
What organelles do eukaryotic cells have?
· Do eukaryotes have a membrane enclosed nucleus? Like a prokaryotic cell, a eukaryotic cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes. However, unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: a membrane-bound nucleus. numerous membrane-bound organelles (including the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria) Click to …
Do eukaryotes cells have a nuclear membrane?
A eukaryotic cell (left) has membrane-enclosed DNA, which forms a structure called the nucleus (located at center of the eukaryotic cell; note the purple DNA enclosed in the pink nucleus). A typical eukaryotic cell also has additional membrane-bound organelles of …
Do only eukaryotic cells have ribosomes?
· In addition, eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles, a feature that is missing in prokaryotic cells. Some of the membrane-bound organelles are Golgi bodies, endoplasmic...
What organism lacks a true membrane bound nucleus?
· Eukaryotic cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus and numerous membrane-enclosed organelles (e.g., mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus) not found in prokaryotes. Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are all eukaryotes. …

Do eukaryotes have membrane enclosed organelles?
Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. There is a wide range of eukaryotic organisms, including all animals, plants, fungi, and protists, as well as most algae. Eukaryotes may be either single-celled or multicellular.
Do eukaryotes have a membrane?
Prokaryotic cells (Figure below) are usually smaller and simpler than eukaryotic cells. They do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles....Prokaryotic Cells.Prokaryotic CellsEukaryotic CellsMembrane-Bound OrganellesNoYesExamplesBacteriaPlants, animals, fungi2 more rows•May 24, 2021
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic nucleus?
The primary distinction between these two types of organisms is that eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and prokaryotic cells do not.
Do prokaryotic cells have a cell membrane?
Prokaryotic cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane, but they have no internal membrane-bound organelles within their cytoplasm. The absence of a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles differentiates prokaryotes from another class of organisms called eukaryotes.
Do all eukaryotes have a nucleus?
The distinguishing feature of eukaryotes from prokaryotes is that they possess a well defined nucleus that is surrounded by inner and outer lipid b...
What do eukaryotic cells have that prokaryotic cells do not?
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that is surrounded by an inner and an outer membrane which forms a nuclear envelope. This feature is missing in the...
What do eukaryotic cells contain?
Eukaryotic cells contain a plasma membrane, internal protein structures such as cilia, flagella, ribosomes, and membrane-bound organelles such as m...
Do prokaryotes have a nucleus?
Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus and lack organelles that are membrane-bound. However they do contain the genetic material, i.e., DNA which is si...
Do prokaryotes have a nucleoid?
Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, have a free-floating chromosome that is usually circular and is not enclosed in a nuclear membrane. Instead, the DNA simply exists in a region of the cell called the nucleoid. Prokaryotic cells only have a small range of organelles, generally only a plasma membrane and ribosomes.
Which type of cell has a free floating chromosome?
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells. Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, have a free-floating chromosome that is usually circular and is not enclosed in a nuclear membrane. Instead, the DNA simply exists in a region of the cell called the nucleoid.
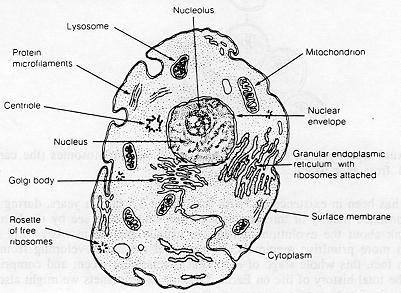
Overview
Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed within a nuclear envelope. Eukaryotes belong to the domain Eukaryota or Eukarya; their name comes from the Greek εὖ (eu, "well" or "good") and κάρυον (karyon, "nut" or "kernel"). The domain Eukaryota makes up one of the three domains of life; bacteria and archaea (the prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asga…
Cell features
Eukaryotic cells are typically much larger than those of prokaryotes, having a volume of around 10,000 times greater than the prokaryotic cell. They have a variety of internal membrane-bound structures, called organelles, and a cytoskeleton composed of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments, which play an important role in defining the cell's organization and shape. Eukaryotic DNA is divided into several linear bundles called chromosomes, which are separated b…
Differences among eukaryotic cells
There are many different types of eukaryotic cells, though animals and plants are the most familiar eukaryotes, and thus provide an excellent starting point for understanding eukaryotic structure. Fungi and many protists have some substantial differences, however.
All animals are eukaryotic. Animal cells are distinct from those of other eukaryotes, most notably plants, as they lack cell walls and chloroplasts and have smaller vacuoles. Due to the lack of a cell …
Reproduction
Cell division generally takes place asexually by mitosis, a process that allows each daughter nucleus to receive one copy of each chromosome. Most eukaryotes also have a life cycle that involves sexual reproduction, alternating between a haploid phase, where only one copy of each chromosome is present in each cell and a diploidphase, wherein two copies of each chromosome are present in each cell. The diploid phase is formed by fusion of two haploid gametes to form …
Classification
In antiquity, the two lineages of animals and plants were recognized. They were given the taxonomic rank of Kingdom by Linnaeus. Though he included the fungi with plants with some reservations, it was later realized that they are quite distinct and warrant a separate kingdom, the composition of which was not entirely clear until the 1980s. The various single-cell eukaryotes were originally placed with plants or animals when they became known. In 1818, the German biologist Georg A. …
Evolutionary history
The origin of the eukaryotic cell is a milestone in the evolution of life, since eukaryotes include all complex cells and almost all multicellular organisms. A number of approaches have been used to find the first eukaryote and their closest relatives. The last eukaryotic common ancestor (LECA) is the hypothetical last common ancestor of all living eukaryotes, and was most likely a biological population.
See also
• Eukaryote hybrid genome
• Evolution of sexual reproduction
• List of sequenced eukaryotic genomes
• Parakaryon myojinensis
External links
• "Eukaryotes" (Tree of Life Web Project)
• "Eukaryote" at the Encyclopedia of Life
• Attraction and sex among our microbial Last Eukaryotic Common Ancestors, The Atlantic, November 11, 2020