Do all polar molecules contain a polar covalent
Covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs, and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding.
What molecules contain polar covalent bonds?
What is Covalent Bond?
- Covalent bonding, in simple words, is the sharing of electrons between atoms to attain the noble gas configuration of the participating individual atoms.
- The atoms in a covalent bond are held together by the electrostatic force of attraction. ...
- The electrons that join atoms in a covalent bond are called the bonding pair of electrons. ...
Which molecule contains a polar covalent bond?
Properties of Covalent Bond
- Most covalent compounds have relatively low melting points and boiling points. ...
- Covalent compounds usually have lower enthalpies of fusion and vaporisation than ionic compounds. ...
- Covalent compounds tend to be soft and relatively flexible. ...
- Covalent compounds tend to be more flammable than ionic compounds. ...
Do polar molecules always contain carbon?
large polar molecules that always have C, H, and O with a 2:1 hydrogen to oxygen ratio;
What molecule is polar and contains polar bonds?
Practice
- How do you identify polar bonds in a molecule?
- What electronegativity difference would indicate a polar bond?
- Is a molecule with symmetric polar bonds a polar molecule?

Do polar molecules have polar covalent bonds?
Therefore, when a hydrogen atom is bonded to common nonmetals, the resulting polar bond has a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom. The magnitude of the polarity of a bond is the dipole moment, (D)....Polar Covalent Bonds.Structural Unit1Bond Moments (D)H—Cl1.1H—Br0.8H—I0.4C—C0.013 more rows
Are polar covalent bonds polar or nonpolar?
Figure 4.4. (b) The fluorine atom attracts the electrons in the bond more than the hydrogen atom does, leading to an imbalance in the electron distribution. This is a polar covalent bond. Any covalent bond between atoms of different elements is a polar bond, but the degree of polarity varies widely.
Which molecule contains only polar covalent bonds?
Polar bonds are intermediate between pure covalent bonds and ionic bonds. They form when the electronegativity difference between the anion and cation is between 0.4 and 1.7. Examples of molecules with polar bonds include water, hydrogen fluoride, sulfur dioxide, and ammonia.
Can a nonpolar molecule contain polar bonds?
This results in a tetrahedral configuration. Therefore, the molecule has no net dipole moment. They all sort of cancel each other out. So, a nonpolar molecule can have polar bonds, but due to symmetry in the molecule, there are no net poles.
Which molecule contain both polar and nonpolar covalent bond?
So the correct answer is hydrogen peroxide.
Are all molecules that have polar covalent bonds also polar molecules quizlet?
are all molecules that have polar bonds polar molecules? no, If the symmetry of the molecule is such that the dipoles of the polar groups oppose and cancel each other out, (say for instance 1,4-dinitrobenzene) - then the molecule will be non-polar.
Why do some molecules contain polar bonds but are not polar molecules?
Polar bonds form between atoms of elements with different electronegativity values. Nonpolar molecules may contain any type of chemical bonds, but the partial charges cancel each other out. Polar molecules contain polar covalent or ionic bonds that are arranges so their partial charges do not cancel each other out.
What is the name of the reaction where a polar-covalent X-H bond forms a strong?
The major exception is acid-base reactions, in which a polar-covalent X-H bond chemically reacts with a Bronsted base to form a new, strong bond to the hydrogen atom. This sort of reaction has a low activation energy and is often exothermic. It is called “dissociation” because it transforms two neutral molecules into a cation and an anion.
What type of bond is formed by sharing electrons between atoms?
Covalent bond is that type of bond that is formed between atoms by sharing of electrons between them.sometimes those atoms that form covalent compound have difference in their electronegativity (that is ability of atoms to attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself in a molecule) so that one atom attract the shared pair of electrons more towards itself so it acquires a slight negative charge on it and the other atom develops a slight positive charge on it.so here covalent bond becomes polar due to creation of charges on atoms in a covalent compound.e.g., HCL is a very good example of
Is a covalent bond polar?
All covalent bonds between two different atoms are polar, only some are less polarised than others. This depends on the difference in electronegativity of the atoms sharing the covalent bond. The greater the polarity difference, the more polar the bond is.
