What is the role of coenzymes in vitamins?
Most water-soluble vitamins act as coenzymes or are required for the synthesis of coenzymes. The fat-soluble vitamins are important for a variety of physiological functions.Antioxidants are able to bind free radicals, preventing such damage from happening. Certain coenzymes, such as CoQ10, are even used as medical interventions.
What is the function of each of the fat-soluble vitamins?
Each of the fat-soluble vitamins performs unique functions in the body. The three active forms of Vitamin A are required for night and color vision, reproduction, and cell maturation and differentiation, the process by which precursor cells develop into a specific cell type.
How do enzymes and vitamins work together?
Vitamins are organic molecules your body needs to assist enzymes in doing their jobs. Some vitamins act as these “coenzymes” while others metabolize, or break down, to supply the coenzyme needed. Folate (vitamin B-9) reduces into the THF coenzyme, for example. How do vitamins help enzymes? An enzyme is a lot like a key.
What are coenzymes and water-soluble vitamins?
Water-soluble vitamins are typically the coenzymes. Your water-soluble vitamins are vitamin C and your B complex vitamins, which include: Each of the B vitamins acts as a coenzyme. For example, vitamin B6 becomes pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) and is needed for the many numerous PLP- dependent enzymatic reactions. [i]
What are the water soluble vitamins?
What are the functions of vitamin A?
What is the role of vitamin D in the body?
How many vitamins are there in the human body?
Where are vitamins stored?
What is vitamin K?
See 3 more
About this website

Can fatty acids act as coenzymes?
Fatty acids are linked to coenzyme A (CoA―SH) in one of two main ways. In higher organisms, enzymes in the cytoplasm called thiokinases catalyze the linkage of fatty acids with CoA―SH to form a compound that can be called a fatty acyl coenzyme A [21].
Which of the following can act as coenzymes?
Vitamins act as coenzymes and activate the protein part of the enzyme.
Are vitamins considered coenzymes?
Coenzymes are organic compounds required by many enzymes for catalytic activity. They are often vitamins, or derivatives of vitamins.
Do B vitamins act as coenzymes?
In essence, the B-complex vitamins act as coenzymes in energy metabolism. The B complex of vitamins includes thiamin (vitamin B1), riboflavin (vitamin B2), niacin, vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), folate (folic acid), vitamin B12 (cobalamin), pantothenic acid, and biotin.
What are coenzymes give examples?
It is not active on its own. While enzymes are proteins, coenzymes are small, nonprotein molecules. Coenzymes hold an atom or group of atoms, allowing an enzyme to work. Examples of coenzymes include the B vitamins and S-adenosyl methionine.
Which of the following vitamins has a coenzyme form?
Nutrition FinaleQuestionAnswerWhich of the following vitamins has a coenzyme form?NiacinAn antioxidant is a substance that protects against oxidative damage.TrueAntioxidants act by enhancing the formation of free radicals.False152 more rows
Which of the following is not a coenzyme?
ATP or adenosine triphosphate is a nucleotide. It is not a co-enzyme.
What are the main coenzymes?
Two of the most important and widespread vitamin-derived coenzymes are nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and coenzyme A. NAD is derived from vitamin B3 and functions as one of the most important coenzymes in a cell when turned into its two alternate forms.
How many types of coenzymes are there?
Coenzymes are further divided into two types. The first is called a "prosthetic group", which consists of a coenzyme that is tightly (or even covalently) and permanently bound to a protein. The second type of coenzymes are called "cosubstrates", and are transiently bound to the protein.
What are the 3 different coenzymes?
Examples of coenzymes: nicotineamideadenine dinucleotide (NAD), nicotineamide adenine dinucelotide phosphate (NADP), and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). These three coenzymes are involved in oxidation or hydrogen transfer.
Does vitamin C function as a coenzyme?
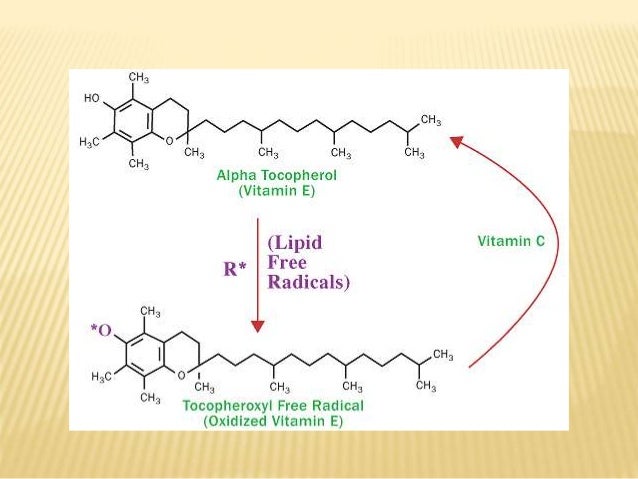
Vitamin C is used as a coenzyme in hydroxylation reactions, such as in the hydroxylation of prolyl and lysyl residues of collagen. It is required for the maintenance of normal connective tissue as well as for wound healing.
