What are diseases caused by chloroplast?
Supplemental Data
- Supplemental Figure S1. PSII fluorescence is reduced in the crl mutant.
- Supplemental Figure S2. ...
- Supplemental Figure S3. ...
- Supplemental Figure S4. ...
- Supplemental Figure S5. ...
- Supplemental Figure S6. ...
- Supplemental Figure S7. ...
- Supplemental Table S1. ...
- Supplemental Table S2. ...
- Supplemental Table S3. ...
What are facts about chloroplasts?
Interesting Facts about Chloroplasts
- Simple cells, like those found in algae, may only have one or two chloroplasts. ...
- Chloroplasts will sometimes move around within the cell in order to position themselves to where they can best absorb sunlight.
- The "chloro" in chloroplast comes from the Greek word chloros (meaning green).
- The most abundant protein in chloroplasts is the protein Rubisco. ...
What are the reactants in chloroplasts?
What are the 3 reactants you need for photosynthesis?
- Photosynthesis is the process plants use to make their own food.
- The reactants of photosynthesis are carbon dioxide and water.
- Light energy from the sun initiates photosynthesis in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
- The products of photosynthesis are glucose and oxygen.
Where in the chloroplast is ATP produced?
~ATP made during photosynthesis is produced in the stroma of the chloroplast. The energy released from electrons excited by light is used to pump protons into the lumen of the thylakoid. How is ATP produced in the light-dependent reaction?

Is ATP synthase in chloroplasts?
The chloroplast adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase is located in the thylakoid membrane and synthesizes ATP from adenosine diphosphate and inorganic phosphate at the expense of the electrochemical proton gradient formed by light-dependent electron flow.
Do mitochondria and chloroplasts have ATP synthase?
The bulk of ATP synthesis in plants is performed by ATP synthase, the main bioenergetics engine of cells, operating both in mitochondria and in chloroplasts.
Where is ATP synthase found in plants?
chloroplastsIn eukaryotes, the ATP synthase complex is located in the inner membrane of mitochondria, with ATP synthesis reaction occurring on the membrane side toward matrix compartment. In plants, the enzyme is in addition localized in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts, with the ATP-forming-moiety facing the stroma.
Do mitochondria have ATP synthase?
The mitochondrial ATP synthase is a membrane protein complex that generates most of the ATP in eukaryotic cells. The synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate proceeds via rotary catalysis, which uses the energy of the electrochemical gradient across the mitochondrial inner membrane.
What do chloroplast and mitochondria have in common?
Chloroplasts (members of the plastid family) and mitochondria are central to the energy cycles of ecosystems and the biosphere. They both contain DNA, organized into nucleoids, coding for critical genes for photosynthetic and respiratory energy production.
How is ATP synthesized in the chloroplasts?
In chloroplasts, photosynthetic electron transport generates a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane which then drives ATP synthesis via ATP synthase.
How does chloroplast affect ATP synthase?
The chloroplast ATP synthase catalyzes the light-driven synthesis of ATP and is activated in the light and inactivated in the dark by redox-modulation through the thioredoxin system. It has been proposed that this down-regulation is important for preventing wasteful hydrolysis of ATP in the dark.
What is ATP synthase in photosynthesis?
ATP synthase is a protein that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). It is classified under ligases as it changes ADP by the formation of P-O bond (phosphodiester bond). ATP synthase is a molecular machine.
Does all life have ATP synthase?
ATP Synthase Definition ATP synthase forms ATP from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and an inorganic phosphate (Pi) through oxidative phosphorylation, which is a process in which enzymes oxidize nutrients to form ATP. ATP synthase is found in all lifeforms and powers all cellular activities.
What does the chloroplast do?
Chloroplasts are plant cell organelles that convert light energy into relatively stable chemical energy via the photosynthetic process. By doing so, they sustain life on Earth.
Where is ATP synthesized in cell?
the mitochondrial matrixIt occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. In the TCA cycle, only one molecule of ATP (GTP) is produced but three molecules of NADH and one molecule of FADH2 (per cycle) are produced, which provide electrons for the electron transport chain and facilitate a large amount of ATP synthesis.
