What type of reaction forms an ester?
What kind of reaction forms an ester? Esters are formed in esterification reactions between carboxylic acids and alcohols, and in acylation reactions between alcohols and either acyl chlorides, or acid anhydrides. Why is the acid hydrolysis of esters a reversible reaction?
What happens when esters are hydrolyzed?
Technically, hydrolysis is a reaction with water. That is exactly what happens when esters are hydrolyzed by water or by dilute acids such as dilute hydrochloric acid. The alkaline hydrolysis of esters actually involves reaction with hydroxide ions, but the overall result is so similar that it is lumped together with the other two.
How do we produce esters?
Let’s explore how we produce esters. Esterification is a reaction type that produces an ester. In this case, we react a carboxylic acid with an alcohol to produce an ester and water. This is a reversible reaction, meaning both the forward reaction and the backward reaction happen at the same time in a state of dynamic equilibrium.
How do you break down an ester?
Esters react in various ways. They are formed in esterification reactions between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. They can also be formed in acylation reactions between alcohols and either acyl chlorides, or acid anhydrides. They are broken down in hydrolysis reactions using either a base or an acid as a catalyst.
What does water do to esters?
Esters can form hydrogen bonds through their oxygen atoms to the hydrogen atoms of water molecules. As a result, esters are slightly soluble in water. However, because esters do not have a hydrogen atom to form a hydrogen bond to an oxygen atom of water, they are less soluble than carboxylic acids.
What does esters react with?
Esters can be cleaved back into a carboxylic acid and an alcohol by reaction with water and a base. The reaction is called a saponification from the Latin sapo which means soap. The name comes from the fact that soap used to me made by the ester hydrolysis of fats.
What does an ester and water make?
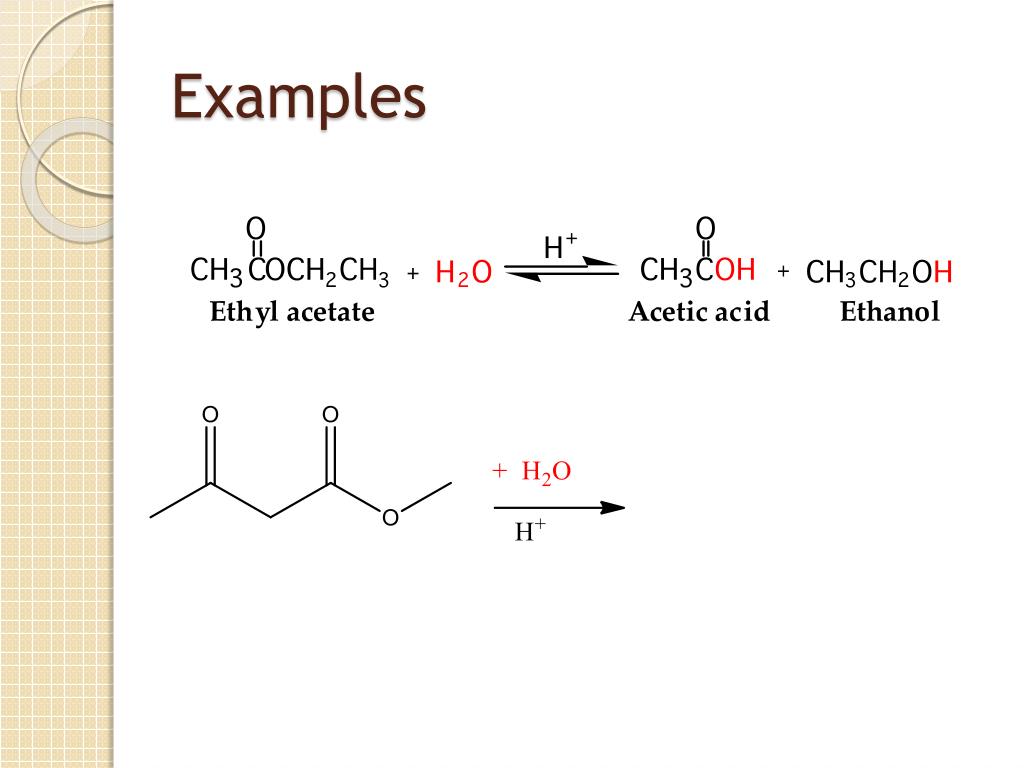
Remember that in acidic hydrolysis, water (HOH) splits the ester bond. The H of HOH joins to the oxygen atom in the OR part of the original ester, and the OH of HOH joins to the carbonyl carbon atom: The products are butyric acid (butanoic acid) and ethanol.
