What happens when a mutation in the operator region of the operon is present?
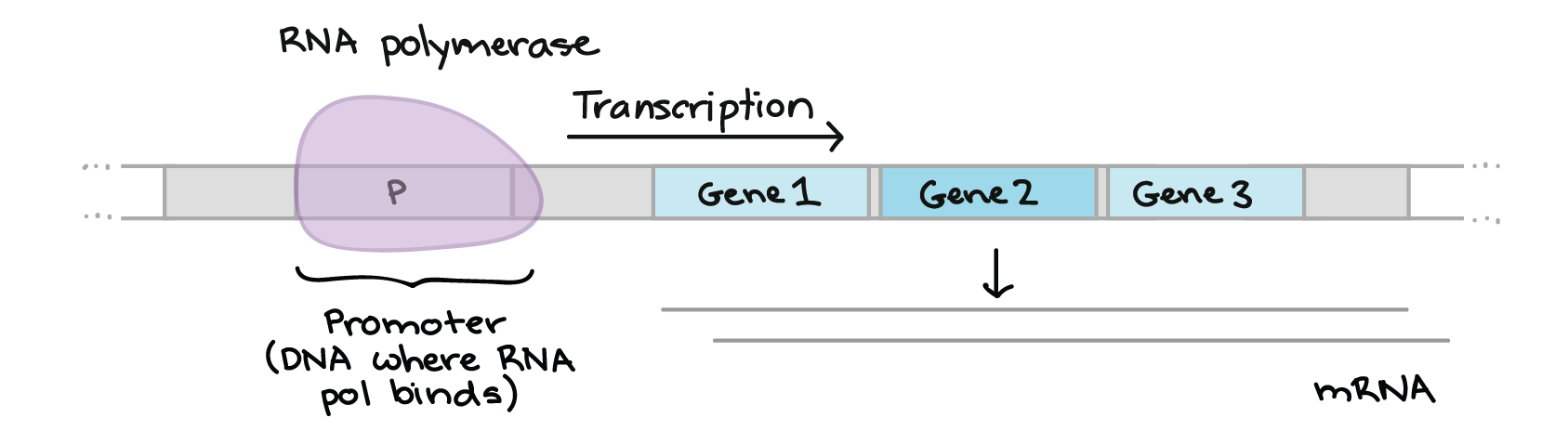
What is the operator in DNA?
When will the structural genes for the trp operon be transcribed?
Do prokaryotes use attenuation?
Does transcription take place in the cell?
See 2 more
About this website

Does attenuation work in eukaryotes?
In the attenuation process, the ribosome will stop in the region of the leader sequence. This will also stop further transcription. This process cannot occur in the eukaryotes as the process of transcription occurs in the nucleus.
Can eukaryotic transcription be regulated by attenuation?
Although the control of gene expression is far more complex in eukaryotes than in bacteria, the same basic principles apply. The expression of eukaryotic genes is controlled primarily at the level of initiation of transcription, although in some cases transcription may be attenuated and regulated at subsequent steps.
Why can't eukaryotic cells regulate transcription by attenuation?
In eukaryotes, there is no precise analogue of attenuation since transcription takes place in the nucleus and translation takes place in the cytoplasm, making this sort of coordinated impact impossible.
Why is attenuation only possible in prokaryotes?
Attenuation is possible because the genetic material of prokaryotes in in the cell's cytoplasm with its ribosomes. In prokaryotes, it is possible for ribosomes to begin translating the mRNA while RNA polymerase is still transcribing the DNA sequence, allowing translation to have an effect on transcription.
What is prokaryotic attenuation?
Transcriptional attenuation occurs when RNA transcription is prematurely terminated due to the formation of a terminator mRNA hairpin structure.
How do eukaryotic cells regulate transcription?
Like prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells also have mechanisms to prevent transcription. Transcriptional repressors can bind to promoter or enhancer regions and block transcription. Like the transcriptional activators, repressors respond to external stimuli to prevent the binding of activating transcription factors.
What are the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene regulation?
Gene expression in prokaryotes is mostly regulated at the transcriptional level (some epigenetic and post-translational regulation is also present), whereas in eukaryotic cells, gene expression is regulated at the epigenetic, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational levels.
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene expression?
Prokaryotic gene expression (both transcription and translation) occurs within the cytoplasm of a cell due to the lack of a defined nucleus; thus, the DNA is freely located within the cytoplasm. Eukaryotic gene expression occurs in both the nucleus (transcription) and cytoplasm (translation).
