
Common Causes
A gallstone that becomes lodged in the neck of the gallbladder can cause inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis). Cholecystitis can cause severe pain and fever. Blockage of the common bile duct. Gallstones can block the tubes (ducts) through which bile flows from your gallbladder or liver to your small intestine.
Related Conditions
If gallstones block your bile ducts, bile could build up in your gallbladder, causing a gallbladder attack, sometimes called biliary colic. Gallbladder attacks usually cause pain in your upper right abdomen, sometimes lasting several hours.
Can gallstones cause inflammation of the gallbladder?
Gallstones may cause no signs or symptoms. If a gallstone lodges in a duct and causes a blockage, the resulting signs and symptoms may include: Sudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the center of your abdomen, just below your breastbone Gallstone pain may last several minutes to a few hours.
What happens if gallstones block the bile ducts?
Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that can form in your gallbladder. Your gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of your abdomen, just beneath your liver. The gallbladder holds a digestive fluid called bile that's released into your small intestine.
What are the signs and symptoms of gallstones?
What are gallstones and how do they form?

What causes gallstones?
Gallstones also may form if the gallbladder does not empty completely or often enough. Certain people are more likely to have gallstones than others because of their risk factors for gallstones, including obesity and certain kinds of dieting.
Why are some people more likely to have gallstones than others?
Certain people are more likely to have gallstones than others because of their risk factors for gallstones, including obesity and certain kinds of dieting.
Can gallstones cause bile duct blockage?
Gallstone complications can occur if your bile ducts stay blocked.
Can gallbladder attacks stop?
If you’ve had one gallbladder attack, more attacks will likely follow. Gallbladder attacks usually stop when gallstones move and no longer block the bile ducts. However, if any of your bile ducts stay blocked for more than a few hours, you may develop gallstone complications.
Can gallstones cause colic?
If gallstones block your bile ducts, bile could build up in your gallbladder, causing a gallbladder attack, sometimes called biliary colic. Gallbladder attacks usually cause pain in your upper right abdomen, sometimes lasting several hours. Gallbladder attacks often follow heavy meals and usually occur in the evening or during the night. If you’ve had one gallbladder attack, more attacks will likely follow.
What are the symptoms of gallstones?
Seek immediate care if you develop signs and symptoms of a serious gallstone complication, such as: Abdominal pain so intense that you can't sit still or find a comfortable position. Yellowing of your skin and the whites of your eyes (jaundice) High fever with chills.
How to prevent gallstones?
Include more fiber-rich foods in your diet, such as fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity and being overweight increase the risk of gallstones.
What causes pain in the pancreas?
Pancreatic juices, which aid in digestion, flow through the pancreatic duct. A gallstone can cause a blockage in the pancreatic duct, which can lead to inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis). Pancreatitis causes intense, constant abdominal pain and usually requires hospitalization. Gallbladder cancer.
What is the fluid in the gallbladder called?
The gallbladder holds a digestive fluid called bile that's released into your small intestine. Gallstones range in size from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. Some people develop just one gallstone, while others develop many gallstones at the same time.
What is the name of the fluid that is produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder?
Gallstones. Gallstones are hardened deposits of bile that can form in your gallbladder. Bile is a digestive fluid produced in your liver and stored in your gallbladder. When you eat, your gallbladder contracts and empties bile into your small intestine (duodenum).
Why is bile so high in bilirubin?
Bilirubin is a chemical that's produced when your body breaks down red blood cells. Certain conditions cause your liver to make too much bilirubin, including liver cirrhosis, biliary tract infections and certain blood disorders. The excess bilirubin contributes to gallstone formation.
What are the different types of gallstones?
Types of gallstones. Types of gallstones that can form in the gallbladder include: Cholesterol gallstones. The most common type of gallstone, called a cholesterol gallstone, often appears yellow in color. These gallstones are composed mainly of undissolved cholesterol, but may contain other components.
What is a gallstone?
