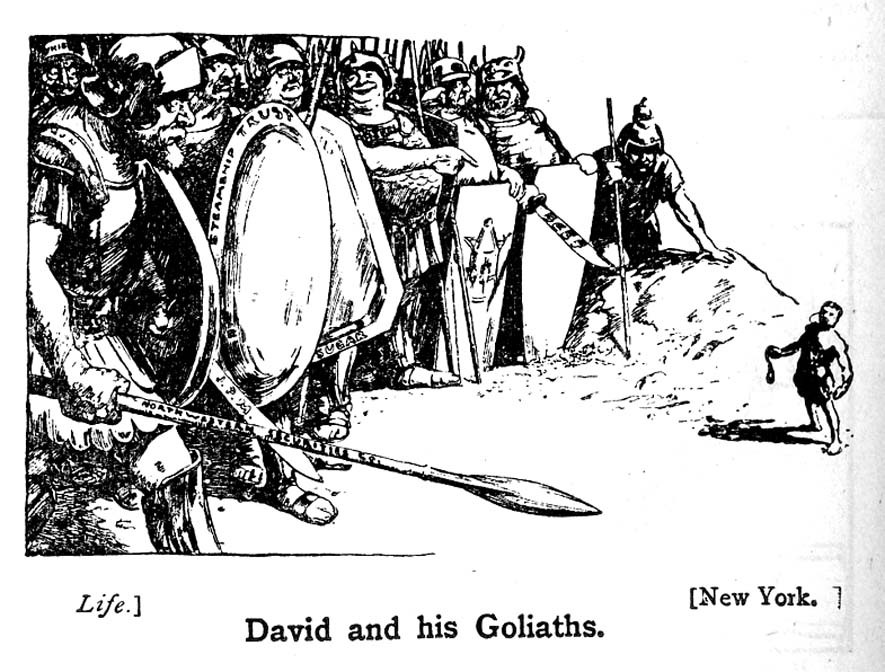
The Clayton Antitrust Act was much more effective than the earlier Sherman Antitrust Act
Sherman Antitrust Act
The Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890 is a United States antitrust law that regulates competition among enterprises, which was passed by Congress under the presidency of Benjamin Harrison.
What is the Clayton Antitrust Act of 1914?
(Show more) Clayton Antitrust Act, law enacted in 1914 by the United States Congress to clarify and strengthen the Sherman Antitrust Act (1890).
Does the Clayton Act apply to trade unions?
Like the Sherman Act, much of the substance of the Clayton Act has been developed and animated by the U.S. courts, particularly the Supreme Court . Since the Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890, courts in the United States had interpreted the law on cartels as applying against trade unions.
What is the difference between the Sherman and Clayton Antitrust Act?
However, the vague language of the bill allowed businesses to continue engaging in operations that discouraged competition and fair pricing. While the Sherman Antitrust Act made monopolies illegal, the Clayton Antitrust Act banned operations conducive to the formation of monopolies.
What happens if you violate the Clayton Antitrust Act?
The Clayton Antitrust Act allows parties injured through violations of the act to sue for damages. Individuals and corporations that violate the act can be sued for three times the amount of damages suffered by the victim.

Was the Clayton Antitrust Act successful?
The main purpose of the Clayton Antitrust Act was to make the open market more fair. The act was successful in this because it enforced the limitation on businesses of creating monopolies and anticompetitive business dealings.
What did the Clayton Antitrust Act accomplish?
The newly created Federal Trade Commission enforced the Clayton Antitrust Act and prevented unfair methods of competition. Aside from banning the practices of price discrimination and anti-competitive mergers, the new law also declared strikes, boycotts, and labor unions legal under federal law.
Was the Sherman Antitrust Act successful?
For more than a decade after its passage, the Sherman Antitrust Act was invoked only rarely against industrial monopolies, and then not successfully. Ironically, its only effective use for a number of years was against labor unions, which were held by the courts to be illegal combinations.
How did the Clayton Antitrust benefit labor?
As such, the Clayton Act prohibits companies from preventing activities of labor unions such as strikes, boycotts, collective bargaining, and compensation disputes. Labor unions can negotiate for better employment benefits and better wages without being accused of price fixing.
What made the Sherman Antitrust Act so ineffective?
For more than a decade after its passage, the Sherman Act was invoked only rarely against industrial monopolies, and then not successfully, chiefly because of narrow judicial interpretations of what constitutes trade or commerce among states.
What did the Clayton Antitrust Act do quizlet?
The Clayton Antitrust Act attempts to prohibit certain actions that lead to anti-competitiveness. Outlaws price discrimination, prohibits tying contracts, prohibits stock acquisition of competing corporations, prohibits the formation of interlocking directorates (director of one firm, is board member on another firm).
What was the biggest problem with the Sherman Antitrust Act?
The Sherman Antitrust Act was not designed to prevent healthy monopolistic competition but to target monopolies that resulted from a deliberate attempt to dominate the marketplace.
What was a difference between the Sherman and Clayton Antitrust Acts apex?
Whereas the Sherman Act only declared monopoly illegal, the Clayton Act defined as illegal certain business practices that are conducive to the formation of monopolies or that result from them.
How did Roosevelt's use of the Sherman Antitrust Act affect business?
The federal government used the Act to invalidate formal and informal arrangements by which different companies in the same industry set prices, though for the first decade of its existence the Act did little to slow the rate of business mergers.
