
Both prokaryotic
Prokaryote
A prokaryote is a unicellular organism that lacks a membrane-bound nucleus, mitochondria, or any other membrane-bound organelle. The word prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό "before" and κάρυον "nut or kernel". Prokaryotes are divided into two domains, Archaea and Bacteria. Species wit…
Ribosome
The ribosome is a complex molecular machine found within all living cells, that serves as the site of biological protein synthesis (translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules.
What are the similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
- Animal cells are eukaryotic.
- Two locations of prokaryotic cells in the human body are in the intestine (where gut bacteria help you digest food) and on your skin (where bacteria thrive).
- Mitochondria are not found in prokaryotic cells; they are only in eukaryotic cells.
Why do prokaryotic cells have no nucleus?
They have no nucleus; instead their genetic material is free-floating within the cell. They also lack the many membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells. Thus, prokaryotes have no mitochondria. How do prokaryotic cells survive in the absence of important organelles like mitochondria and nucleus?
Which description distinguishes eukaryotes from prokaryotes?
Eukaryotes: What Are the Differences?
- Understanding Cells and Cell Membranes. The cell is a fundamental component of our modern definition of life and living things. ...
- Prokaryotes. Prokaryotes are organisms made up of cells that lack a cell nucleus or any membrane-encased organelles.
- Eukaryotes. ...
Is DNA replication prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
The DNA replicates before the cell division occurs. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA replicate in a semi-conservative manner. However, there are a few differences between the prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA replication based on their size and complexity in genetic material.
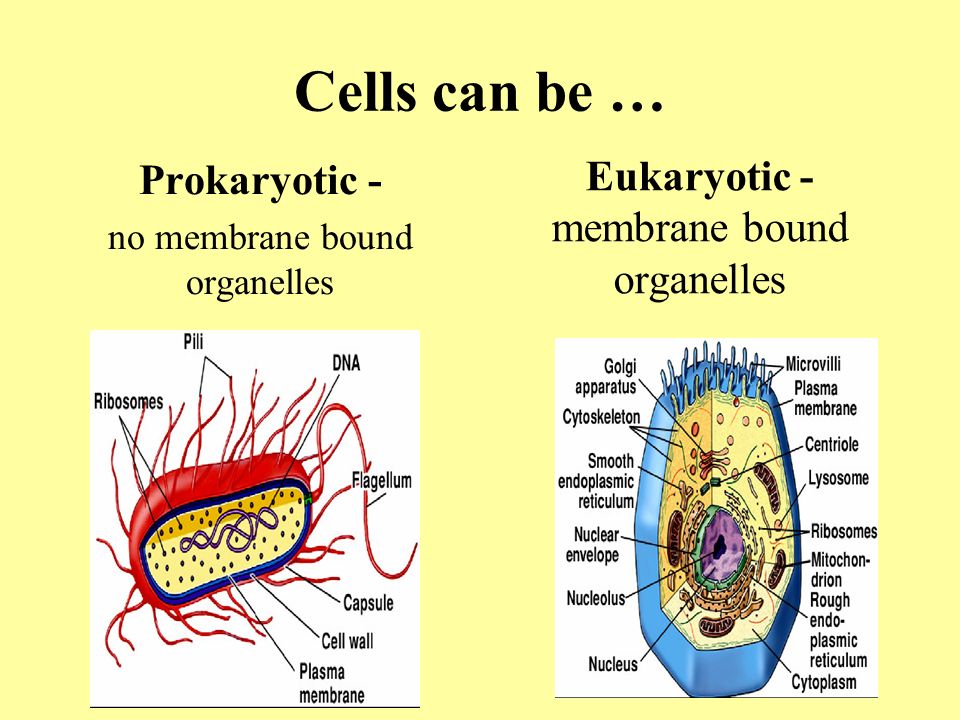
Do prokaryotes have a cell membrane?
Prokaryotic cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane, but they have no internal membrane-bound organelles within their cytoplasm. The absence of a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles differentiates prokaryotes from another class of organisms called eukaryotes.
Do eukaryotic cells have a cell membrane?
In eukaryotic cells, the membrane that surrounds the nucleus — commonly called the nuclear envelope — partitions this DNA from the cell's protein synthesis machinery, which is located in the cytoplasm.
