
Summary
- Lysosomes are cell organelles almost exclusively found in eukaryotic animal cells
- Lysosomes are membrane-bound spherical sacs filled with hydrolytic enzymes
- These enzymes can break down many types of biomolecules such as proteins and fats
- They are not found in plants, but vacuoles perform the role of lysosomes in plant cells
Which organelles are useless in eukaryotic cells?
- Nucleus
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi Body
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast (in eukaryotic Plant cell not Animal)
- Lysosomes
- Vacuoles (small and many in Animal cell and large and single in Plant cell)
- Ribosome
- Centrioles (in algae, fungi and Animal cells not in higher Plants)
- Cytoskeletal structures (Microtubules, Microfilaments etc)
What are the four organelles in eukaryotic cells?
Vesicles and vacuoles
- Animal cells versus plant cells. At this point, you know that each eukaryotic cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, a nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondria, peroxisomes, and in some, vacuoles.
- The centrosome. The centrosome is a microtubule-organizing center found near the nuclei of animal cells. ...
- Lysosomes. ...
- The cell wall. ...
- Chloroplasts. ...
- The central vacuole. ...
Are chloroplasts found only in eukaryotic cells?
Mitochondria and chloroplast are two organelles found in eukaryotic cells. Chloroplast is only found in plants while majority of eukaryotic cells have mitochondria. Even though both organelles are found in eukaryotic cells, both mitochondria and chloroplast have characteristics often found in prokaryotic cells.
Are mitochondria found in all eukaryotic cells?
Mitochondria are found in the cells of nearly every eukaryotic organism, including plants and animals. Cells that require a lot of energy, such as muscle cells, can contain hundreds or thousands of mitochondria. A few types of cells, such as red blood cells, lack mitochondria entirely.
Do all eukaryotic cells have lysosomes?
lysosome, subcellular organelle that is found in nearly all types of eukaryotic cells (cells with a clearly defined nucleus) and that is responsible for the digestion of macromolecules, old cell parts, and microorganisms.
Are lysosomes in eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Eukaryotic cellsEukaryotic cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus and numerous membrane-enclosed organelles (e.g., mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus) not found in prokaryotes. Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are all eukaryotes.
Are lysosomes prokaryotic cells?
No, prokaryotic cells do not have lysosomes. This is due to the fact that lysosomes are formed by the endoplasmic reticulum as well as golgi bodies – which are membrane bound organelles exclusive to eukaryotes.
Does a eukaryotic animal cell have lysosomes?
Lysosomes are found in nearly every animal-like eukaryotic cell. They are so common in animal cells because, when animal cells take in or absorb food, they need the enzymes found in lysosomes in order to digest and use the food for energy.
What is not found in eukaryotic cells?
The primary distinction between these two types of organisms is that eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and prokaryotic cells do not. The nucleus is where eukaryotes store their genetic information.
What do prokaryotes and eukaryotes have in common?
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have structures in common. All cells have a plasma membrane, ribosomes, cytoplasm, and DNA. The plasma membrane, or cell membrane, is the phospholipid layer that surrounds the cell and protects it from the outside environment.
Which structure is found in all eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells are very diverse in shape, form and function. Some internal and external features, however, are common to all. These include a plasma (cell) membrane, a nucleus, mitochondria, internal membrane bound organelles and a cytoskeleton.
Do animal cells have lysosomes?
Lysosomes are membrane bounded organelles found in animal and plant cells.
What cellular features are present in eukaryotes and not present in prokaryotes?
Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. Differences in cellular structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes include the presence of mitochondria and chloroplasts, the cell wall, and the structure of chromosomal DNA.
Do all cells have lysosomes?
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles found in every eukaryotic cell.
Is lysosomes absent in plant cell?
Lysosomes are present in plant cells but are very uncommon. This is due to the fact that the function of lysosomes is performed by the cell walls – which prevent foreign substances from entering the cell.
Do bacteria cells have lysosomes?