Gallstones are stone-like objects that develop in the gallbladder or bile ducts ( the pipe-like system within the liver). Gallstones can range dramatically in size, from tiny grains of sand to golf ball-sized objects. Interestingly, small stones can often cause the most trouble. These are stones that can leave the gallbladder and get stuck.
Where are gallstones found?
Gallstones are most commonly found in the gallbladder, as cholesterol stones. Gallstones can also travel from the gallbladder to the common bile duct, which is the largest of the ducts (pipes) in the liver. Common bile duct stones are much less common than gallstones.
How does the gallbladder work?
The gallbladder is connected to other parts of the digestive system through a series of ducts, or tunnels. These ducts help to carry bile and aid in the entire process of breaking down food. Ultimately, the bile finds its way into the common bile duct, where it passes through a special sphincter (a valve made of muscle), into the small intestine. Once there, the bile can mix directly with food that’s waiting to be digested. The common bile duct then empties bile into the duodenum, the first portion of the very lengthy small intestine.
What is the purpose of gallstones?
Gallstones. The gallbladder stores and releases bile to help digest fats. Gallstones, stone-like objects often made of cholesterol or bilirubin, can develop in the gallbladder or bile ducts. These stones can cause pain and other complications. Treatment options often involve minimally invasive surgery to remove the gallstones, ...
What is the gallbladder?
The gallbladder is a small organ tucked up under the liver, on the right side of your body. It is shaped like a swollen pea pod. The gallbladder’s job is to store and dispense bile—a fluid that helps digest fats in the food you eat. Similarly to a pea pod, the gallbladder is green.
Where is the gallbladder attack?
Upper part of the abdomen, on the right side. Between the shoulder blades. Under the right shoulder. When people experience pain with gallstones, it is sometimes referred to as a gallbladder attack or biliary colic.There are two special conditions that could mimic gallstone symptoms.
How long does gallstone pain last?
Pain is the main symptom most people experience with gallstones. This pain is steady and can last from around 15 minutes to several hours. The episodes, which can be severe, generally subside after one to three hours or so.
What foods cause steatorrhea?
Common foods and drink known to cause steatorrhea include: nuts, especially whole nuts with the skin or shell intact. oily, high-fat fish, such as escolar or oilfish which can be mislabelled butterfish or fatty tuna. excessive alcohol. artificial fats. naturopathic or essential oils. coconut and palm kernel oil.
What are the symptoms of steatorrhea?
Symptoms. Symptoms of mild steatorrhea may include foul-smelling stool, a stool that floats, and a stool that is difficult to flush away. Steatorrhea is when a person has a loose but bulky stool with globs of fat and noticeable oil separation. Mild or short-term cases of steatorrhea may cause some limited discomfort.
How much fat does steatorrhea excrete?
Steatorrhea is typically defined as excreting more than 7 g of fat in a 24-hour period when consuming 100 g of fat daily.
What is fatty stool?
Steatorrhea, or fatty stool, occurs when there is too much fat in the stool. Stool or feces contain a mixture of undigested nutrients. These include proteins, fibers, and salts. Stool also typically contains mucous, dead cells, or any other waste the body is able to excrete. In this article, learn about what causes fatty stool and how it is treated.
How to treat steatorrhea?
Home remedies to treat steatorrhea may include reducing dietary fat, quitting smoking, and staying hydrated. The treatment for steatorrhea depends on the cause and severity of symptoms. Mild cases of steatorrhea can often be successfully treated at home with rest and basic care.
What causes a light brown stool?
stool that appears to be covered in a thick, greasy film. abdominal pain, cramping, bloating, and gassiness. Malnutrition and dehydration may be caused by severe or chronic cases of steatorrhea.
Does steatorrhea need medical intervention?
Severe or chronic cases of steatorrhea will normally need medical intervention. People with steatorrhea because of an underlying medical condition will also usually need medical treatment.
What are the symptoms of steatorrhea?
