What type of muscle is found in blood vessels?
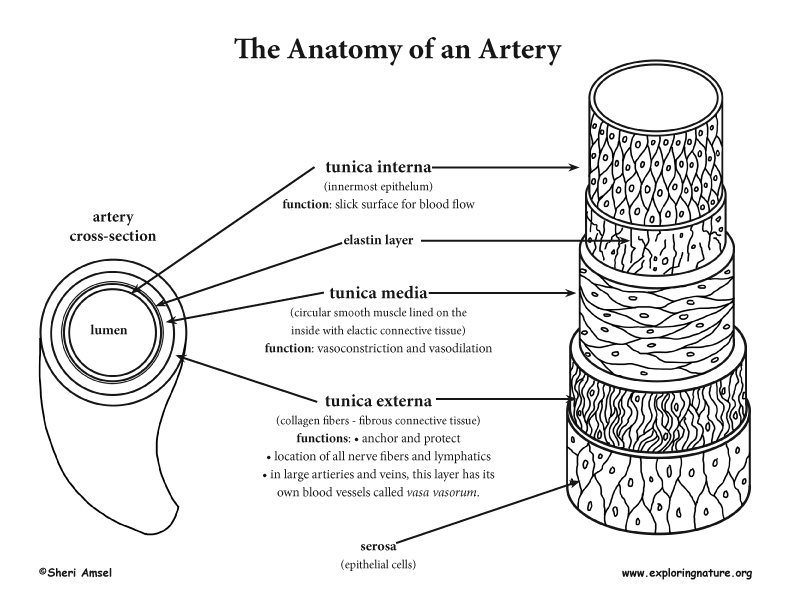
Muscles. Blood vessels contain only smooth muscle cells. These muscle cells reside within the tunica media along with elastic fibers and connective tissue. Although vessels only contain smooth muscles, the contraction of skeletal muscle plays an important role in the movement of blood from the periphery towards the heart in the venous system.
What is the difference between vascular and vascular smooth muscle?
Vascular smooth muscle refers to the particular type of smooth muscle found within, and composing the majority of the wall of blood vessels. Contents. Structure. Vascular smooth muscle refers to the particular type of smooth muscle found within, and composing the majority of the wall of blood vessels.
What is the main function of vascular smooth muscle tone?
Thus the main function of vascular smooth muscle tone is to regulate the caliber of the blood vessels in the body. Excessive vasoconstriction leads to high blood pressure, while excessive vasodilation as in shock leads to low blood pressure.
What is the function of smooth muscle in the heart?
Function. Vascular smooth muscle contracts or relaxes to change both the volume of blood vessels and the local blood pressure, a mechanism that is responsible for the redistribution of the blood within the body to areas where it is needed (i.e. areas with temporarily enhanced oxygen consumption).

Do blood vessels contain smooth muscle?
Blood vessels contain only smooth muscle cells. These muscle cells reside within the tunica media along with elastic fibers and connective tissue.
Are blood vessels smooth or cardiac muscle?
Smooth muscle, found in the walls of the hollow internal organs such as blood vessels, the gastrointestinal tract, bladder, and uterus, is under control of the autonomic nervous system.
Which blood vessel has no smooth muscle?
Smooth muscle cells are the most abundant cell type in blood vessel walls. They occur in all vessels except capillaries and pericytic venules.
What blood vessel has smooth muscle?
Arterioles provide blood to the organs and are chiefly composed of smooth muscle.
Where is smooth muscle found?
Smooth muscle fibers are located in walls of hollow visceral organs (such as the liver, pancreas, and intestines), except the heart, appear spindle-shaped, and are also under involuntary control. Skeletal muscle fibers occur in muscles which are attached to the skeleton.
Are capillaries made of smooth muscle?
The capillaries do not have this smooth muscle in their own wall, and so any change in their width is passive. Any signaling molecules they release (such as endothelin for constriction and nitric oxide for dilation) act on the smooth muscle cells in the walls of nearby, larger vessels, e.g. arterioles.
Why do blood vessels have smooth muscle?
Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) constitute the major cells in the media layer of arteries, and are critical to maintain the integrity of the arterial wall. They participate in arterial wall remodeling, and play important roles in atherosclerosis throughout all stages of the disease.
Is artery is a smooth muscle?
The prime function of the arterial smooth muscle cell (SMC) in adult individuals is to contract and relax, thereby regulating blood flow to target tissues. However, in several vascular diseases, arterial SMCs in the adult vessel undergo major changes in structure and function.
Why do veins have smooth muscle?
The smooth muscle layers are used to contract or dilate the veins, to accommodate changes in blood volume.
Do veins have more smooth muscle than arteries?
The walls of veins have the same three layers as the arteries. Although all the layers are present, there is less smooth muscle and connective tissue. This makes the walls of veins thinner than those of arteries, which is related to the fact that blood in the veins has less pressure than in the arteries.
Which blood vessels have smooth muscle and can be controlled by the nervous system?
Arteries have a great deal more smooth muscle within their walls than veins, thus their greater wall thickness. This is because they have to carry pumped blood away from the heart to all the organs and tissues that need the oxygenated blood.
