of pericarditis.
What does EKG show in a patient with tamponade?
In patients with cardiac tamponade, the EKG may show signs of pericarditis, with especially low QRS voltages and electrical alternans 3.
What is pericardial friction rub?
The presence of a pericardial friction rub on physical examination is pathognomonic for acute pericarditis. It is generated by friction between the two inflamed layers of the pericardium.
What is the first line of treatment for acute pericarditis?
Aspirin or NSAIDs are recommended as first-line therapy for acute pericarditis with gastroprotection.
What are the two forms of pericarditis?
There are two forms of pericarditis: acute and chronic. This article will focus on the former, as it has implications for all clinicians and the ECG. Acute pericarditis causes chest pain, which may be very difficult to discern from pain caused by acute myocardial infarction.
What causes acute pericarditis?
Causes of acute pericarditis/myocarditis. The most frequent cause of pericarditis is infections, in particular viral infections. This explains why pericarditis may affect individuals of all ages. However, a wide range of local and systemic conditions may cause pericarditis. The most common causes are as follows:
What is the ECG used for?
The ECG is used to diagnose acute pericarditis. One must always rule out the most serious differential diagnosis, which is ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEM). In order to provide the reader with knowledge on this matter, we will now discuss the characteristics of all ECG changes seen in acute pericarditis, and contrast them to ECG changes seen in STEMI.
What is the pericardium?
The pericardium is a double-walled sac in which the heart and the roots of the great vessels are contained (Figure 1). The pericardial sac encloses the pericardial cavity which contains pericardial fluid. Numerous conditions may cause inflammation in the pericardium, ...
How long does it take for pericarditis to change?
ECG changes in pericarditis are rather static and changes slowly over the course of several days to weeks.
Does pericarditis radiate to the back?
Moreover, the pain in acute pericarditis may also , as in STEMI, radiate to the neck, shoulders or back. However, acute pericarditis is more likely if inspiration and supine position worsens the chest pain, and sitting upright and leaning forward alleviates the chest pain; the pain in STEMI is unaffected by position.
Is pericarditis a myocardial sac?
Note that pericarditis (inflammation of the pericardial sac) is difficult to discern from myocarditis (inflammation of the myocardial tissue) and because they tend to accompany each other, the term perimyocarditis is often used. Image by Bruce Blausen, Blausen Gallery 2014.
What is the purpose of a pericarditis test?
The test can be used to look for thickening that may be a sign of constrictive pericarditis. Your doctor may order this test to rule out other causes of sudden chest pain, such as a blood clot in a lung (pulmonary embolus) or a tear in your aorta (aortic dissection). Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
What is the sound of pericarditis?
During the exam, the doctor will place a stethoscope on your chest to listen to your heart sounds. Pericarditis causes a specific sound, called a pericardial rub. The noise occurs when the two layers of the sac surrounding your heart (pericardium) ...
What is the best medicine for pericarditis?
Pericarditis pain can usually be treated with over-the-counter pain relievers, such as aspirin or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others). Prescription-strength pain relievers also may be used. Colchicine (Colcrys, Mitigare). This drug reduces inflammation in the body.
Why does my heart make a noise?
The noise occurs when the two layers of the sac surrounding your heart (pericardium) rub against each other. Blood tests are usually done to check for signs of a heart attack, inflammation and infection. Other tests used to diagnose pericarditis include: Electrocardiogram (ECG).
What is ECG test?
Electrocardiogram (ECG). An electrocardiogram is a quick and painless test that records the electrical signals in your heart. Sticky patches (electrodes) with wires attached connect to a monitor. They record the electrical signals that make your heart beat.
What is the purpose of a cardiac MRI?
Cardiac MRI uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create cross-sectional images of your heart that can reveal thickening, inflammation or other changes in the pericardium.
What does chest x-ray show?
Chest X-ray. A chest X-ray can show changes in the size and shape of your heart. The images may show an enlarged heart if excess fluid has collected in the pericardium. Echocardiogram. Sound waves (ultrasound) create images of the moving heart.
How does a doctor diagnose pericarditis?
A doctor diagnoses pericarditis based on your medical history, a physical exam and test results.
How to tell if pericardium is inflamed?
Physical exam. When the pericardium is inflamed, the fluid between the sac's two layers of tissue increases. So your doctor will look for signs of excess fluid in your chest. A common sign is the pericardial rub. This is the sound of the pericardium rubbing against the outer layer of your heart.
What is the condition that causes scar tissue in the heart?
Chronic constrictive pericarditis is a rare disease that takes time to develop. It leads to scar-like tissue forming throughout the sac around the heart. As the sac becomes stiff and unable to move properly, the scarred tissue starts to compress the heart and prevent it from functioning well.
What does a CT show on a chest X-ray?
It can show fluid build-up in the pericardium. Cardiac CT (computed tomography) : This X-ray takes a clear, detailed picture of your heart and pericardium and helps to rule out other causes of chest pain.
What kind of doctor treats pericarditis?
Primary care doctors, such as a family doctor, internist or pediatrician, often diagnose and treat pericarditis. A cardiologist, pediatric cardiologist or infectious disease specialist may be involved, depending on the patient’s age and medical conditions.
What does chest pain feel like?