Are esters stable in water?
Ethers are insoluble in water because due to the bigger size of the alkyl groups, the oxygen atom in ethers fails to form intermolecular H-bonds with water.
What reaction forms ester and water?
The reaction, called Fischer esterification, is characterized by the combining of an alcohol and an acid (with acid catalysis) to yield an ester plus water. Under appropriate conditions, inorganic acids also react with alcohols to form esters.
How do you activate an ester?
In organic chemistry, an active ester is an ester functional group that is highly susceptible toward nucleophilic attack. Activation can be imparted by modifications of the acyl or the alkoxy components of a normal ester, say ethyl acetate. Typical modifications call for electronegative substituents.
What is the hydrolysis of ester?
Ester is heated in reflux with dilute hydrochloric acid (dilute acid). Reactions are reversible. This is termed Ester Hydrolysis.
What is ester water?
ester, any of a class of organic compounds that react with water to produce alcohols and organic or inorganic acids. Esters derived from carboxylic acids are the most common.
How do you separate an ester from water?
The ester can be separated from the carboxylic acid, alcohol, water and sulphuric acid in the mixture by fractional distillation.
Are esters freely soluble in water?
Ester is fairly soluble in water.
Which esters are soluble in water?
The names of the esters which are soluble in water are methyl formate (contains 2 carbon atoms), ethyl formate (containing three carbon atoms), methyl acetate (contains three carbon atoms) and ethyl acetate (contains four carbon atoms) are easily soluble in water.
Are esters hydrophobic?
Consequently, esters and ketones bearing typical polar groups are not classified into hydrophilic compounds, but into "hydroneutral" compounds positioned between hydrophilic and hydrophobic ones.
Do esters react with amines?
Esters can also react with amines or ammonia to form amides. This reaction doesn't involve acid catalysis, so the first step is nucleophilic attack at the carbonyl carbon.
Can ester react with ketone?
Another type of crossed Claisen condensation occurs when a ketone is reacted with an ester. The use of an ester without alpha-hydrogens is not necessary due to the greater reactivity of the ketone. The alpha-hydrogens of the ketone are much more acidic (pKa~20) than those of the ester (pKa~25).
Do esters react with HCL?
When ethyl ethanoate is heated under reflux with a dilute acid such as dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulfuric acid, the ester reacts with the water present to produce ethanoic acid and ethanol.
Do esters react with NaOH?
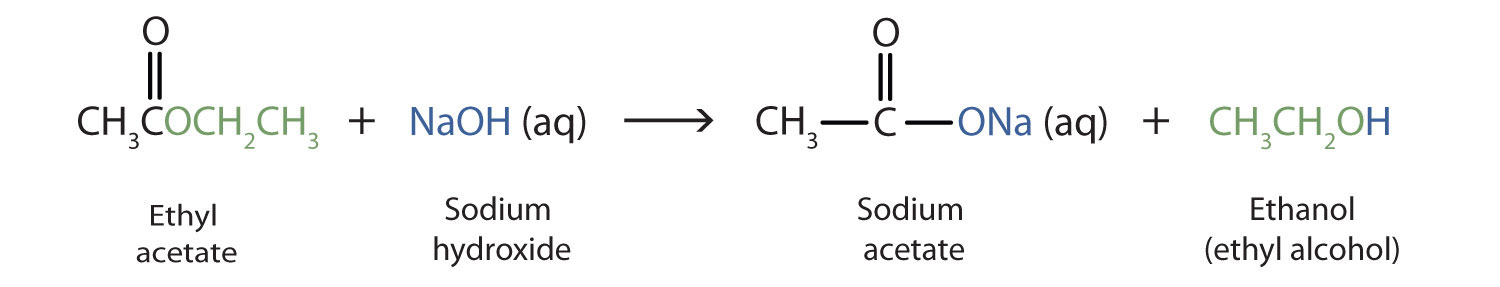
Ester Hydrolysis with NaOH or base catalysed ester hydrolysis is the reaction of an ester with water under a basic medium. In it, an ester is heated under reflux with dilute NaOH to yield carboxylate salt and alcohol. It is also known as saponification reaction, i.e. it is used to synthesise soap.