How did the Clayton Antitrust Act work to strengthen the Sherman Antitrust Act?
Key Takeaways. The Clayton Antitrust Act of 1914 continues to regulate U.S. business practices today. Intended to strengthen earlier antitrust legislation, the act prohibits anticompetitive mergers, predatory and discriminatory pricing, and other forms of unethical corporate behavior.
Why was the Clayton Antitrust Act popular among labor leaders?
The primary reason that labor unions liked the Clayton Antitrust Act was that it specifically made unions legal and made any law that prohibited labor...
What was the Clayton Act and how did it affect the issuance of injunctions in labor disputes?
By 1912, labor had organized widely, and it played a pivotal role in electing Woodrow Wilson and giving him a Democratic Congress, which responded in 1914 with the Clayton Act's “labor exemption.” Section 6 of the Clayton Act says that labor unions are not “illegal combinations or conspiracies in restraint of trade, ...
What is the Clayton Antitrust Act in simple terms?
The Clayton Antitrust Act is a piece of legislation, passed by the U.S. Congress and signed into law in 1914, that defines unethical business practices, such as price fixing and monopolies, and upholds various rights of labor.
What are the four main points of the Clayton Antitrust Act?
The Clayton Act, authored by Alabama congressman Henry Clayton, outlawed, among other things, anticompetitive mergers and acquisitions, interlocking directorates, and price discrimination.
Who does the Clayton Act protect?
The Clayton Antitrust Act is one of several antitrust laws passed in the US. Its goal is to prevent anticompetitive behavior by businesses and protect consumers from monopolies — as well as the inflated prices monopolies can lead to.
Which of the following was true of the Clayton Antitrust Act?
Which of the following was true of the Clayton Anti-Trust Act? It outlawed price discrimination and exempted labor unions from anti-trust laws.
What was the Clayton Act?
Whereas the Sherman Act only declared monopoly illegal, the Clayton Act defined as illegal certain business practices that are conducive to the formation of monopolies or that result from them.
Who enforces the Clayton Act?
The Clayton Act and other antitrust and consumer protection regulations are enforced by the Federal Trade Commission. The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica This article was most recently revised and updated by Adam Augustyn, Managing Editor, Reference Content.
Which amendment made the Clayton Act more enforceable?
Two sections of the Clayton Act were later amended by the Robinson-Patman Act (1936) and the Celler-Kefauver Act (1950) to fortify its provisions. The Robinson-Patman amendment made more enforceable Section 2, which relates to price and other forms of discrimination among customers.
What was the Celler-Kefauver Act?
In contrast, the Celler-Kefauver Act went further by restricting even mergers of companies in different industries (i.e., conglomerate mergers).
What is the Clayton Antitrust Act?
The Clayton Antitrust Act, passed in 1914, continues to regulate U.S. business practices today. Intended to strengthen earlier antitrust legislation, the act prohibits anticompetitive mergers, predatory and discriminatory pricing, and other forms of unethical corporate behavior. The Clayton Antitrust Act also protects individuals by allowing ...
How does the Clayton Antitrust Act protect individuals?
The Clayton Antitrust Act also protects individuals by allowing lawsuits against companies and upholding the rights of labor to organize and protest peacefully. There have been several amendments to the act, expanding its provisions.
What Is the Clayton Act’s Overall Goal?
The Clayton Act, in conjunction with other antitrust laws, is responsible for making sure that companies behave themselves and that there is fair competition in the marketplace, which, according to economic theory, should lead to lower prices, better quality, greater innovation, and wider choice.
What is the Clayton Act?
In addition, the Clayton Act specifies that labor is not an economic commodity. It upholds issues conducive to organized labor, declaring peaceful strikes, picketing, boycotts, agricultural cooperatives, and labor unions were all legal under federal law. There are 26 sections to the Clayton Act.
Which agency enforces the Clayton Antitrust Act?
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the Antitrust Division of the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) enforce the provisions of the Clayton Antitrust Act, which continue to affect American business practices today.
What is the Celler-Kefauver Act?
The Celler-Kefauver Act prohibited one company from acquiring the stock or assets of another firm, if an acquisition reduced competition. It further extended antitrust laws to cover all types of mergers across industries, not just horizontal ones within the same sector.
How did the 20th century dominate the industry?
corporations began to dominate entire industry segments by engaging in predatory pricing, exclusive dealings, and mergers designed to destroy competitors. 1
History of The Clayton Act
- In the 1880s and 1890s, the United States experienced rapid economic growth. The economic expansion attracted immigrants from Europe who were enticed by higher wages offered in the United States. Many of these immigrants were employed in rapidly growing industries such as ra…
Specifics of The Clayton Antitrust Act
- As of 2016, the Clayton Antitrust Act comprised 26 sections. The following are some of the most notable sections that influence business practices in the United States:
Exemptions to The Clayton Act: Labor Unions
- Unlike the Sherman Act, the Clayton Antitrust Act exempts labor unions and agricultural activities from their regulations. According to the law, the labor of a human being does not constitute a trade or a commodity, and should not be subject to the same regulations as companies engaging in trade. As such, the Clayton Act prohibits companies from preventing activities of labor unions …
Related Readings
- CFI is the official provider of the global Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)™certification program, designed to help anyone become a world-class financial analyst. To keep advancing your career, the additional CFI resources below will be useful: 1. Competitive Advantage 2. Market Power 3. Oligopoly 4. Sherman Antitrust Act