The chest pain may feel like a heart attack. If you experience chest pain, call 911 right away because you may be having a heart attack. Fever is another common symptom of acute pericarditis. Other symptoms are weakness, trouble breathing and coughing. Palpitations, which are feelings that your heart is skipping a beat, ...
What does a chest xray show?
Chest X-ray : A chest X-ray takes pictures of the inside of the chest, including your heart, lungs and blood vessels. The pictures can show whether you have an enlarged heart, which can be a sign of excess fluid in your pericardium.
What is the pain in the chest from pericarditis?
The chest pain of pericarditis can vary from severe substernal discomfort to a vague "ache". The chest pain is usually positional, not related to exertion and often radiates to the neck, ridge of the trapezius muscle or shoulder.
What are the criteria for acute pericarditis?
A. A. Currently, the diagnosis of acute pericarditis is based on demonstrating at least two of the following four criteria: 1. Non-ischemic chest pain, 2. ECG evidence of PR depression or ST segment deviation, 3. Detection of a pericardial rub on auscultation and 4.
How long after contrast injection does gadolinium go into the pericardium?
Figure 2: Diffuse abnormal pericardial uptake of gadolinium, diagnostic of pericarditis, using delayed enhancement imaging 10 to 15 minutes after contrast injection. The inflammatory process allows redistribution of gadolinium into the pericardial interstitium. Note the absence of a pericardial effusion.
Does pericarditis have chest pain?
Figure 5: Distribution of pericarditis by age group. Note that very few patients with cardiac MRI findings of pericarditis have no chest pain.
Does MRI detect water?
With most inflammatory disorders, accumulation of interstitial water is a component of the pathologic process. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is ideally suited for the detecting the exact anatomic location of non-physiologic water, including edema. With T2 weighted cardiac MRI pulse sequences, water appears "bright" and is easily detected, given the excellent spatial resolution of MRI (see Figure 1). T2 weighted imaging does not require contrast injection. However, use of gadolinium contrast with delayed enhancement imaging offers an additional method of detecting abnormal redistribution of water into the pericardial interstitium (see Figure 2). Both Figures 1 and 2 are examples of pericarditis without associated pericardial effusion. A more "classic" example of pericarditis with effusion is shown in Figure 3.
Can pericarditis be detected with CMR?
Boniface et al 3 presented data at the 2014 American Heart Association Scientific Sessions on CMR evaluation of 708 patients with chest pain who had a negative ischemic evaluation, but complained of persistent chest discomfort and were labeled as non-cardiac chest pain. Cardiac MRI of these patients revealed that 143 of 708 (20.2%) had evidence of pericarditis, undetected by standard diagnostic criteria. These data suggest that 1 out 5 patients with recurrent chest pain and a negative ischemic evaluation may actually have pericarditis. More recent data from Morgenstern et al 4 showed that that the likelihood of detecting pericarditis with CMR in patients with chest pain was highest among patients under age 40, and much less likely in patients over age 60 (see Figure 5).
Can pericarditis be detected on echocardiography?
Patients with non-ischemic chest pain suspicious for pericarditis, but no detectable effusion on 2-D echocardiography.
What is the most sensitive sign for pericardial effusion?
The most sensitive sign for a pericardial effusion on CXR is enlargement of the cardiac silhouette (cardiothoracic ratio (CTR) >50%) (Figure 1). This has reasonable sensitivity (71%), but low specificity (41%). Specificity increases as cardiomegaly increases (76% with CTR of 60%), but sensitivity falls. 3
Why is the left parietal pericardium thick?
The thickening of the left parietal pericardium is due to the malignant involvement. Note the air is predominantly in the non-dependent (superior) pericardium on this erect radiograph. Pneumopericardium in a patient who has had da pericardial drain (open arrow) for a malignant (metastatic disease) pericardial effusion.
What is a globular pericardial effusion?
A pericardial effusion will generally symmetrically expand the pericardial contour. This gives rise to a " globular " configuration. Features on a frontal CXR include flattening of the upper heart borders followed by broad bulging. For those preferring pareidolic terms (pareidolia refers to the human ability to recognize shapes in an unrelated image) this is referred to as " flask-shaped " or the " water bottle sign " (presumably after the older style round leather canteen). An alternative term is the " chicken on a fence " sign (the chicken representing the cardiac silhouette sitting on the diaphragm). 4
Why is a cardiac silhouette well defined?
Some describe a "well defined" cardiac silhouette due to dampening of cardiac motion artefact by the pericardial fluid. There are many other technical factors at play (including exposure time and post processing), making this very subjective.
How to distinguish calcifications on CXR?
The key to distinguishing calcifications on a CXR is recognizing their anatomical location. Other common calcifications include myocardial infarction (typically have a shorter arc); left atrial calcification (can produce a rounded appearance, particularly in a dilated atrium); coronary artery calcification (tubular and curvilinear), valvular calcification and pleural calcification.
Can a cardiac defect cause herniation?
These appearances highlight that herniation through defects can be of either cardiac structures out of the pericardium, or extracardiac structures (such as lung) into the pericardium. A diaphragmatic pericardial defect can result in herniation of abdominal structures – of which bowel is most visible on the CXR.