Which B vitamins are coenzymes?
In essence, the B-complex vitamins act as coenzymes in energy metabolism. The B complex of vitamins includes thiamin (vitamin Bl), riboflavin (vitamin B2), niacin, vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), folate (folic acid), vitamin B12 (cobalamin), pantothenic acid, and biotin.
Which of the following describes coenzymes?
So, the correct answer is 'An organic molecule that enhances enzyme activity' .
Which of the following best describes coenzymes?
Which statement best describes coenzymes? Coenzymes assist enzymes in accepting and donating molecules during reactions.
Which of the following is a coenzyme that is derived from ATP?
ATP has adenine and ribose in it's structure (see DNA). Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a redox coenzyme.
Which of the following are reduced coenzymes quizlet?
Reduced coenzymes include NADH, FADH2 and coenzyme Q. Most organisms carry out aerobic respiration, where oxygen is the final electron acceptor and water is the reduced form.
Vitamins That Function As Coenzymes | Healthfully
Biotin works as a coenzyme for other enzymes that catalyze various chemical reactions in metabolism. For instance, biotin works with the enzyme pyruvate carboxylase, which is essential to the Kreb’s cycle, a complex series of chemical reactions that provides cells with energy.
Vitamins and Coenzymes - Biology Encyclopedia - cells, body, function ...
Vitamins are chemical compounds that are vital to life and indispensable to body functions. They often exist as provitamins, inactive forms that must be converted into active vitamins before they can perform metabolic tasks in the body's cells.
Vitamins and Coenzymes - University of Texas at Dallas
Water - Soluble Vitamins. Vitamin B1 - thiamine ; Converted to thiamine pyrophosphate coenzyme ; Acts by nucleophilic attack on C = O ; Permits C - C bond cleavage and formation
Coenzyme: Definition, Function & Examples | Biology Dictionary
NAD is derived from vitamin B3 and functions as one of the most important coenzymes in a cell when turned into its two alternate forms. When NAD loses an electron, the low energy coenzyme called NAD + is formed. When NAD gains an electron, a high-energy coenzyme called NADH is formed.
What is the role of thiamin in the body?
Thiamin, or vitamin B1, functions as a coenzyme in the oxidation of glucose. Thiamin serves as a coenzyme for several enzymes that take part in metabolic reactions. Eat meats, leafy green vegetables, whole grains and legumes to benefit from thiamin.
What is the role of folic acid in DNA?
Folic acid works as a coenzyme in synthesizing several amino acids, purines and thymine, which are used in making DNA. A deficiency of folic acid results in anemia and growth failure. Folic acid is found in many foods, including dark green vegetables such as spinach, beef, eggs and whole grains. It is also synthesized by intestinal bacteria.
How does biotin work?
Biotin works as a coenzyme for other enzymes that catalyze various chemical reactions in metabolism. For instance, biotin works with the enzyme pyruvate carboxylase, which is essential to the Kreb’s cycle, a complex series of chemical reactions that provides cells with energy. Biotin occurs in legumes, egg yolks, nuts and liver. Intestinal bacteria also synthesize biotin.
What are the functions of the B complex?
Members of the vitamin B complex serve as coenzymes that assist every cell in the human body. They help the body metabolize carbohydrates, proteins and fats and build DNA for new cells. Without its coenzyme, an enzyme will not function. Vitamins work together in impressive ways as coenzymes or precursors to coenzymes. Precursors are substances that can be converted into active vitamins and coenzymes.
What is riboflavin in food?
Riboflavin occurs in many foods, including milk, grains and meats.
What is a coenzyme?
Coenzyme: A substance that enhances the action of an enzyme. Coenzymes are small molecules. They cannot by themselves catalyze a reaction but they can help enzymes to do so..
What are the cofactors and coenzymes?
The cofactors and coenzymes (organic cofactors) that help enzymes catalyze reactions.
What is the role of vitamins in catalysis?
Vitamins are potent organic (carbon- based) compounds that mainly function as coenzymes (or parts of coenzymes) that individually act in concert with each enzyme to accomplish a specific type of reaction catalysis process.
What is the name of the coenzyme that makes up the niacinamide?
The Nicotinamide is also know as nicotine acid amide and niacinamide. The occurrence of coenzymes is in vitamin form NAD+ (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP+ (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
What is thiamine a coenzyme?