Can covalent bonds be heterolyzed?
Generally we observe “heterolysis” of a covalent bond when there’s something else around that can form a strong bond to one of the resulting ions. For example, the SN1 reaction.
Is ozone polar or nonpolar?
Nope. For example ozone. All of the bonds (both of them!!!) are oxygen-oxygen bonds. Perfectly nonpolar. But ozone is polar. why? Because on the central oxygen there are three regions of electron density and one of those regions is unlike the other two as it contains a lone pair of valence electrons. The geometry is nearly trigonal planar and that all is enough to make ozone polar. Polarity is about unlike regions of electron density around a central atom.
Is a linear molecule polar or nonpolar?
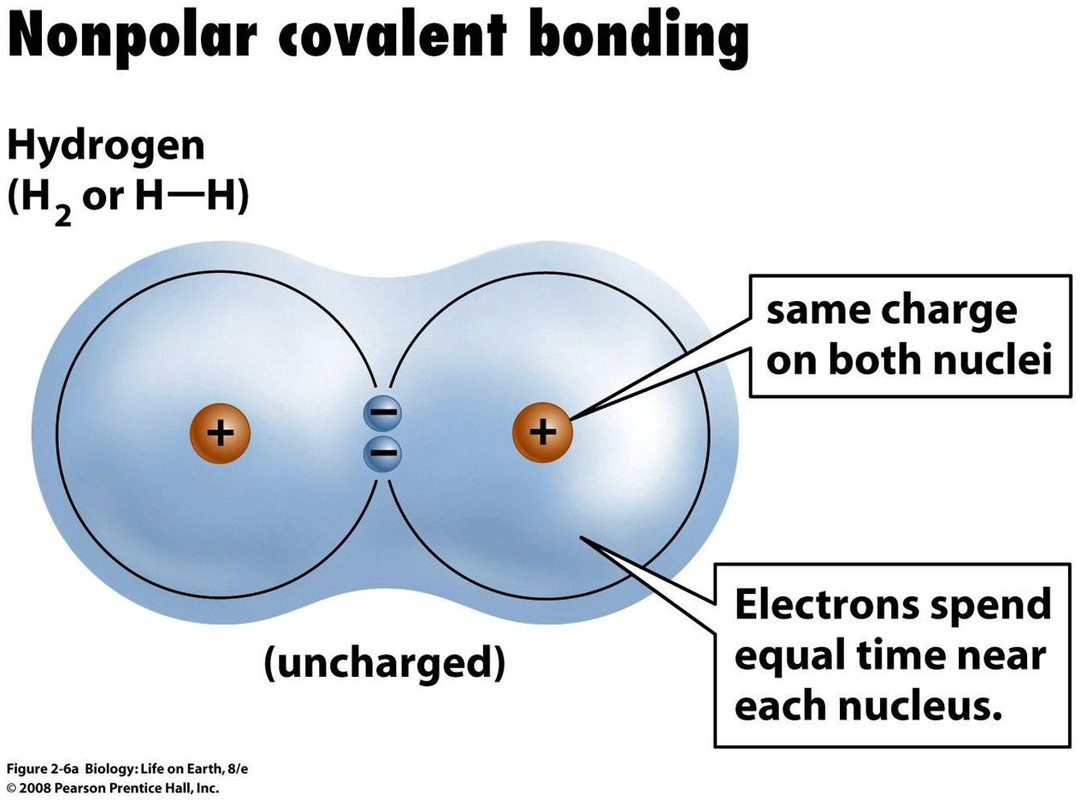
No. Some linear molecules that are elements (i.e. made up of the same type of atom) are non-polar (because there is no electronegativity difference between the two atoms). Example:- N2, H2, Cl2, O2, F2, Br2, I2. These are all linear molecules.
Does ozone have covalent bonds?
However, this does not mean that polar molecules must have polar covalent bonds. For example, ozone, O3, has non polar covalent bonds, but the O3 molecule itself is polar. This is due to its bent shape, which results in a net dipole moment.
What is polar covalent bond?