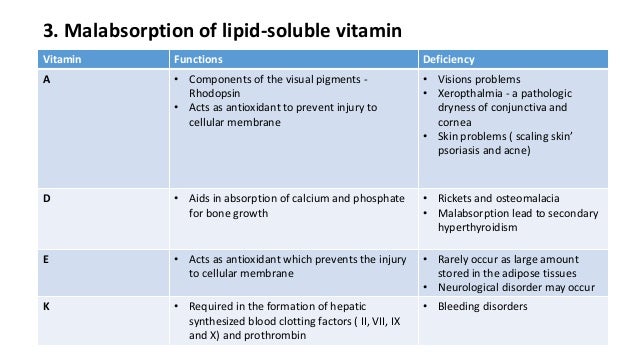
Patients with steatorrhea present with bulky, pale, foul-smelling oily stools. These fatty stools tend to float in the toilet bowl and often challenging to flush as well. In the early stages, steatorrhea may be asymptomatic and go unnoticed. Patients also have other nonspecific manifestations of fat malabsorption such as chronic diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, bloating sensation, and weight loss. Children may present with growth failure and delayed puberty. In severe cases, loss of subcutaneous fat and muscle wasting may be evident. Manifestations of fat-soluble vitamin (A, D, E, and K) deficiencies can accompany fat malabsorption. Celiac patients can present with a variety of extraintestinal signs such as anemia, oral ulcers, and dermatitis herpetiformis rash. Abdominal pain is a predominant symptom in patients with chronic pancreatitis but also reported in other conditions such as SIBO, inflammatory bowel disease, and celiac disease. CF patients have sinopulmonary manifestations. Jaundice, fatigue, and pruritis are suggestive of cholestatic liver diseases such as PBC or PSC. Signs for end-stage liver disease such as splenomegaly, ascites can be noted in PBC or PSC.
What is the management of steatorrhea?
The management of steatorrhea is complex and new approaches have been introduced. To achieve satisfactory outcomes, the basic and clinical aspects of steatorrhea must be clearly defined. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of steatorrhea and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating and improving care for patients suffering from steatorrhea.
What causes EPI in the pancreas?
EPI due to chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis (CF), and conditions resulting in pancreatic duct obstruction or resection of the pancreas (e.g., pancreatic tumors)
What is cholestatic liver disease?
Cholestatic Diseases: The mechanisms underlying the development of chronic cholestatic liver diseases , including PBC and PSC, are not entirely understood. Both these disorders are characterized by portal inflammation and progressive fibrosis and eventually resulting in end-stage liver disease. Here, the reduction in bile flow results in the accumulation of toxic bile products, which leads to biliary epithelial damage.[21] This decrease in bile reaching the small bowel interferes with fat absorption and causes steatorrhea in these patients.
Is steatorrhea underreported?
Therefore, the exact prevalence and incidence of steatorrhea are challenging to estimate and often go underreported. Also, the epidemiology of steatorrhea depends on the epidemiology of various underlying causes, which is a topic of the discussion below.
Is celiac disease on the rise?
The prevalence of celiac disease is on the rise, and a recent study reported a global seroprevalence of 1.4%.[14] Also, there are differences in the prevalence depending on geographical location. Reports of a biopsy-proven celiac disease show lower prevalence rates in South America and Africa and higher rates in Europe and Oceania.[14] For example, in Europe, Germany has a lower prevalence of celiac disease, and the highest prevalence was in Sweden and Finland.[14] Celiac disease has a higher prevalence in certain high-risk groups such as type 1 diabetes mellitus, Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, IgA deficiency, William syndrome, and in first-degree relatives of celiac disease. [8][15]
How do you know if you have gallstones?
Eighty percent of people with gallstones do not have any symptoms and do not need treatment. When gallstones do cause symptoms, they include: 1 abdominal pain, usually high in the abdomen and often on the right side (where the gallbladder is located). The pain can spread to the back. Pain from gallstones can be steady or come and go. It can last between 15 minutes and several hours each time it occurs. 2 sensitivity to high fat meals. Fats trigger the gallbladder to contract and can worsen pain. 3 unexplained belching, gas, nausea, or a general decrease in appetite.