What is an ester?
Full Article. ester, any of a class of organic compounds that react with water to produce alcohols and organic or inorganic acids. Esters derived from carboxylic acids are the most common. The term ester was introduced in the first half of the 19th century by German chemist Leopold Gmelin. Carboxylic acid esters, formula RCOOR′ (R ...
How is an ester converted to another ester?
One ester may be converted to another ester by reaction (transesterified) with an alcohol, a carboxylic acid, or a third ester in the presence of a catalyst. The hydrolysis of esters in the presence of alkalies such as potassium hydroxide (lye) or sodium—a reaction called saponification —is utilized in the preparation of soaps from fats ...
What is the functional group of a carboxylic ester?
carboxylic acid: Carboxylic esters. The functional group of a carboxylic ester is an acyl group bonded to OR or OAr, where R represents an alkyl group and... The reverse of the esterification reaction is an example of hydrolysis. Esters may also be obtained by reaction of acid halides or acid anhydrides with alcohols or by reaction of salts ...
What is phosphate ester?
Phosphate esters are biologically important ( nucleic acids belong to this group) and are used widely in industry as solvents, plasticizers, flame retardants, gasoline and oil additives, and insecticides. Esters of sulfuric and sulfurous acids are used in the manufacture of dyes and pharmaceuticals. Dimethyl sulfate, the best-known ester of ...
What is the formula for carboxylic acid esters?
Carboxylic acid esters, formula RCOOR′ (R and R′ are any organic combining groups), are commonly prepared by reaction of carboxylic acids and alcohols in the presence of hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid, a process called esterification.
What is polymethyl methacrylate?
Polymethyl methacrylate is a glass substitute sold under the names Lucite and Plexiglas; polyethylene terephthalate is used as a film (Mylar) and as textile fibres sold as Terylene, Fortrel, and Dacron. Esters are also formed from alcohols and such inorganic acids as sulfuric, phosphoric, and nitric acids.
What is the purpose of volatile esters?
Certain volatile esters are used as solvents for lacquers, paints, and varnishes; for this purpose, large quantities of ethyl acetate and butyl acetate are commercially produced. Waxes secreted by animals and plants are esters formed from long-chain carboxylic acids and long-chain alcohols.
What is the reaction of a base and an ester called?
When a base (such as sodium hydroxide [NaOH] or potassium hydroxide [KOH]) is used to hydrolyze an ester, the products are a carboxylate salt and an alcohol. Because soaps are prepared by the alkaline hydrolysis of fats and oils, alkaline hydrolysis of esters is called saponification (Latin sapon, meaning “soap,” and facere, meaning “to make”). In a saponification reaction, the base is a reactant, not simply a catalyst. The reaction goes to completion:
What is the name of the reaction where an ester is replaced by another group?
In typical reactions, the alkoxy (OR′) group of an ester is replaced by another group. One such reaction is hydrolysis, literally “splitting with water.”. The hydrolysis of esters is catalyzed by either an acid or a base. Acidic hydrolysis is simply the reverse of esterification.
What is the most important reaction of esters?
Hydrolysis is a most important reaction of esters. Acidic hydrolysis of an ester gives a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Basic hydrolysis of an ester gives a carboxylate salt and an alcohol.
What is the product of acidic hydrolysis?
The H of HOH joins to the oxygen atom in the OR part of the original ester, and the OH of HOH joins to the carbonyl carbon atom: The products are butyric acid (butanoic acid) and ethanol.
What is the end result of the acid portion of an ester?
In basic hydrolysis, the molecule of the base splits the ester linkage. The acid portion of the ester ends up as the salt of the acid (in this case, the potassium salt). The alcohol portion of the ester ends up as the free alcohol.
Is acidic hydrolysis reversible?