In which part of mitochondria does ATP synthesis occur?
inner membraneHint: The ATP synthesis occurs within the fold in the inner membrane of a mitochondrion. The passage of energy-rich electrons among cytochromes and coenzymes drains the energy from the electrons to make ATP from ADP and phosphate ions.
ATP Synthesis in Chloroplast Definition
Adenosine 5’ triphosphate (ATP) is an energy-rich molecule and is spent and generated by living cells by several cellular processes. It can be generated not only by metabolizing the organic and inorganic compounds but can also be generated by absorbing the sunlight and transforming it into a form of chemical energy.
Overview of ATP Synthesis In Chloroplast
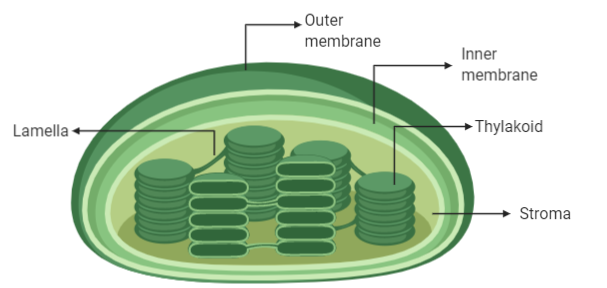
The chloroplast is a unique cell structure found in the cells of most autotrophs. They serve as the kitchen of the cell and prepare food for the whole cell. ATP and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) are the products that are generated by the chloroplast’s cellular action.
Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation
In this type, both the photosystems operate together and produce ATP, NADPH, and also oxygen. This takes place in the membrane of the grana present in the chloroplast which possesses both the required photosystems. The PS II absorbs light of shorter wavelengths and passes it to its chlorophyll- reaction center P680 which becomes excited.
Cyclic Photophosphorylation
The dark reaction requires 3 ATP and 2 NADPH to reduce one molecule of carbon dioxide to one carbohydrate molecule. When two pairs of electron on undergoing non-cyclic photophosphorylation yields 2 ATP and 2 NADPH. But, one more ATP is required and this need is fulfilled by cyclic photophosphorylation.
Chemiosmotic Hypothesis
The chemiosmotic hypothesis puts forward the explanation of how ATP is synthesized in the chloroplast.ATP synthesis via photosynthesis reaction is connected with the generation of proton motive force (PMF) across the thylakoid membrane. The establishment of a proton gradient across the membranes occurs through the following reactions.
Protons find a path
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthases are dynamos that interconvert rotational and chemical energy. Capturing the complete structure of these multisubunit membrane-bound complexes has been hindered by their inherent ability to adopt multiple conformations. Srivastava et al.
Structured Abstract
Green plant chloroplasts convert light into chemical energy, and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) generated by photosynthesis is the prime source of biologically useful energy on the planet.
Abstract
The chloroplast adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase uses the electrochemical proton gradient generated by photosynthesis to produce ATP, the energy currency of all cells. Protons conducted through the membrane-embedded F o motor drive ATP synthesis in the F 1 head by rotary catalysis.
Overall structure and rotary conformations of cF 1 F o
We isolated native cF 1 F o from market spinach and reconstituted it into lipid nanodiscs (fig. S1A). The isolated complex contained all protein subunits and was highly pure and fully autoinhibited (fig. S1B). When detached from F o by detergent, F 1 was hydrolytically active (fig. S1, B to D).
Structure of the cF 1 head with bound nucleotides
Compared with mitochondrial ATP synthase, detailed information on the structure of the chloroplast complex is limited. In crystal structures of the catalytic subunits, the α 3 β 3 subcomplex is symmetrized and does not contain nucleotides ( 25, 26 ).
Connection of F 1 head to the peripheral stalk
The peripheral stalk of cF 1 F o consists of subunits δ, b and b′. The δ subunit (called oligomycin sensitivity-conferring protein in mitochondria) connecting the peripheral stalk to the F 1 head consists of two domains.
Proton translocation through cF o
The proton translocation pathway is formed by the a subunit and its interface with the c-ring. All 14 subunits of the chloroplast c-ring rotor are equally well resolved ( Fig. 1 ). The crystal structure of an isolated c 14 -ring from pea chloroplasts ( 34) fits the density well.