Do cancer cells have unique antigens?
Tumor-specific antigens (TSAs) are unique to tumor cells. Some evidence links the immune response in cancer patients to mutations in tumor cells (1–4. Any molecule capable of being recognized by the immune system is considered an antigen... read more ).
What antigens are tumors?
There are two major classes of tumor antigen which are targeted by T cell immunotherapies – private antigens and public shared antigens. Public shared antigens are common to multiple patients and are split into two categories: Tumor-specific antigens (TSA), found on cancer cells only, not on healthy cells.
Where do tumor antigens come from?
Tumor-associated antigens (TAA) can derive from any protein or glycoprotein synthesized by the tumor cell. TAA proteins can reside in any subcellular compartment of the tumor cell; ie, they may be membrane-bound, (more...)
Are antigens on normal cells?
An antigen is a marker that tells your immune system whether something in your body is harmful or not. Antigens are found on viruses, bacteria, tumors and normal cells of your body.
What are three likely sources of tumor antigen?
Antigens of three classes can induce tumor-specific T cell responses because they display a tumor-specific pattern of expression [30]: antigens derived from viral proteins, antigens derived from point mutations, and antigens encoded by cancer-germline genes (Figure 1).
Is a tumor antigen A protein?
A protein or other molecule that is found only on cancer cells and not on normal cells. Tumor-specific antigens can help the body make an immune response against cancer cells.
What are the important antigens to produce tumor immunity?
The two most thoroughly characterized oncofetal antigens are carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and α-fetoprotein (AFP). Most human and experimental tumors express higher than normal levels or abnormal forms of surface glycoproteins and glycolipids, which may be diagnostic markers and targets for therapy.
What is a tumor rejection antigen?
Tumor rejection antigens are peptides of tumor-cell proteins that are presented to T cells by MHC molecules. These peptides can become the targets of a tumor-specific T-cell response because they are not displayed on the surface of normal cells, at least not at levels sufficient to be recognized by T cells.
What are antigens in cancer?
Antigens have been identified in most of the human cancers, including Burkitt lymphoma, neuroblastoma, melanoma, osteosarcoma, renal cell carcinoma, ...
What are tumor antigens?
Tumor Antigens. Many tumor cells produce antigens, which may be released in the bloodstream or remain on the cell surface. Any molecule capable of being recognized by the immune system is considered an antigen. Antigens have been identified in most of the human cancers, including Burkitt lymphoma, neuroblastoma, melanoma, osteosarcoma, ...
What is a tumor specific antigen?
Tumor-specific antigens (TSAs) are unique to tumor cells. TSAs and TAAs typically are portions of intracellular molecules expressed on the cell surface as part of the major histocompatibility complex. Introduction of new genetic information from a virus (eg, human papillomavirus E6 and E7 proteins in cervical cancer)
Why are antigens buried in the cell membrane?
Uncovering of antigens normally buried in the cell membrane because of defective membrane homeostasis in tumor cells. Release of antigens normally sequestered within the cell or its organelles when tumor cells die. Some recent evidence links immune response in cancer patients to mutations in tumor cells ( 1–4 ).
What is the role of the immune system in tumors?
A key role of the immune system is detection of these antigens to permit subsequent targeting for eradication. However, despite their foreign structure, the immune response to tumor antigens varies and is often insufficient to prevent tumor growth (see also Host Response to Tumors ). Tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) are relatively restricted ...
What is the term for the accumulation of proteins that are normally not expressed or are expressed at very low levels?
Alteration of oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes by carcinogens, which result in formation of neoantigens (novel protein sequences or accumulation of proteins that are normally not expressed or are expressed at very low levels, such as ras or p53), either by generating the novel protein sequence directly or by inducing accumulation of these proteins
What are tumor markers?
Tumor markers are substances made either by the body in response to cancer or by the cancer itself. Found in blood, urine, and tissue samples, these markers are indicative of a specific disease process and can help doctors distinguish between the types and/or stages of cancer.
How many CA 27.29 tests are able to correctly identify breast cancer?
In fact, a 2007 Journal of Clinical Oncology study reported that less than 60% of CA 27.29 tests were able to correctly identify breast cancer even when the malignancy was positively detected on a PET/CT scan. 5
Is mammography the best screening for breast cancer?
Instead, routine mammography remains the preferred method of breast cancer screening, whether for new or recurring disease. 6
Can a CA 27.29 be used as a biopsy?
Although tumor marker tests like the CA 27.29 can aid in the management of breast cancer, neither they or any other blood or imaging test can definitively diagnose the disease. Only a breast biopsy can.
Is the breast cancer test less sensitive?
Since that time, numerous studies have shown that the test is far less sensitive than previously thought and that it lacked the specificity to differentiate breast cancer from other benign or malignant causes. 4
Is it safe to use a tumor marker test for breast cancer?