How many women have gallstones?
About 1 in 5 women and 1 in 10 men have a gallstone by age 60. They are more likely to happen to older people, those who are overweight, and those who suddenly lose weight. Women who have had multiple pregnancies, taken birth control pills, or took estrogen after menopause are also more likely to develop gallstones.
Why does my gallbladder hurt after eating?
It can be very painful if the gallbladder squeezes against a gallstone, or if a gallstone blocks bile from being released into the intestines.
How long does it take for gallstones to go away?
Even when gallstone symptoms go away on their own, they return within two years in about two of three people. Most people whose gallstones cause symptoms will continue to have symptoms until the gallbladder is removed, although medications or procedures to break up the stones may also be used.
How long does gallstone pain last?
Pain from gallstones can be steady or come and go. It can last between 15 minutes and several hours each time it occurs. sensitivity to high fat meals. Fats trigger the gallbladder to contract and can worsen pain. unexplained belching, gas, nausea, or a general decrease in appetite.
What does an ultrasound show if a stone is blocking the movement of bile?
If a stone is blocking the movement of bile, an ultrasound might show widened bile ducts. Your doctor may also order blood tests to evaluate injury to the liver and pancreas.
What is the purpose of bile?
Bile makes it easier for you to digest fat. It also contains some waste products, including cholesterol and bilirubin, a substance created when old red blood cells are destroyed.
What causes steatorrhea and steatorrhea?
One of the most common causes of malabsorption is cystic fibrosis. This is an inherited condition that affects your sweat and mucous glands, as well as various organs in your body. Another cause of malabsorption that can lead to steatorrhea is chronic pancreatitis.
What causes steatorrhea in the small intestine?
Another cause of malabsorption that can lead to steatorrhea is chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatitis is an inflammation of your pancreas, an organ near your stomach. It releases enzymes to help you digest fat, protein, and carbohydrates in your small intestine.
Why is it important to treat steatorrhea?
Treating steatorrhea is really about treating the underlying cause or causes of this condition. And because malabsorption can have many causes, it will be important to get a reliable diagnosis.
What happens when your digestive system gets rid of too many fats instead of absorbing them?
With EPI, steatorrhea happens when your digestive system gets rid of too many fats instead of absorbing them. This usually occurs when fat-digesting enzymes in your pancreas drop to 5 to 10 percent of typical levels.
Why do my stools float?
They tend to float because they have a higher gas content. The stools also tend to be covered in a greasy film. You might even see drops of oil in the water inside the toilet bowl. Steatorrhea is only one of several common symptoms of malabsorption. Others include:
What does it mean when you have too much fat in your feces?
Too much fat in your feces is called steatorrhea. It can be a sign of malabsorption. This means your body either isn’t absorbing nutrients properly or isn’t making the enzymes or bile needed to digest food effectively. If you’re experiencing steatorrhea, make an appointment to talk with your doctor.
What causes pancreatitis?
Chronic pancreatitis can have many different causes. Some examples include alcohol use disorder, smoking, and family history.
Overview
Presence of excess fat in feces.
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
- Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that can form in your gallbladder. Your gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of your abdomen, just beneath your liver. The gallbladder holds a digestive fluid called bile that's released into your small intestine. Gallstones range in size from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. Some people …
Complications
- Gallstones may cause no signs or symptoms. If a gallstone lodges in a duct and causes a blockage, the resulting signs and symptoms may include: 1. Sudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the upper right portion of your abdomen 2. Sudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the center of your abdomen, just below your breastbone 3. Back pain between your shoulder blades 4. Pain in …
Prevention
- It's not clear what causes gallstones to form. Doctors think gallstones may result when: 1. Your bile contains too much cholesterol.Normally, your bile contains enough chemicals to dissolve the cholesterol excreted by your liver. But if your liver excretes more cholesterol than your bile can dissolve, the excess cholesterol may form into crystals and eventually into stones. 2. Your bile c…