Does crossing over occur every time meiosis
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsᵻs/ is a specialized type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multicellular eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the l…
What happens in meiosis during the event called crossing over?
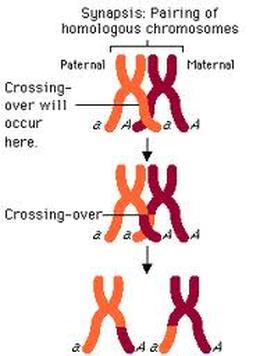
Crossing over is the swapping of genetic material that occurs in the germ line. During the formation of egg and sperm cells, also known as meiosis, paired chromosomes from each parent align so that similar DNA sequences from the paired chromosomes cross over one another. Crossing over results in a shuffling of genetic material and is an important cause of the genetic variation seen among offspring.
What are the 10 stages of meiosis?
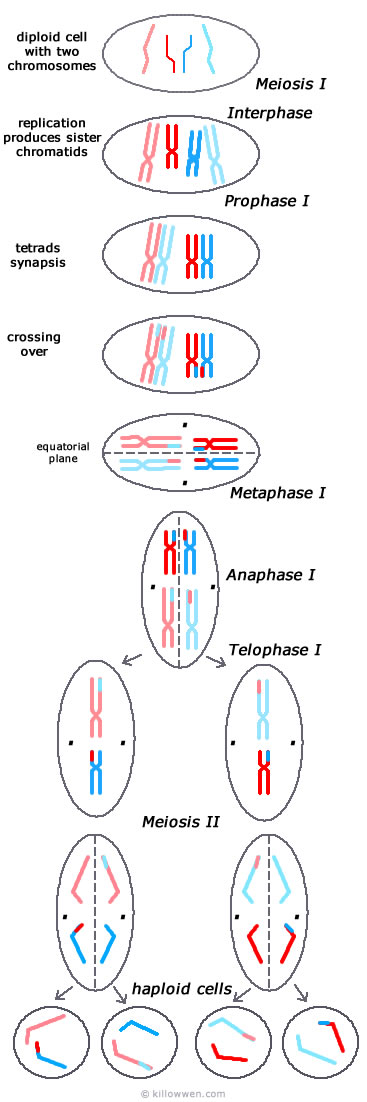
The ten stages of meiosis are two separate instances of P.M.A.T., or prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. These phases occur during meiosis I and meiosis II. The 10 stages are as follows: Are you a student or a teacher?
Why does crossing over rarely occur in mitosis?
Why does crossing over not happen in mitosis? The stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. No, homologous chromosomes act independently from one another during alignment in metaphase and chromatid segregation in anaphase.
Why does crossing over occur in prophase one?
Crossing over (recombination) only occurs during Prophase 1 of Meiosis because at this point homologous chromosomes line up at the centre of the cell. …. However, after meiosis 1, the newly formed cells consist of single chromosomes, instead of homologous chromosomes. Therefore, crossing over cannot occur after meiosis 1.

What are examples of crossing over?
Remember the example of the superpowers. If one parent has a trait for a superpower and another that turns one's off, crossing over will make it so...
What is crossing over and what phase does it occur?
Crossing over is the process of swapping DNA sequences between the chromatids of paired homologous chromosomes. This process occurs during the prop...
When did the chromosomes cross over?
Chromosomes cross over early on in meiosis I, during a step called prophase. It is during this step that chromatids swap DNA.
What is Crossing Over in Meiosis?
Everyone is unique. People can have traits that are extremely similar to their parents, but no one is a perfect blend of them. It is despite the fact a person's genes directly come from their parents. Siblings, except identical twins, are not copies of one another - even if they share the same parents. What causes this to happen? Why is it that a person can have their father's nose, their mother's eyes, even their grandmother's hair, yet be utterly distinct from all of them? How can siblings come from the same parents and yet appear completely different from one another? All this can be attributed to crossing over, the single most important process in terms of genetic variation. What, then, is crossing over?
What is the process of crossing over?
Crossing over is the process of swapping DNA sequences between the chromatids of paired homologous chromosomes. This process occurs during the prophase of meiosis I.
What is the damage caused by DNA recombination?
Over time, the DNA within a chromosome can become damaged due to errors made when copying it, damage from the environment, or a host of other potential causes. Within chromosomes, the damage is sometimes done to both strands of DNA. This severe form of damage is known as a double-strand break. To fix them, cells can exchange DNA segments between homologs using the crossover. In this instance, there are no chromatids involved, and the chromosomes are not separated afterward.
What happens when chromatids cross over?
Once paired, chromatids undergo crossing over between their homologs. What this means is that the individual chromatids exchange segments of their DNA with each other. It results in chromatids with wholly unique DNA sequences. To illustrate: imagine a chromosome that originated with the mother of an organism. Once it has paired with its counterpart from the father, their chromatids exchange DNA. The resultant chromatid now consists mainly of the DNA of the mother but also partly that of the father. It means that a chromatid that has undergone crossover has a unique DNA sequence that also originates from the combined DNA of its parents.
How do homologs swap genes?
One chromosome carries a gene for super strength, while the other has a gene that does not allow flight. When they swap genes, the chromosomes will end up with either the super strength or no-flight gene . Once the genes are separated during meiosis, the resultant cells can carry one gene or the other but not both. This principle is known as the independent assortment. The principle states that traits from different genes get sorted into gametes independently of one another. This means that the trait a cell receives for one gene does not influence the trait that is received for another.
What are the two main stages of meiosis?
Meiosis proceeds through two main stages: meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis I, they must first create copies of all their chromosomes. Once this is finished, meiosis I proceed to prophase. During prophase, these chromosomes are paired with nearly identical ones, i.e. those from the father are paired with those from the mother. The pairs are called homologous chromosomes. Individual homologous chromosomes are called homologs. When homologous chromosomes duplicate, there is a period where two copies of the same chromosome are paired with two copies of their homolog. The individual copies are called chromatids.
How do gametes form?
To create gametes, a special cell called a precursor must undergo a process called meiosis. Meiosis is a multi-step process in which a cell with a set of chromosomes creates four new cells with half that set. During meiosis, there is an important step to genetic variation. This step is called crossing over, or a crossover, and is unique to gametes. Crossing over occurs when chromosomes "trade" sections of their DNA, shuffling genes between them. It is because of this trade that variation of physical traits arises. When does this happen, and why do chromosomes cross?
Why is crossing over important in genetic mapping?
The process of crossing over was used in genetic mapping to understand the order of genes on a chromosome, and to determine the distance between them. This works on the basis that if two genes are present far apart on the chromosome, the frequency of crossing over between the two will be greater.
What is the process of meiosis?
This process takes place with the help of two underlying mechanisms of meiosis: the process of gamete formation and fertilization ―the fusion of the male and female gametes. Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that takes place only in specialized sex cells or gametes.
What is the name of the process where two chromosomes cross over?
In prophase I, homologous chromosomes align lengthwise or pair with each other, and exchange of genetic material between the two chromosomes takes place, which is known as crossing over.
Why is meiosis important?
Meiosis is required in the maintenance of chromosome number as well as bring about an increase in genetic diversity. In this BiologyWise post, we explain the process of crossing over and why is it important.
What happens to the complementary DNA sequence as it continues to synthesis?
As the synthesis of the complementary DNA sequence continues, it displaces the original complementary strand. ♦ The displaced complementary DNA strand then anneals itself to the strand that was originally complementary to the invading strand. The structure that is thus formed is known as a Holliday junction.