As of November 2007, the American Society of Clinical Oncologists (ASCO) has advised against the use of the tumor marker tests to monitor for recurrence in people with no signs or symptoms of breast cancer.
Why are tumor antigens useful?
Tumor antigens, because of their relative abundance in tumor cells are useful in identifying specific tumor cells. Certain tumors have certain tumor antigens in abundance. Certain tumor antigens are thus used as tumor markers. More importantly, tumor antigens can be used in cancer therapy as tumor antigen vaccines.
What are tumor specific antigens?
Mutation of protooncogenes and tumor suppressors which lead to abnormal protein production are the cause of the tumor and thus such abnormal proteins are called tumor-specific antigens. Examples of tumor-specific antigens include the abnormal products of ras and p53 genes.
What is the spectrum of target antigens associated with tumor immunity and allo-immunity after allogen?
The spectrum of target antigens associated with tumor immunity and allo-immunity after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Host-derived T and B cells can be induced to recognize tumor-associated antigens, whereas donor-derived B and T cells can recognize both tumor-associated antigens and alloantigens.
Why is the classification of tumor antigens imperfect?
This classification, however, is imperfect because many antigens thought to be tumor-specific turned out to be expressed on some normal cells as well. The modern classification of tumor antigens is based on their molecular structure and source. Accordingly, they can be classified as;
What is the mechanism of tumor antigenesis?
Mechanism of tumor antigenesis. Processing of tumor antigens recognized by CD8+ T cells. Normal proteins in the body are not antigenic because of self-tolerance, a process in which self-reacting cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and autoantibody -producing B lymphocytes are culled "centrally" in primary lymphatic tissue ...
What is tumor antigen?
Tumor antigen is an antigenic substance produced in tumor cells, i .e., it triggers an immune response in the host. Tumor antigens are useful tumor markers in identifying tumor cells with diagnostic tests and are potential candidates for use in cancer therapy. The field of cancer immunology studies such topics.
What are the two categories of human tumor antigens?
Initially tumor antigens were broadly classified into two categories based on their pattern of expression: Tumor-Specific Antigens (TSA), which are present only on tumor cells and not on any other cell and Tumor-Associated Antigens (TAA), ...
What tests are needed to diagnose cancer?
Though blood and urine tests can help give your doctor clues, other tests are usually necessary to make the diagnosis. For most forms of cancer, a biopsy — a procedure to obtain a sample of suspicious cells for testing — is usually necessary to make a definitive diagnosis.
What is a cancer blood test?
Cancer blood tests: Lab tests used in cancer diagnosis. Cancer blood tests and other laboratory tests may help your doctor make a cancer diagnosis. Reduce your anxiety by learning about cancer blood tests and how they're used. By Mayo Clinic Staff. If it's suspected that you have cancer, your doctor may order certain cancer blood tests ...
What are some examples of tumor markers?
Examples of tumor markers include prostate-specific antigen (PSA) for prostate cancer, cancer antigen 125 (CA 125) for ovarian cancer, calcitonin for medullary thyroid cancer, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) ...
What is circulating tumor cell test?
One circulating tumor cell test has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration to monitor people with breast, colorectal or prostate cancer.
Why do you need a tumor marker?
Your doctor may use these tests to determine whether your cancer is responding to treatment or whether your cancer is growing. In most cases, after you complete your cancer treatment, using cancer blood tests isn't helpful for watching for a return of the cancer.
What are some examples of blood tests used to diagnose cancer?
Examples of blood tests used to diagnose cancer include: Complete blood count (CBC).
Does blood work for cancer mean you have cancer?
Because your doctor has ordered cancer blood tests to look for signs of cancer, it doesn't mean that a cancer diagnosis has been made and you have cancer. Find out what your doctor might be looking for when cancer blood tests are done.
Why do cancer cells evade the immune system?
Cancer cells can often evade the immune system by inhibiting immune cells from differentiating them from other cells.
How do cancer cells affect the body?
Cancer cells pile up to form tumors and spread into surrounding tissue. These cells can also break away and travel to other parts of the body. To complicate matters, cancer cells can affect the behavior of normal cells.
What is the difference between benign and malignant cells?
There’s a big difference between benign and malignant cells. Benign cells are noncancerous. They sometimes overproduce and form tumors, but they don’t have the ability to invade other tissue. They’re not usually life threatening, but they can be if they grow too large or push into an organ.
What is malignant cancer?
Malignant cells are cancerous and potentially life threatening. They have the ability to invade nearby tissues and spread throughout the body. When a malignant tumor is removed, any cells left behind can result in new growth. That’s why cancer often requires additional treatment, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or radiation, ...
How does cancer come from?
Cancer typically derives from damage to DNA through inherited genetic mutations or something you’re exposed to in your daily life. You can’t control genetic mutations, but some lifestyle changes can help lower your risk of developing cancer, including getting certain cancer screenings to stop cancer before it starts.