Acidic hydrolys is is simply the reverse of esterification. The ester is heated with a large excess of water containing a strong-acid catalyst. Like esterification, the reaction is reversible and does not go to completion. As a specific example, butyl acetate and water react to form acetic acid and 1-butanol. The reaction is reversible and does not ...
What are esters?
Ethyl acetate, systematically known as ethyl ethanoate, is one of the most common esters. If you give it a sniff, it smells characteristically fruity, like pear drops. We use it in a variety of different ways: as a solvent and diluent, to decaffeinate coffee and tea leaves, as a flavouring, and in toiletries.
Esterification
Esterification is a reaction type that produces an ester. In this case, we react a carboxylic acid with an alcohol to produce an ester and water. This is a reversible reaction, meaning both the forward reaction and the backward reaction happen at the same time in a state of dynamic equilibrium .
Hydrolysis of esters
We can break down esters in two similar ways, using either an acid or a base as a catalyst. These reactions are known as hydrolysis reactions.
Saponification
We mentioned above that we can make soaps out of different fats and oils. This is known as saponification .
Biodiesel
In 2006, a shuttle bus operating at Yale University was successfully converted to run on 100 percent biodiesel - a form of renewable fuel derived from plants. This was a major step towards lowering the environmental impact of the transport industry. Before we finish, let’s quickly explore what biodiesel actually is.
Reactions of Esters
Esters are formed in esterification reactions between carboxylic acids and alcohols, and in acylation reactions between alcohols and either acyl chlorides, or acid anhydrides.
What is the salt of a carboxylic acid?
A salt of a carboxylic acid is formed - in this case, the sodium salt of a big acid such as octadecanoic acid (stearic acid). These salts are the important ingredients of soap - the ones that do the cleaning.
How to hydrolyze ethyl ethanoate?
First, hydrolysing ethyl ethanoate using sodium hydroxide solution: . . . and then hydrolysing methyl propanoate in the same way: Notice that you get the sodium salt formed rather than the carboxylic acid itself. This mixture is relatively easy to separate.
What is the reaction of ester?
The reaction is catalysed by dilute acid, and so the ester is heated under reflux with a dilute acid like dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulphuric acid. Here are two simple examples of hydrolysis using an acid catalyst. First, hydrolysing ethyl ethanoate: . . . and then hydrolysing methyl propanoate: Notice that the reactions are reversible.
How do esters hydrolyze?
This page describes ways of hydrolysing esters - splitting them into carboxylic acids (or their salts) and alcohols by the action of water, dilute acid or dilute alkali. It starts by looking at the hydrolysis of simple esters like ethyl ethanoate, and goes on to look at hydrolysing bigger, more complicated ones to make soap.
What is the reaction of alkaline hydrolysis?
The alkaline hydrolysis of esters actually involves reaction with hydroxide ions , but the overall result is so similar that it is lumped together with the other two. Hydrolysis using water or dilute acid. The reaction with pure water is so slow that it is never used. The reaction is catalysed by dilute acid, and so the ester is heated ...
What acid to add to a solution after distillation?
That's easy! If you want the acid rather than its salt, all you have to do is to add an excess of a strong acid like dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulphuric acid to the solution left after the first distillation. If you do this, the mixture is flooded with hydrogen ions.
What is the name of the alkaline hydrolysis of esters?
Because of its relationship with soap making, the alkaline hydrolysis of esters is sometimes known as saponification. Questions to test your understanding.
What is the hydrolysis of ester?
Esters are hydrolyzed into carboxylic acid and alcohol. The hydrolysis of an ester is catalyzed either by mineral acids e.g. hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sulphuric acid (H 2 SO 4) or alkali. e.g potassium hydroxide (KOH) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
What is the name of the process of hydrolysis of an ester in the presence of a strong alkali?
The hydrolysis of an ester in the presence of a strong alkali such as sodium hydroxide into the sodium salt of carboxylic acid and alcohol is known as base-catalyzed hydrolysis or saponification.
What is the name of the reaction in which the hydroxyl group of an ester is replaced by water?
The hydrolysis of an ester is a reaction in which the (-OR) group of the ester is replaced by the hydroxyl (-OH) group from water. This reaction can be catalyzed either by an acid or a base.
What happens when ester reacts with sodium hydroxide?