A polar covalent bond exists when atoms with different electronegativities share electrons in a covalent bond. Consider the hydrogen chloride (HCl) molecule. Each atom in HCl requires one more electron to form an inert gas electron configuration. Chlorine has a higher electronegativity than hydrogen, but the chlorine atom’s attraction ...
What is the polarity of a carbon bond?
Bonds between carbon and other elements such as oxygen and nitrogen are polar. The polarity of a bond depends on the electronegativities of the bonded atoms. Large differences between the electronegativities of the bonded atoms increase the polarity of bonds. The direction of the polarity of common bonds found in organic molecules is easily predicted. The common nonmetals are more electronegative than carbon. Therefore, when a carbon atom is bonded to common nonmetal atoms, it has a partial positive charge.
How many electrons are in a covalent bond?
In the simplest view of a covalent bond, a pair of electrons is shared by two atoms in the space between them. Each atom formally provides one electron to the bond and these negatively charged electrons are simultaneously attracted to the positive charges of both nuclei.
What is the effect of polarization on a polymer?
This acts to store energy and contributes to the capacitive nature of the material. The response times of the electronic and atomic shifts are extremely fast so that, at normal dielectric measurement frequencies, this effect is always present. These induced dipoles are responsible for nonpolar or symmetrically polar polymers having permittivities of 2 or greater. The permittivity due to these induced dipoles is known as the unrelaxed or infinite frequency permittivity (ϵu ). At the frequency range typically found in dielectric experiments (10 −3 to 10 8 Hz), induced dipoles react so quickly to an electric field that ϵu is frequency independent.
How many electrons does boron have?
In these molecules, the boron atom has only six electrons surrounding it so it interacts readily with species that can function as electron pair donors. For example, when F − reacts with BF 3 the product is BF 4− in which sp3 hybrids are formed so such species are tetrahedral ( Td symmetry). In most cases, molecules containing boron exhibit one of these types of bonding to boron. The boron hydrides represent a special situation that is described later.
Why do polar molecules have a negative end?
Polar molecules have a negative “end” and a positive “end.” They tend to associate because the positive end of one molecule attracts the negative end of another molecule. The physical properties of polar molecules reflect this association. An increased association between molecules decreases their vapor pressure, which in turn results in a higher boiling point, because more energy is required to vaporize the molecules. The molecular weights and molecular shapes of acetone and isobutane are similar ( Figure 2.1 ), but acetone boils at a higher temperature than isobutane. Acetone contains a polar carbonyl group, whereas isobutane is a nonpolar molecule. The higher boiling point of acetone results from strong the dipole-dipole interaction of the polar carbonyl group.
What is the magnitude of polarity?
The magnitude of the polarity of a bond is the dipole moment, (D). The dipole moments of several bond types are given in Table 1.2. The dipole moment of a specific bond is relatively constant from compound to compound. When carbon forms multiple bonds to other elements, these bonds are polar. Both the carbon-oxygen double bond in formaldehyde (methanal) and the carbon—nitrogen triple bond in acetonitrile (cyanomethane) are polar.
What type of bond is polar?
A polar bond is a type of covalent bond in which the electrons forming the bond are unequally distributed. In other words, the electrons spend more time on one side of the bond than the other.
What is polar bond?
A polar bond is a covalent bond between two atoms where the electrons forming the bond are unequally distributed. This causes the molecule to have a slight electrical dipole moment where one end is slightly positive and the other is slightly negative. The charge of the electric dipoles is less than a full unit charge, so they are considered partial charges and denoted by delta plus (δ+) and delta minus (δ-). Because positive and negative charges are separated in the bond, molecules with polar covalent bonds interact with dipoles in other molecules. This produces dipole-dipole intermolecular forces between the molecules.
What type of bond is formed between two nonmetal atoms?
Polar covalent bonds form between two nonmetal atoms that have sufficiently different electronegativities from each other. Because the electronegativity values are slightly different, the bonding electron pair isn't equally shared between the atoms. For example, polar covalent bonds typically form between hydrogen and any other nonmetal.
What is a nonpolar covalent bond?
Pure covalent bonds (nonpolar covalent bonds) share electron pairs equally between atoms. Technically, nonpolar bonding only occurs when the atoms are identical to each other (e.g., H 2 gas), but chemists consider any bond between atoms with a difference in electronegativity less than 0.4 to be a nonpolar covalent bond.