Thiamine is also known as Thio-vitamine, Thaimin or Vitamin B1. This coenzyme involves in the catabolism of sugar and amino acids..
What is the name of the organic non-protein molecules that bind with the protein molecule to form the active enzyme?
In technical terms, coenzymes are organic non-protein molecules that bind with the protein molecule (apoenzyme) to form the active enzyme..
What is the other name for folic acid?
The folic acid is also know as folacin or vitamin B9. The other form of water soluble vitamin B9 is folate, pteroyl-l-glutamate and pteroyl-l-glutamic acid..
Water soluble vitamins
Water soluble vitamins can be directly absorbed from the intestine into the bloodstream.
Fat soluble vitamins
Fat soluble vitamins enter the body in the same manner as lipids and therefore a small amount of fat intake along with them is essential for their better absorption.
Recommended dietary allowance (RDA)
Recommended dietary allowance is the average day-to-day dietary intake level of a nutrient sufficient to meet the needs of almost any healthy person based on age and gender.
Adequate intake (AI)
Adequate intake is a recommended intake value based on observed or experimentally determined estimates of nutrient intake by a group of healthy people that are assumed to be sufficient.
Tolerable upper intake level (UL)
Tolerable upper intake level is the highest level of daily intake of a specific nutrient which probably does not pose a risk of adverse health effects in almost all individuals of a specified age and gender.
What are the functions of fat soluble vitamins?
Fat-soluble vitamins – vitamins A, D, E, and K – act more like hormones and perform several roles in your body. They directly contribute to these metabolic processes. For example, vitamin K helps to prevent excess blood clotting. Vitamin E protects cells against damage from free radicals, also known as oxidants.
How do vitamins help enzymes?
An enzyme is a lot like a key. It has a specific shape and purpose. Like a key opening a lock on a door , an enzyme at its active site unlocks a chemical reaction that breaks down or binds molecules. The active site is where the enzyme connects with the molecule that it will act on, called a substrate.
Why is vitamin C a B vitamin?
There is a good reason vitamin C is grouped with B vitamins. All of these vitamins all rely on water to be absorbed by your body.
Why do enzymes need helpers?
Some enzymes need helpers to make the biochemical reactions possible. These coenzymes supply chemical components required by the enzyme to drive the reaction.
What are water soluble vitamins?
Water-soluble vitamins are typically the coenzymes. Your water-soluble vitamins are vitamin C and your B complex vitamins, which include: Each of the B vitamins acts as a coenzyme. For example, vitamin B6 becomes pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) and is needed for the many numerous PLP- dependent enzymatic reactions.
What do coenzymes do in redox reactions?
Here’s what coenzymes do: For redox reactions (where they break down a substance), they either transfer electrons to the substrate or take electrons away. They add small molecular groups to the substrate called functional groups. These molecular groups are needed for the reaction to produce new substances.
Why are enzymes plentiful?
Those enzymes are plentiful because you ate it fresh from the ground.
What are the water soluble vitamins?
The water-soluble vitamins include vitamin C and the group of eight vitamins known collectively as Vitamin B. They are not readily stored and are excreted in urine when consumed in excess of the body's needs. Vitamin C 's roles include assisting in the production and maintenance of collagen, a protein found in bones, skin, teeth, and tendons. Vitamin C also plays roles in supporting the immune system and producing thyroxine, the hormone that regulates body temperature and metabolism .
What are the functions of vitamin A?
The three active forms of Vitamin A are required for night and color vision, reproduction, and cell maturation and differentiation , the process by which precursor cells develop into a specific cell type. Vitamin A also plays a role in fighting infections and in the development and maintenance of bone. Beta-carotene and other provitamin forms of vitamin A known as carotenoids are antioxidants , chemicals that block the harmful cancercausing effects of oxidizing agents (oxygenlike molecules) on cells. This antioxidant property may also play a role in vitamin A's prevention of heart disease.
What is the role of vitamin D in the body?
Vitamin D plays a role in the differentiation of cells in the intestines, skin, immune system, and bones. It also regulates blood calcium levels, which are important in maintaining proper bone density.
How many vitamins are there in the human body?
There are thirteen individual vitamins required by the human body for growth and maintenance of good health.
Where are vitamins stored?
Once absorbed, they can be stored indefinitely in the liver and fatty tissues of the body. This capacity for storage can lead to unwanted toxic buildup of certain vitamins, A, D, and K in particular, that can cause great harm. Deficiencies of any vitamin can also be harmful. The National Academy of Sciences publishes recommended intake values for all thirteen vitamins.
What is vitamin K?
Vitamin K is involved in synthesizing proteins that help blood clot. It is also necessary for making a key protein important in bone formation. In addition to dietary sources of vitamin K, the body can use vitamin K manufactured by bacteria that live in the intestines.