What stops transcription in eukaryotes?
Transcription termination occurs in a reaction coupled to RNA 3′-end processing. Most eukaryotic mRNA precursors are cleaved in a site-specific manner in the 3′-untranslated region, followed by polyadenylation of the upstream cleavage product. A large number of proteins is involved in these reactions.
Where does attenuation occur?
Classically, attenuation occurs when the transcribed RNA upstream of an operon has the ability to fold into two mutually-exclusive RNA-fold structures, one which is termed an antiterminator and the other a terminator.
How attenuation regulates protein synthesis in prokaryotic cells?
Attenuation occurs by a mechanism by which rapid translation of the nascent transcript causes the termination of transcription. As the transcript is being produced, if ribosomes attach and rapidly translate the transcript, a secondary structure is generated in the mRNA that is a termination signal for RNA polymerase.
What does attenuated mean in biology?
Attenuated: Weakened, diluted, thinned, reduced, weakened, diminished. The use of "attenuated" in medicine is not new. In the 16th century, eating dried figs was claimed to attenuate the body fluids. Now "attenuated" refers to procedures that weaken an agent of disease (a pathogen).
Which operon is regulated by attenuation?
The trp operonThe trp operon is regulated by the trp repressor. When bound to tryptophan, the trp repressor blocks expression of the operon. Tryptophan biosynthesis is also regulated by attenuation (a mechanism based on coupling of transcription and translation).
What are three mechanisms by which transcription factors regulate eukaryotic gene expression?
Solution. Eukaryotic cells have three mechanisms that control transcription of genes - transcription factors, cell specialization, and RNA interference. Transcription factors are able to bind on the spot of DNA molecule right before gene starts and attract RNA polymerase.
How is transcription regulated in prokaryotes?
The regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cells occurs at the transcriptional level. There are three ways to control the transcription of an operon: repressive control, activator control, and inducible control.
What are the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene regulation?
Gene expression in prokaryotes is mostly regulated at the transcriptional level (some epigenetic and post-translational regulation is also present), whereas in eukaryotic cells, gene expression is regulated at the epigenetic, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational levels.
chapter 12 homework genetics Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which statement describes an operon?, An operon is a group of genes under the control of a single promoter. Match each type of operon with the descriptions below. 1)Inducible2)Repressible3)Constitutive, Match the description of transcriptional control to the corresponding transcriptional regulator. There is one description for ...
chapter 16 Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Prokaryotic gene regulation:, Eukaryotic gene regulation:, Positive gene regulation: and more.
Solved What effect on the expression of the trp operon might | Chegg.com
What effect on the expression of the trp operon might you expect if the trp codons in the leader sequence of the trp operon were replaced by codons for isoleucine?
What happens when a mutation in the operator region of the operon is present?
A mutation in the operator region of the operon has altered the binding site of the repressor so that the repressor cannot bind to the operator.
What is the operator in DNA?
The operator is a DNA sequence that binds to the lacI repressor protein.
When will the structural genes for the trp operon be transcribed?
The structural genes for the trp operon will only be transcribed when isoleucine levels are low.
Do prokaryotes use attenuation?
Prokaryotes commonly use attenuation as a mechanism to control gene expression, but eukaryotes do not . Why do you think that attenuation is more common in prokaryotes than eukaryotes?
Does transcription take place in the cell?
Yes, some transcription must take place in order to produce the permease to allow lactose to enter the cell, in order to produce β-galactosidase to make allolactose, and because although the repressor protein keeps transcription at a very low basal level, some transcripts will be produced and translated.
What happens when a mutation in the operator region of the operon is present?
A mutation in the operator region of the operon has altered the binding site of the repressor so that the repressor cannot bind to the operator.
What is the operator in DNA?
The operator is a DNA sequence that binds to the lacI repressor protein.
When will the structural genes for the trp operon be transcribed?
The structural genes for the trp operon will only be transcribed when isoleucine levels are low.
Do prokaryotes use attenuation?
Prokaryotes commonly use attenuation as a mechanism to control gene expression, but eukaryotes do not . Why do you think that attenuation is more common in prokaryotes than eukaryotes?
Does transcription take place in the cell?
Yes, some transcription must take place in order to produce the permease to allow lactose to enter the cell, in order to produce β-galactosidase to make allolactose, and because although the repressor protein keeps transcription at a very low basal level, some transcripts will be produced and translated.