What part of the cell is responsible for making proteins?
ribosomesThe endoplasmic reticulum can either be smooth or rough, and in general its function is to produce proteins for the rest of the cell to function. The rough endoplasmic reticulum has on it ribosomes, which are small, round organelles whose function it is to make those proteins.
What organelle allows materials in and out of the cell?
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
Which cells have a cell membrane?
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, a double layer of lipids that separates the cell interior from the outside environment. This double layer consists largely of specialized lipids called phospholipids.
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell membrane?
The primary distinction between these two types of organisms is that eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and prokaryotic cells do not.
What is not found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Explanation: Unlike eukaryotes, prokaryotes have no membrane-bound organelles. This means that they lack a nucleus, mitochondria, and other advanced cell structures.
What are 5 differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotes don't have membrane-bound organelles whereas eukaryotes have....What is the difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells?Prokaryotic CellEukaryotic cellEndoplasmic reticulum absentEndoplasmic reticulum presentMitochondria absentMitochondria presentCytoskeleton absentCytoskeleton presentRibosomes smallerRibosomes larger19 more rows•May 20, 2022
What is the cell membrane of a prokaryotic cell?
A prokaryotic cell membrane is actually a fluid phospholipid bi-layer submerged with proteins. The cell membranes of prokaryotic cells have two phospholipid layers. A prokaryotic cell membrane is a thin lipid bilayer. The thickness of the prokaryotic cell membrane is about 7 nm.
How small is a prokaryotic cell?
4. The size of the prokaryotic cell is very small (0.05 to 10µm).
What are the cells of an organism?
There are many species of organisms on earth. The body of all these organisms is made up of tiny billions of cells that cannot be seen with the naked eye. In 1665 scientist Robert Hooke first discovered the cell. The cells are arranged one on top of the other to form organisms. The size of a cell is about 0.1 micrometer to 100 micrometers. The unicellular smallest cell is mycoplasma galliseticum. The diameter of the smallest cell is about 10 micrometers. Cells are the building blocks of an organism’s body. On the basis of the nucleus, the cells are classified into two types eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. The structure of all cells is different. As an example, eukaryotic cells are composed of cell walls, cell membranes, nucleus, cytoplasm, and some cell organelles located in the cytoplasm. On the other hand, prokaryotic cells are composed of capsules, cell walls, cell membranes, cytoplasm, genetic material, pili, and flagella. Each cell has a specific cell membrane. The cell membrane of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is the topic of the discussion below (3).
What is the plasma membrane?
The plasma or cell membrane is semipermeable, quasi-fluid, and dynamic. This plasma membrane separates the prokaryotic cell from the surrounding environment. The prokaryotic cell membrane is made of 40% lipids and 60% proteins and no cholesterol. The prokaryotic cell membrane consists of monounsaturated fatty acids. The phospholipid layer has two ends, the head part is of glycerol and the tail part consists of two molecule fatty acids. The head is called polar hydrophilic ends and the tail is called non-polar hydrophobic ends. The cell membrane of prokaryotic cells folds inwards to form mesosomes (4) & (3).
What is the meaning of the word "eukaryotic"?
The eukaryotic word comes from two Greek words Eu and karyon. The word Eu means, “well” or “good” and the karyon means, “nut” or “kernel”.
Which type of cell has ribosomes?
5. The ribosomes of eukaryotic cells are large in size. And ribosomes of both 70s and 80s types are present in eukaryotic cells.
Which cell membrane controls diffusion and osmosis?
2. The process of diffusion and osmosis of cells is controlled by the prokaryotic cell membrane.
What is the outer membrane of a prokaryotic cell called?
These cell membranes are called the inner and outer membrane based on their location in relation to the cell. Prokaryotes contain another protective layer called the cell wall or cellular envelope, which isn't to be confused with the cell membrane.
Where is the cell wall in prokaryotes?
The cell wall sits right outside the cell membrane in prokaryotes. Alright, let's take a moment to review what we've learned. As we learned prokaryotes and eukaryotes are the two main types of cells that exist.
Why is the cell membrane called the phospholipid bilayer?
The cell membrane is also called the phospholipid bilayer. This is because it is composed of two phospholipid molecules that are oriented towards each other.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Not only does the cell membrane hold the contents of the cell together , it also protects the cell like a bouncer at a club. The cell membrane decides what materials can enter the cell just as a bouncer decides what people can enter the club.
