
In flatworms
Trematoda
Trematoda is a clade within the phylum Platyhelminthes. It includes two groups of parasitic flatworms, known as flukes. They are internal parasites of molluscs and vertebrates. Most trematodes have a complex life cycle with at least two hosts. The primary host, where the fluk…
What is the digestive tract called in flatworms?
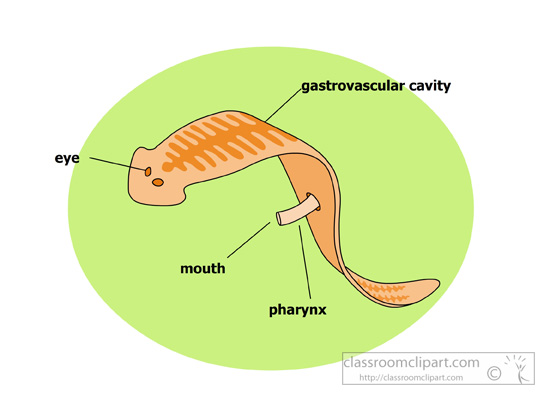
Their digestive tracts are labeled “Gastrovascular cavity” and “Intestines.” Strictly speaking, these digestive tracts can’t be called systems because they aren’t composed of multiple organs. Flatworms are usually said to be at a level of complexity below the organ system grade.
What is the difference between segmented worms and flatworms?
Flatworms have incomplete digestive system (one opening i.e. mouth),where as segmented worms have complete digestive tract (one mouth and one anus,two openings). Microbiologist, outdoorsman, bridge player.
What is the habitat of a flatworm?
Free-living flatworms are mostly predators, and live in water or in shaded, humid terrestrial environments, such as leaf litter. Cestodes (tapeworms) and trematodes (flukes) have complex life-cycles, with mature stages that live as parasites in the digestive systems of fish or land vertebrates, and intermediate stages that infest secondary hosts.
What is the scientific name for a flat worm?
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths (from the Greek πλατύ, platy, meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), helminth-, meaning "worm") [4] are a phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates.

Do flatworms have simple organ systems?
Flatworms have a mesoderm cell layer and simple organ systems. They also show cephalization and bilateral symmetry. Many flatworms are parasites with vertebrate hosts.
Which organ system is absent in flatworms?
Flatworms lack a respiratory or circulatory system; these functions take place by absorption through the body wall. Nonparasitic forms have a simple, incomplete gut; even this is lacking in many parasitic species. Movement in some flatworms is controlled by longitudinal, circular, and oblique layers of muscle.
What sense organs do flatworms have?
Flatworms have prominent eyespots. These constitute the flatworm's most prominent sensory organs. However, while the eyespots resemble eyes, the organs are much more simple. Eyespots consist of a single layer of photosensitive cells.
Does a flatworm have a circulatory system?
Flatworms have no circulatory system. Animals without a circulatory system have limited abilities to deliver oxygen and nutrients to their body cells because of the way that molecules behave.
Does a flatworm have a digestive system?
Most other flatworms, however, have conspicuous digestive systems. The digestive system of turbellarians typically consists of mouth, pharynx, and intestine. In the order Acoela, however, only a mouth is present; food passes directly from the mouth into the parenchyma, to be absorbed by the mesenchymal cells.
Do flatworms have internal organs?
Unlike most triploblastic animals, they have no body cavity and no blood system. The gut, if present, has a single opening to the exterior. As in other bilateral animals, there is an anterior brain and associated sense organs. Flatworms have elaborate hermaphroditic reproductive systems.
Why dont flatworms have a circulatory system?
Flatworms breathe through their moist body surface (skin) and diffusion of oxygen takes place directly. By this diffusion process, each cell can meet its oxygen requirements thus there is no need for the circulatory system to circulate oxygen and nutrients.
What type of circulatory system do flatworms have?
Flatworms do not have a circulatory system in the usual sense. There are no veins, lymph nodes, or arteries. Instead, because they are fairly small in size and are so flat, flatworms are able to breathe through their 'skin,' which is really just integument, a moist outer covering.
Does a flatworm have a brain?
The planarian is the simplest living animal having a body plan of bilateral symmetry and cephalization. The brain of these free-living flatworms is a bilobed structure with a cortex of nerve cells and a core of nerve fibres including some that decussate to form commissures.
What do all flatworms have?
Flatworms have no true body cavity, but they do have bilateral symmetry. Most flatworms have a distinct head region that includes nerve cells and sensory organs. The development of a head region, called cephalization, evolved at the same time as bilateral symmetry in animals.