Bacterial cells. Hint:-The lysosomes are the membrane-bound organelles present in the cell. They have various digestive enzymes enclosed in a membrane. These digestive enzymes can digest and kill the virus and bacteria that enter the cell.
Define Lysosome.
Lysosomes are defined as sphere-shaped vesicles or sacs filled with hydrolytic enzymes that have the ability to break down almost all types of biom...
Who discovered Lysosomes?
Lysosomes were discovered by a Belgian biologist, Christian de Duve, and was awarded a Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology in the year 1974. He i...
What type of cells possesses lysosomes?
Only eukaryotic animal cells contain lysosomes. Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria do not contain lysosomes or any of the other membrane-bound org...
Do plants cells have lysosomes?
Plants do not possess lysosomes; however, the role of lysosomes are undertaken by the vacuoles. Findings even suggest that vacuoles contain hydrol...
What is a lumen in a lysosome?
Lumen is the area within the membrane-bound exterior of the lysosome. It contains cellular debris suspended in hydrolytic enzymes. It is also acidi...
Why are Lysosomes known as Suicidal Bags?
The main function of lysosomes is to breakdown and recycle cellular debris, discarded cellular contents and foreign pathogens, however, the digesti...
Where are the enzymes needed by lysosomes made?
The enzymes are synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and once synthesized; the enzymes are brought in from the Golgi apparatus in tiny ve...
What are lysosomal storage diseases?
Any mutations that occur in the nuclear genes may result in over 30 diverse human genetic ailments. These ailments are collectively called lysosoma...
What are lysosomes?
Lysosomes are defined as sphere-shaped vesicles or sacs filled with hydrolytic enzymes that have the ability to break down almost all types of biomolecules. They essentially help clean up and recycle cellular debris and wastes.
Where are lysosomes found?
Lysosomes are predominantly found in eukaryotic animal cells and are responsible for breaking down cellular debris. In plants, the role of lysosomes is undertaken by the vacuoles as traditional cell biology dictates.
What is the pH level of lysosomes?
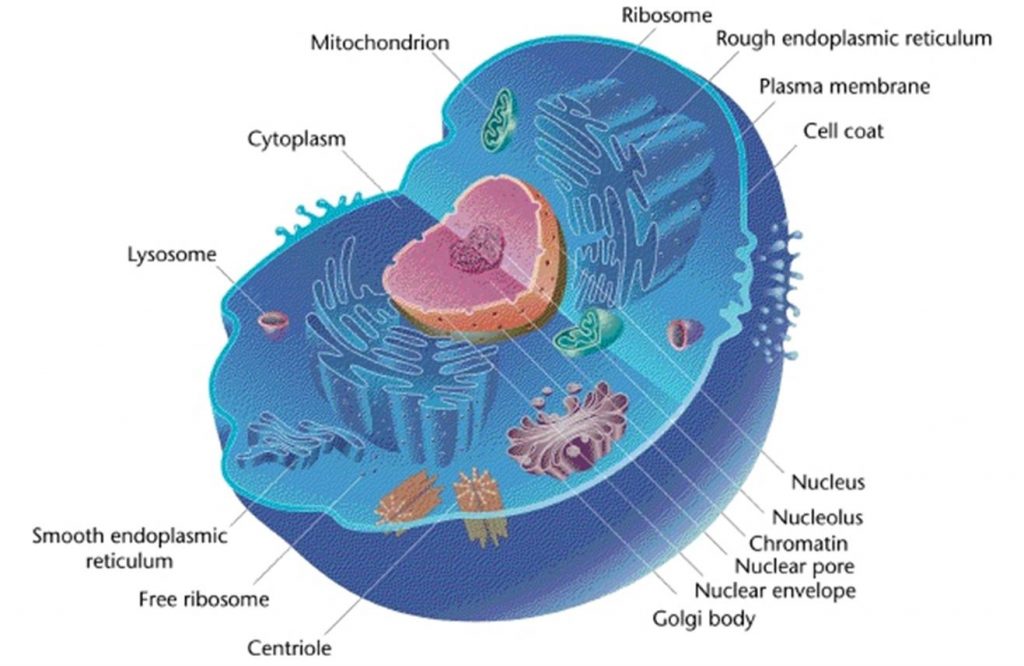
The diagram below shows the lysosome structure within a cell. The pH level of the lumen lies between 4.5 and 5.0, which makes it quite acidic.