When ester reacts with sodium hydroxide, it produces alcohol and sodium salt of carboxylic acid. This reaction is known as base-catalyzed hydrolysis of ester or saponification.
What are the two acids that are used in the hydrolysis of ester?
The mineral acids such as sulphuric acid and hydrochloric acid are used as catalysts in the hydrolysis of an ester. They provide an H + ion and increase the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon.
What is the best way to make an ester?
In this method, alcohols are treated with carboxylic acids in the presence of acids to form esters. Fischer esterification is generally the preferred way of esterification.
What increases the rate of ester hydrolysis?
The rate of ester hydrolysis can also be enhanced by increasing the reactivity of a nucleophile. The hydroxide ion should be used instead of water. It means that alkalis are suited as well to increase the rate of hydrolysis. Alkalis like NaOH, KOH, Mg (OH) 2, and Ca (OH) 2, etc can be used.
What are the properties of ester?
Properties of Esters. Esters are derived from carboxylic acids. A carboxylic acid contains the -COOH group, and in an ester the hydrogen in this group is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. This could be an alkyl group like methyl or ethyl, or one containing a benzene ring such as a phenyl or benzyl group. The most commonly discussed ester is ethyl ...
What are fats and oils made of?
Fats and oils as big esters. Esters can be made from carboxylic acids and alcohols. This is discussed in detail on another page; in general terms, the two combine together, losing a molecule of water in the process. Consider a very simple ester such as ethyl ethanoate.
What are the physical properties of fats and oils?
The physical properties of fats and oils. Solubility in water. Melting point. Contributors. Esters are derived from carboxylic acids. A carboxylic acid contains the -COOH group, and in an ester the hydrogen in this group is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. This could be an alkyl group like methyl or ethyl, or one containing a benzene ring such as ...
Why do esters have solubility?
The reason for this trend in solubility is that although esters cannot hydrogen bond with each other, they can hydrogen bond with water molecules. One of the partially-positive hydrogen atoms in a water molecule can be sufficiently attracted to one of the lone pairs on one of the oxygen atoms in an ester, forming a hydrogen bond. Dispersion forces and dipole-dipole attractions are also present.
What are the physical differences between animal fats and vegetable oils?
The physical differences observed between a fat (like butter) and an oil (like sunflower oil) are due to differences in melting points of the mixture of esters they contain.
Why do trans fats have higher melting points than cis conformations?
Trans -fats and oils have higher melting points than their corresponding cis - conformations because the packing is not interrupted to the same degree. Naturally occurring unsaturated fats and oils tend to adopt the cis - conformations.
Why does a higher number of double bonds result in a lower melting point?
A greater number of double bonds, or degree of unsaturation, in the molecules results in a lower melting point, because the van der Waals forces are less effective. The efficacy of van derWaals forces depends on the ability of molecules to pack closely together. The presence of carbon-carbon double bonds in the chains disrupts otherwise tidy packing. Here is a simplified diagram of a saturated fat:
What is the product of acidic hydrolysis?
Write an equation for the acidic hydrolysis of ethyl butyrate (CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 COOCH 2 CH 3) and name the products.SolutionRemember that in acidic hydrolysis, water (HOH) splits the ester bond. The H of HOH joins to the oxygen atom in the OR part of the original ester, and the OH of HOH joins to the carbonyl carbon atom: The products are butyric acid (butanoic acid) and ethanol.
What is base hydrolysis?
Base hydrolysis or saponification reaction: It is a hydrolysis of an organic compound under basic condition in which a carboxylic acid salt is one of the products. In ester saponification reaction, NaoH or KOH is used as a base.
What is a thioester?
Thioesters & Phosphoesters: Thioesters are sulfur-containing analogs of esters in which an -SR group has replaced the -OR group.
Why are phosphate esters important?
Phosphate esters of simple sugars or monosaccharides are very important in the energy harvesting biochemical pathways.
Can esters be converted to alcohol?
Esters can be converted back to carboxylic acids and alcohols under either acidic or basic conditions. Under acidic conditions, the process sis called hydrolysis and the products are the acid and alcohol. Under basic conditions, the process is called saponification and the products are acid salts and alcohol.