What are 3 characteristics of flatworms?
Platyhelminthes have the following important characteristics: They are triploblastic, acoelomate, and bilaterally symmetrical. They may be free-living or parasites. The body has a soft covering with or without cilia.
Do flatworms have a nervous system?
The bilaterally flattened body of flatworms preserves a common organization of the central nervous system (CNS). The CNS of flatworms consists of: (i) the orthogon, composed of main longitudinal nerve cords and transverse commissures that form a ladder-like network.
How many hearts does a flatworm have?
five pairsThe Difference Between Flatworms and Roundworms While earthworms may seem simple because they lack many visible external organs, they have complex inner organs including five pairs of heart-like structures called aortic arches, which they use to pump oxygenated blood to the rest of their bodies.
How can flatworms survive without a respiratory system?
Structure and Function of Flatworms They have a flat body because they do not have a coelom or even a pseudocoelom. They also lack a respiratory system. Instead, their cells exchange gases by diffusion directly with the environment.
Do flatworms have excretory organs?
Flatworms have an excretory system with a network of tubules throughout the body that open to the environment and nearby flame cells, whose cilia beat to direct waste fluids concentrated in the tubules out of the body.
What is the flatworm excretory organ called?
Rennate glands- It is a secretory-excretory organ present in the nematodes. Note: Platyhelminthes are the simplest animals having a dedicated excretory system. The flame cells function as a kidney for removing waste materials. The bundles of flame cells are called protonephridia.
What is the excretory organ of a flatworm?
flame cells(2) Flatworms have an excretory system that consists of two tubules. The cells in the tubules are called flame cells; they have a cluster of cilia that propel waste matter down the tubules and out of the body.
Which worm lacks a digestive system?
Flatworms are worm species that do not have a complete digestive tract with only one opening in the mouth and do not contain the anus structure.
How do flatworms digest?
They have simple digestive systems, with mouths to take in food and long digestive tracts to diffuse it around the body. Most flatworms take in food via their mouth, then move it into a digestive gut that attaches to the digestive structures. The food then breaks down and is absorbed out into the rest of the organism.
What are the defining features of flatworms?
What are the defining features of a flatworm? Flatworms are soft, flattened worms that have tissues and internal organ systems. They are the simplest animals to have three embryonic germ layers, bilateral symmetry, and cephlization.
What is not found in flatworms?
Flatworms have no true body cavity and no blood vessels. Flatworms can be free-living or parasitic.
Which of the following is absent in Platyhelminthes?
In Platyhelminthes, endoderm, ectoderm and mesoderm are present. However, the mesoderm is present patched between the endoderm and the ectoderm, and it does not line the gut. Q.
Do flatworms have a nervous system?
The bilaterally flattened body of flatworms preserves a common organization of the central nervous system (CNS). The CNS of flatworms consists of: (i) the orthogon, composed of main longitudinal nerve cords and transverse commissures that form a ladder-like network.
Which of the following group of system are absent in Platyhelminthes?
The animals in which the body cavity is absent are called acoelomates, e.g., platyhelminthes (Figure 4.3c).
What type of digestive system does a flatworm have?
Like the cnidarians, flatworms have a digestive system with only a single opening into the digestive cavity, but in independently living marine flatworms the cavity branches into all parts of the body (Fig. 3.37 B). These flatworms feed through a pharynx.
Do flatworms have no digestive system?
Flatworms are acoelomate, triploblastic animals. They lack circulatory and respiratory systems, and have a rudimentary excretory system. This digestive system is incomplete in most species.
What is flatworm lacks a digestive tract?
One parasitic group, the tapeworms (cestodes), lacks a digestive system altogether , and absorb digested food from the host. Flatworms have an excretory system with a network of tubules attached to flame cells, whose cilia beat to direct waste fluids concentrated in the tubules out of the body through excretory pores.
Do flatworms have tissues and organs?
Flatworms are generally hermaphroditic-functional reproductive organs of both sexes occurring in one individual. Like other advanced multicellular animals, they possess three embryonic layers-endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm-and have a head region that contains concentrated sense organs and nervous tissue (brain).
Why can't flatworms be called systems?
Strictly speaking, these digestive tracts can’t be called systems because they aren’t composed of multiple organs. Flatworms are usually said to be at a level of complexity below the organ system grade. Most textbooks say organ level, but I could make an argument for organ system level.
Which organs are not part of the digestive system?
While not part of the digestive system, the liver, gall bladder and pancreas help digestion to take place, so they form a kind of “peripheral” digestive system.
Where does the digestive process occur?