Why are phospholipid tails oriented toward each other?
This is why tails are oriented toward each other so they are away from the water inside and outside of the cell. While most prokaryotes only have one cell membrane, gram negative bacteria have two cell membranes.
How many cell membranes does a Gram negative bacteria have?
While most prokaryotes only have one cell membrane, gram negative bacteria have two cell membranes. Gram negative bacteria, such as Salmonella and E. Coli, have two cellular membranes with a gap in between called the periplasmic space. These cell membranes are called the inner and outer membrane based on their location in relation to the cell.
What is the membrane of a cell?
Think of the cell membrane as a water balloon that holds the water inside the balloon. The cell membrane holds everything inside the cell, including the cytoplasm, a gooey material the fills up the inside of the cell just as the water fills the inside of the balloon. All the organelles of a cell are suspended in the cytoplasm and surrounded by the cell membrane.
Why are prokaryotic cells different from eukaryotic cells?
The reason for the difference in cell sizes between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells belongs to the different structure and organization between the two types of cells. The lack of membrane-bound organelles in prokaryotes might be the most noticeable difference. While eukaryotic cells contain organelles enclosed in membranes – two examples ...
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Differences in Organization. Prokaryotic cells engage in reproduction through a process of cell division called binary fission. Eukaryotic cells use a different process of cell division called mitosis, which involves a constant cycle of cell growth and development.
What are the two main categories of cells?
All of these cells, whether they operate as a solitary bacterial cell or as part of a complex system such as the human body, can be sorted into two main categories: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells .
How do eukaryotes reproduce?
Eukaryotes reproduce sexually through meiosis, which allows for genetic variance. Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually, copying themselves. Despite this, gene transfer processes still allow for genetic variance. One of these is transduction in which viruses move DNA from one bacterium to another.
Which is larger, prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
Most prokaryotes are unicellular and are either archaea or bacteria. Their cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes include larger, more complex organisms such as plants and animals. Only eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus. Prokaryotes divide via using binary fission, while eukaryotic cells divide via mitosis.
Which domain has eukaryotic cells?
Eukarya. The organisms in Archaea and Bacteria are prokaryotes, while the organisms in Eukarya have eukaryotic cells. The Archaea domain has subcategories, but scientific sources differ on whether these categories are phyla or kingdoms. They are:
Where does DNA store in a prokaryote?
Instead, most of their DNA is in one chromosome-like structure that sits in an area of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid. This nucleoid does not have a membrane of its own.
What Are Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are both types of cells; in fact, they’re the only two cell types on Earth. Prokaryotic organisms are always unicellular and may be bacteria or archaea. Eukaryotic organisms, however, may be unicellular or multicellular and include plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
What is the difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
The main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is that eukaryotes contain membrane-bound organelles, and prokaryotes do not. This means that prokaryotes do not have a nucleus; instead, they keep their DNA in a cell region called the nucleoid. Unlike the eukaryotic nucleus (which is surrounded by a nuclear envelope) the nucleoid is membrane-less, so the DNA is free-floating in the cytoplasm.
How did eukaryotes evolve?
It’s difficult to know exactly where eukaryotes came from, but the leading hypothesis is that they evolved as a result of endosymbiosis. The endosymbiotic theory suggests that cell organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts were once independent organisms that formed symbiotic relationships with other prokaryotes. At some point, they were engulfed by larger prokaryotes and lived inside them. Over many years of evolution, the two became so dependent on one another that they could no longer live alone, and complex eukaryotic cells were formed as a result.
How big are prokaryotic cells compared to eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotes typically measure 0.2 – 2.0µm in diameter, whereas eukaryotic cells are 1 – 100 µm in diameter.
What are the two types of cells?
All cells on Earth can be divided into two types: prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes are always unicellular organisms and may be bacteria or archaea. Eukaryotes may be unicellular or multicellular and include plants, animals, fungi, and protists are all made up of eukaryotic cells.
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
Prokaryotes reproduce asexually and usually divide by binary fission. During this process the cell splits in two, producing two genetically-identical daughter cells. Single eukaryotic cells reproduce via mitosis or meiosis, while multicellular eukaryotic organisms typically reproduce sexually.
What are the organelles of eukaryotic cells?
These include: Mitochondria. Golgi apparatus. Nuclei. Lysosomes. Chloroplasts.