How to reduce the risk of cancer?
What can you do to lower your risk of cancer? 1 Avoid tobacco. This includes cigars, cigarettes, pipes, and smokeless tobacco products. In the United States, 1 out of every 3 cancer deaths can be attributed to smoking. 2 Get regular cancer screenings. Some screenings, like Pap smears and colonoscopies, can detect abnormal cells before they have the chance to turn cancerous. Other screenings, like a mammogram, can detect localized cancer cells before they start to spread. 3 Drink alcohol in moderation. Alcoholic drinks contain ethanol, which increases the risk of cancer over time. Alcohol should be limited to one drink per day for women and two for men. 4 Protect your skin from sun. Avoid UV rays by covering your skin and using broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. Try to avoid spending time in the midday sun and don’t use tanning beds or sun lamps. 5 Stick to a healthy, balanced diet. Try to include plenty of vegetables, fruit, and whole grains in your diet. Limit processed foods, sugars, red meats, and processed meats. 6 Exercise. Physical inactivity can raise the risk of cancer. Try to do at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise per week.
How many cancer deaths are caused by smoking?
In the United States, 1 out of every 3 cancer deaths can be attributed to smoking. Get regular cancer screenings. Some screenings, like Pap smears and colonoscopies, can detect abnormal cells before they have the chance to turn cancerous.
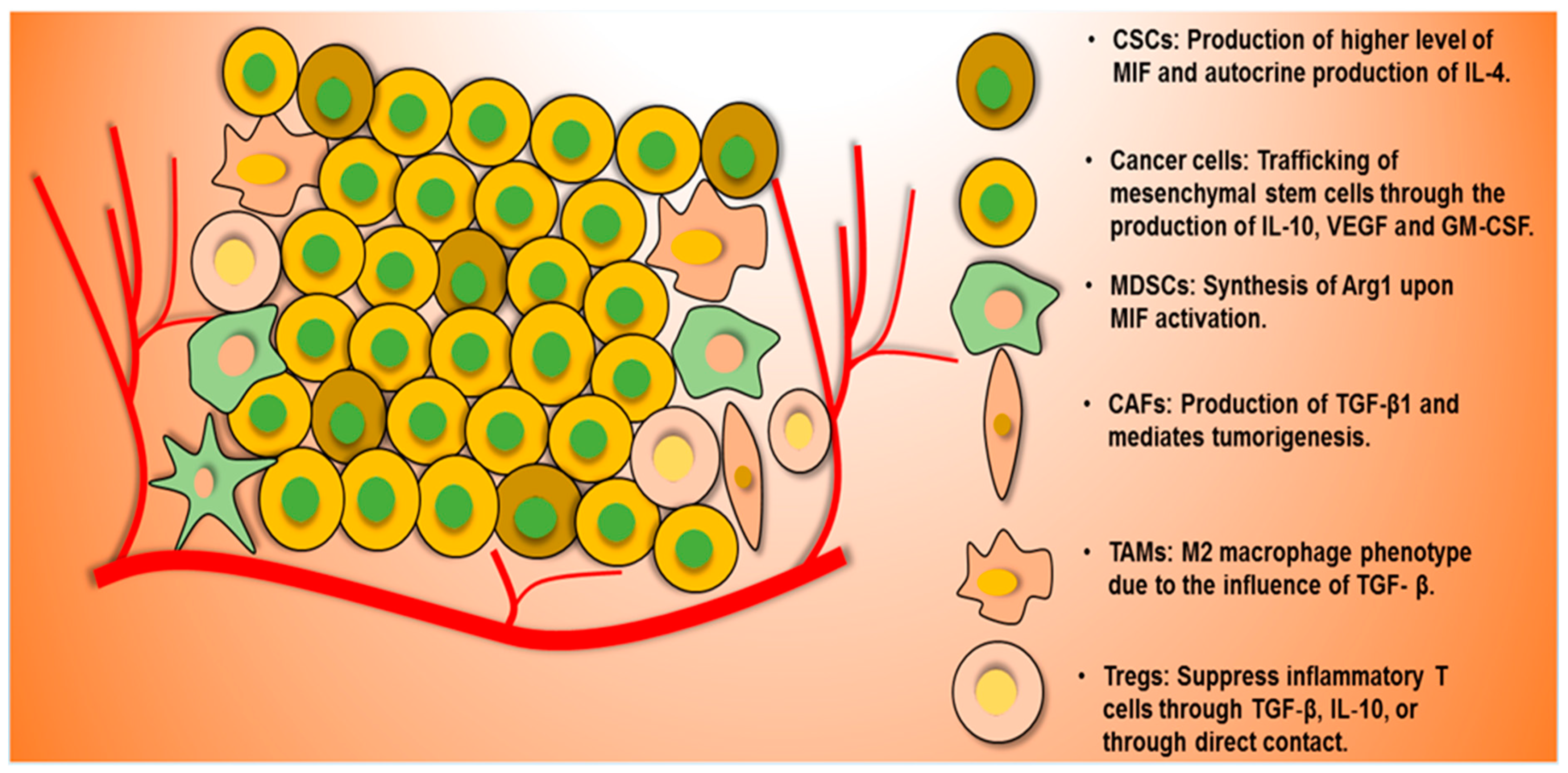
Overview
Cancer/testis (CT) antigens are a group of proteins united by their importance in development and in cancer immunotherapy. In general, expression of these proteins is restricted to male germ cells in the adult animal. However, in cancer these developmental antigens are often re-expressed and can serve as a locus of immune activation. Thus, they are often classified as tumor antigens. The expression of CT antigens in various malignancies is heterogeneous and often correlates with tu…
History
With the development of tumor-associated antigens (TAA), the first clone of a human tumor antigen, melanoma antigen-1 (MAGE-1) was reported in 1990s, which elicited an autologous cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) response in a melanoma patient. Further studies found that MAGE-1 (renamed MAGE-A1 later) was expressed in various cancers of different histological origin but not in normal tissues excluding testis and placenta. Later on, using T-cell epitope cloning technology, …
Category
CT antigens can be divided by whether they are encoded on the X chromosome (X-CT antigens genes) or not (non-X-CT antigens genes). It has been estimated that 10% of genes on the X chromosome belong to X-CT antigens families. The X-CT antigens genes represent more than half of all CT antigens and often constitute multigene families organized in well-defined clusters long the X chromosome, while the genes of non-X-CT antigens are distributed throughout the genom…
Mechanism
The expression of CT antigens genes are exclusively regulated by epigenetic events both in normal and cancer tissues, while DNA methylation and histone post-translational modification remain the most widely characterized epigenetic factors here.
DNA methylation is commonly found to lead to silencing of gene expression with the covalent addition of a methyl group catalyzed by DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs). It is found so far that …