Which best describe the blood vessels?
The vessels that carry blood away from the heart are called arteries, and their very small branches are arterioles. Very small branches that collect the blood from the various organs and parts are called venules, and they unite to form veins, which return the blood to the heart.
Do blood vessels contain cardiac muscle?
Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in your heart, where it performs coordinated contractions that allow your heart to pump blood through your circulatory system.
What is smooth muscle example?
Smooth muscle is a type of tissue found in the walls of hollow organs, such as the intestines, uterus and stomach. You can also find smooth muscle in the walls of passageways, including arteries and veins of de cardiovascular system.
What are characteristics of cardiac muscle?
Cardiac muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) are striated, branched, contain many mitochondria, and are under involuntary control. Each myocyte contains a single, centrally located nucleus and is surrounded by a cell membrane known as the sarcolemma.
What are examples of cardiac muscle?
The heart consists mostly of cardiac muscle cells (or myocardium). The outstanding characteristics of the action of the heart are its contractility, which is the basis for its pumping action, and the rhythmicity of the contraction.
What is Vascular Smooth Muscle?
Structure. Vascular smooth muscle refers to the particular type of smooth muscle found within, and composing the majority of the wall of blood vessels .
What are the pathological conditions that are associated with the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells?
Excessive proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells contributes to the progression of pathological conditions, such as vascular inflammation, plaque formation, atherosclerosis, restenosis, and pulmonary hypertension.
What receptors cause vasodilation?
beta-2 receptors. Agonism of beta-2 receptors causes vasodilation and low blood pressure (i.e. the effect is opposite of the one resulting from activation of alpha-1 and alpha-2 receptors in the vascular smooth muscle cells).
What is the function of smooth muscle tone?
Thus the main function of vascular smooth muscle tone is to regulate the caliber of the blood vessels in the body. Excessive vasoconstriction leads to high blood pressure, while excessive vasodilation as in shock leads to low blood pressure .
What muscle is responsible for redistribution of blood?
Vascular smooth muscle contracts or relaxes to change both the volume of blood vessels and the local blood pressure, a mechanism that is responsible for the redistribution of the blood within the body to areas where it is needed (i.e. areas with temporarily enhanced oxygen consumption).
Which receptors exert opposite physiologic effects in the vascular smooth muscle under activation?
The adrenergic receptors exert opposite physiologic effects in the vascular smooth muscle under activation:
Why do arteries have a greater wall thickness than veins?
This is because they have to carry pumped blood away from the heart to all the organs and tissues that need the oxygenated blood. The endothelial lining of each is similar.
How does smooth muscle contract?
Like all muscle tissue, the function of smooth muscle is to contract. The image above shows how the actin and myosin fibers shorten, effectively shrinking the cell. However, there are some important differences in how the smooth muscle contracts, compared to other types of muscle. In skeletal muscle, a signal from the somatic nervous system traverses to the muscle, where it stimulates organelles in the muscle cell to release calcium. The calcium causes a protein to detach from actin , and myosin quickly binds to the opening on actin. Since there was always available ATP, the myosin uses it to quickly contract the cell.
What is smooth muscle?
Smooth muscle is a type of muscle tissue which is used by various systems to apply pressure to vessels and organs. Smooth muscle is composed of sheets or strands of smooth muscle cells. These cells have fibers of actin and myosin which run through the cell and are supported by a framework of other proteins. Smooth muscle contracts under certain stimuli as ATP is freed for use by the myosin. The amount of ATP released depends on the intensity of the stimuli, allowing smooth muscle to have a graded contraction as opposed to the “on-or-off” contraction of skeletal muscle.
Why is smooth muscle adapted to many areas of the body?
This specialized function of contracting for long periods and hold that force is why smooth muscle has been adapted to many areas of the body. Smooth muscle lines many parts of the circulatory system, digestive system, and is even responsible for raising the hairs on your arm.
Why is smooth muscle important?
Smooth muscle, because of its ability to contract and hold , is used for many function in many places of the body. Besides those listed above, smooth muscle is also responsible for contracting the irises, raising the small hairs on your arm, contracting the many sphincters in your body, and even moving fluids through organs by applying pressure to them. While smooth muscle doesn’t contract or release as quickly as skeletal or cardiac muscle, it is much more useful for providing consistent, elastic tension.
Why do both tissues contract in a solution of calcium ions?
Both tissues would contract in a solution of calcium ions, because calcium induces both systems. 2. Smooth muscle cells are connected to each other through regions called adherens junctions. These regions contain many fibrous proteins for strength when the cells pull against each other.
Which muscle has access to ATP?
A is correct. By putting the tissues in a solution of free ATP, we can distinguish between the smooth and skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscle already has access to ATP, and would not contract when put in this solution. Smooth muscle uses a series of proteins to inhibit free ATP and prevent myosin from working.
Which muscle lines the digestive system?
Smooth muscle also lines the majority of the digestive system, for similar reasons. However, the cells in the digestive system have different stimuli than those in the circulatory system. For instance, sheets of smooth muscle tissue in the gut react to you swallowing.