The small intestine is where the main part of digestion occurs and where absorption of nutrients happens. Most of the digestion happens in the beginning of the small intestine, called the duodenum. Different enzymes work to aid digestion as the food travels along. Each enzyme works to break down a respective macronutrient—fat, protein or carbohydrates. Each of those nutrients is metabolized differently during the digestive process.
How long is the small intestine?
The small intestine is over 20 feet long. The interior of the small intestine is covered with a special lining of fingerlike projections called villi. These increase the body’s ability to absorb nutrients. Fatty acids are absorbed directly into the bloodstream or the lymphatic system.
Do flatworms have digestive tracts?
Your assumption is wrong. Most turbellarians, digeneans, and monogeneans have digestive tracts. Almost the only flatworms that don’t are tapeworms. They don’t need one because the adults live in the host small intestine surrounded by food that’s already digested. They absorb the nutrients through their body surface.
Do tapeworms digest food?
Digesting food takes a lot of work but tapeworms have evolved an ingenious way to avoid doing it -- they let their hosts digest food for them. On the outside of their bodies, tapeworms have a skin-like covering tough enough to withstand being dissolved by digestive juices, yet porous enough to allow tiny bits of food to pass through. Even though they lack digestive systems as we know them, with mouths, stomachs and intestines, tapeworms have a primitive gut extending throughout their bodies. When muscles
Can worms eat apples?
They eat mostly dirt and also the whole thing about the worm in your Apple is not true it's virtually impossible for an earthworm to bury itself into a fresh Apple or to eat its way out they couldn't do it if they wanted to because they do not have teeth or anything that making used to chew or dismember food in any way earthworms have to eat soft mushy food Susanna roof worm did eat an apple they would have to wait until the apple is decomposed to the point that it doesn't even look like an apple even if the worm did somehow get access inside a fresh Apple EG if you poke a hole into the Apple
Overview
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths (from the Greek πλατύ, platy, meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), helminth-, meaning "worm") are a phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates. Unlike other bilaterians, they are acoelomates (having no body cavity), and have no specialized circulatory and respiratory organs, which restric…
Description
Platyhelminthes are bilaterally symmetrical animals: their left and right sides are mirror images of each other; this also implies they have distinct top and bottom surfaces and distinct head and tail ends. Like other bilaterians, they have three main cell layers (endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm), while the radially symmetrical cnidarians and ctenophores (comb jellies) have only two cell layers…
Major subgroups
Early classification divided the flatworms in four groups: Turbellaria, Trematoda, Monogenea and Cestoda. This classification had long been recognized to be artificial, and in 1985, Ehlers proposed a phylogenetically more correct classification, where the massively polyphyletic "Turbellaria" was split into a dozen orders, and Trematoda, Monogenea and Cestoda were joined in the ne…
Classification and evolutionary relationships
The relationships of Platyhelminthes to other Bilateria are shown in the phylogenetic tree:
The internal relationships of Platyhelminthes are shown below. The tree is not fully resolved.
The oldest confidently identified parasitic flatworm fossils are cestode eggs found in a Permian shark coprolite, but helminth hooks still attached to Devonian acanthodians and placoderms might also represent parasitic flatworms with simple life cycles. The oldest known free-living platyhel…
Evolution
An outline of the origins of the parasitic life style has been proposed; epithelial feeding monopisthocotyleans on fish hosts are basal in the Neodermata and were the first shift to parasitism from free living ancestors. The next evolutionary step was a dietary change from epithelium to blood. The last common ancestor of Digenea + Cestoda was monogenean and most likely sanguinivorous.
Interaction with humans
Cestodes (tapeworms) and digeneans (flukes) cause diseases in humans and their livestock, whilst monogeneans can cause serious losses of stocks in fish farms. Schistosomiasis, also known as bilharzia or snail fever, is the second-most devastating parasitic disease in tropical countries, behind malaria. The Carter Center estimated 200 million people in 74 countries are infected with the disease, and half the victims live in Africa. The condition has a low mortality rate, but usually …
See also
• Miracidium
• Regenerative medicine
• Schistosoma
Further reading
• Campbell, Neil A. (1996). Biology (Fourth ed.). New York: Benjamin/Cummings Publishing. p. 599. ISBN 0-8053-1957-3.
• Crawley, John L.; van de Graff, Kent M., eds. (2002). A Photographic Atlas for the Zoology Laboratory (Fourth ed.). Colorado: Morton Publishing Company. ISBN 0-89582-613-5.
• The Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia (6th ed.). Columbia University Press. 2004. Retrieved 8 February 2005.