Where are lysosomes synthesized?
Lysosomes comprise of over 50 different enzymes. They are synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Once synthesized, the enzymes are brought in from the Golgi apparatus in tiny vesicles or sacs, which then merges with bigger acidic vesicles.
What is the function of lysosomes?
The main function of lysosomes is to breakdown and recycle cellular debris, discarded cellular contents and foreign pathogens , however, the digestive enzymes may end up bursting from the lysosome, damaging the cell themselves, and this can cause the cell to die.
How big are lysosomes?
The sizes of lysosomes vary, with the largest ones measuring in more at than 1.2 μm.
Who discovered the lysosome?
The term was coined by Christian de Duve, a Belgian biologist, who discovered it and ultimately got a Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology in the year 1974. Let us have a detailed overview of lysosome structure, functions and diseases associated with it.
What is the membrane of an eukaryotic cell?
Like prokaryotes, eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane ( Figure ), a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that separates the internal contents of the cell from its surrounding environment. A phospholipid is a lipid molecule with two fatty acid chains and a phosphate-containing group. The plasma membrane controls the passage of organic molecules, ions, water, and oxygen into and out of the cell. Wastes (such as carbon dioxide and ammonia) also leave the cell by passing through the plasma membrane.
Which part of the chromosome is responsible for synthesis of ribosomes?
We already know that the nucleus directs the synthesis of ribosomes, but how does it do this? Some chromosomes have sections of DNA that encode ribosomal RNA. A darkly staining area within the nucleus called the nucleolus (plural = nucleoli) aggregates the ribosomal RNA with associated proteins to assemble the ribosomal subunits that are then transported out through the pores in the nuclear envelope to the cytoplasm.
What are the differences between plant and animal cells?
Animal cells each have a centrosome and lysosomes; whereas, most plant cells do not. Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts and other specialized plastids, and a large central vacuole; whereas, animal cells do not.
What are the functions of peroxisomes?
They carry out oxidation reactions that break down fatty acids and amino acids. They also detoxify many poisons that may enter the body. (Many of these oxidation reactions release hydrogen peroxide, H 2 O 2, which would be damaging to cells; however, when these reactions are confined to peroxisomes, enzymes safely break down the H 2 O 2 into oxygen and water.) For example, peroxisomes in liver cells detoxify alcohol. Glyoxysomes, which are specialized peroxisomes in plants, are responsible for converting stored fats into sugars. Plant cells contain many different types of peroxisomes that play a role in metabolism, pathogene defense, and stress response, to mention a few.
What are the structures that make proteins?
They may be attached to the plasma membrane's cytoplasmic side or the endoplasmic reticulum's cytoplasmic side and the nuclear envelope's outer membrane ( Figure ). Electron microscopy shows us that ribosomes, which are large protein and RNA complexes, consist of two subunits, large and small ( Figure ). Ribosomes receive their “orders” for protein synthesis from the nucleus where the DNA transcribes into messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA travels to the ribosomes, which translate the code provided by the sequence of the nitrogenous bases in the mRNA into a specific order of amino acids in a protein. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.
Where is the centrosome located?
The centrosome is a microtubule-organizing center found near the nuclei of animal cells. It contains a pair of centrioles, two structures that lie perpendicular to each other ( Figure ). Each centriole is a cylinder of nine triplets of microtubules.
Which organelle houses DNA?
Typically, the nucleus is the most prominent organelle in a cell ( Figure ). The nucleus (plural = nuclei) houses the cell’s DNA and directs the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins. Let’s look at it in more detail ( Figure ).