Function
Germ cells share some features with cancers. The motile and penetrating features and colonization of primitive germ cells resemble the migration of cancer cells from primary tumor to metastasis. Also, during spermatogenesis, germ cells exhibit characteristics similar to cancer cells. These phenomena led to the hypothesis that the activation of CT antigens in normal stomatic tissues related to tumorigenesis. Although the function of CT antigens is far from unde…
Therapeutic potential
In normal tissues, CT antigens are exclusively expressed in testis, making it no access to the immune system. Besides, the existence of blood-testis barrier and the lack of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I expression on the surface of germ cells prevent the immune system interacting with CT antigens proteins and recognizing it as invading structures. Thus, CT antigens can be regarded as essentially tumor-specific targets when they are expressed in cancers.
Purpose of Test
Risks
- The CA 27.29 is a blood-based test requiring one full test tube of blood, which is collected with a blood draw. As such, the risks of the test are relatively small. Injection site pain, bruising, or bleeding are possible, as is light-headedness or fainting. Infection is rare, but can occur.
Before The Test
- It is rare that the CA 27.29 is ordered on its own. Your oncologist will more than likely order a battery of tests to monitor your cancer or its response to therapy. This may include a complete blood count (CBC), liver functions tests, and kidney function tests. No preparation is needed for any of these tests.
During The Test
- When you arrive for the test, you will need to check in, complete a registration form, and make payment for any out-of-pocket costs. A consent form may be provided. A phlebotomist will perform the blood draw.
After The Test
- After the test, it is not uncommon to feel mild soreness at the puncture site for the first couple of hours. Redness or bruising may also occur. Once the bleeding is fully stopped, you can remove the adhesive bandage. However, if the puncture wound is visible, you need to keep it covered to prevent infection. Although infection is rare, it can sometimes occur. Call your healthcare provid…
Interpreting Results
- The results of your blood test should be available within three to five working days. The report will include a reference range, outlining levels of the CA 27.29 antigen that are considered normal or abnormal. The reference range is based on the expected values in a population of people. While the CA 27.29 reference range can vary slightly from one lab to the next, it is generally accepted t…
Summary
- The CA 27.29 blood test can help your doctor monitor your cancer and its response to treatment. Taken together with other tools and clinical monitoring, this is a helpful test to have. It is mostly noninvasive with minimal pain and adds to the larger clinical picture. While it is not helpful for diagnosis or staging, it can be used in other ways.
A Word from Verywell
- The CA 27.29 test is an important tool for monitoring the treatment and care of metastatic breast cancer. The test can be used to monitor your response to treatment and/or assess whether cancer is active or spreading, but it has its limitations. Even if a value is high, you should not assume that cancer is the cause. The CA 27.29 is only useful when used in combination with oth…