How do ionic bonds form?
Ionic bonds form between atoms when the electronegativity difference between them is greater than 1.7. Technically ionic bonds are completely polar bonds, so the terminology can be confusing.
Why do polar covalent bonds interact with dipoles?
Because positive and negative charges are separated in the bond, molecules with polar covalent bonds interact with dipoles in other molecules. This produces dipole-dipole intermolecular forces between the molecules. Polar bonds are the dividing line between pure covalent bonding and pure ionic bonding. Pure covalent bonds (nonpolar covalent bonds) ...
What are some examples of polar bonds?
Examples of molecules with polar bonds include water, hydrogen fluoride, sulfur dioxide, and ammonia.
What is the polarity of a covalent bond?
The dipole moment is defined as the product of charge and distance of separation of charge. The dipole moment is denoted by ‘μ’ and its unit are Debye (or) esu cm.
What is polar bond?
In general, a polar bond is a certain class of a covalent bond. We can also say that it is the dividing line between the formation of a pure covalent bond and an ionic bond. However, if we want to define it more accurately, a polar covalent bond is a bond that exists between two atoms consisting of electrons that are unevenly distributed. Due to this state, the molecules tend to have some electrical dipole moment wherein the two ends are either slightly positive or negative.
What type of bond is formed between two nonmetal atoms?
Polar covalent bonds are usually formed between two nonmetal atoms having different electronegativities. Let us consider A and B in which them is electronegativity difference is not equal to zero contains a covalent bond between them.
What is the bond length of HCl?
5. The bond length of HCl is 1.27A. Calculate its Dipole moment.
Why do compounds exist as solids?
Physical state: These compounds can exist as solids due to greater force of interactions. Melting and boiling points: These have greater melting and boiling point than non-polar compounds. Conductivity: They conduct electricity in the solution state due to the mobility of ions.
Is water soluble in polar solids?
Answer: Water has the capacity to break the detractions between the atoms in the molecule hence polar solids are soluble water.
Is polar covalent a tendency?
It has no units simple it is a tendency. The covalent bond formed between two atoms in molecules whose electronegative difference exists is known as a polar covalent bond.
Why is a molecule nonpolar?
So this means that both sides of the molecule are negatively charged. Meaning the molecule is non-polar because we're missing one side having a positive charge. If we look at just the bond between the carbon and the oxygen, then we see a polar bond.
Why are atoms nonpolar?
The overall atom is non-polar because there are two negatively charged sides instead of one positive side and one negative side. The bonds in the molecule are polar because electronegativity causes one side of the bond to be positive and the other side to be negative. Answer link.
Why is oxygen polar?
If we look at just the bond between the carbon and the oxygen, then we see a polar bond. This is because oxygen is slightly more electronegative than carbon.
What does it mean when a molecule is linear?
Lets say you have a linear shaped molecule. In this case, I'm using CO2. NOTE: Linear refers to the way that the atoms form a line with an angle of 180 degrees. Now, you can see that there are no electrons around the central atom. Instead, they are on the outside atoms. So this means that both sides of the molecule are negatively charged.
When do polar and nonpolar molecules occur?
Polar molecules occur when there is an electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms. Non polar molecules occur when electrons are shared equal between atoms of a diatomic molecule or when polar bonds in a larger molecule cancel each other out. Is HCL polar or nonpolar?
Why is a molecule nonpolar?
A molecule may be nonpolar either when there is an equal sharing of electrons between the two atoms of a diatomic molecule or because of the symmetrical arrangement of polar bonds in a more complex molecule . For example, boron trifluoride (BF3) has a trigonal planar arrangement of three polar bonds at 120°.
Do polar bonds cancel?
If the polar bonds are evenly (or symmetrically) distributed, the bond dipoles cancel and do not create a molecular dipole. Click to see full answer.
Is HCL polar or nonpolar?
HCL is a polar molecule as chlorine has a higher electronegativity than the hydrogen. Thus, it attracts electrons to spend more time at its end, giving it a negative charge and hydrogen a positive charge. How do you know if Br2 is polar or nonpolar?