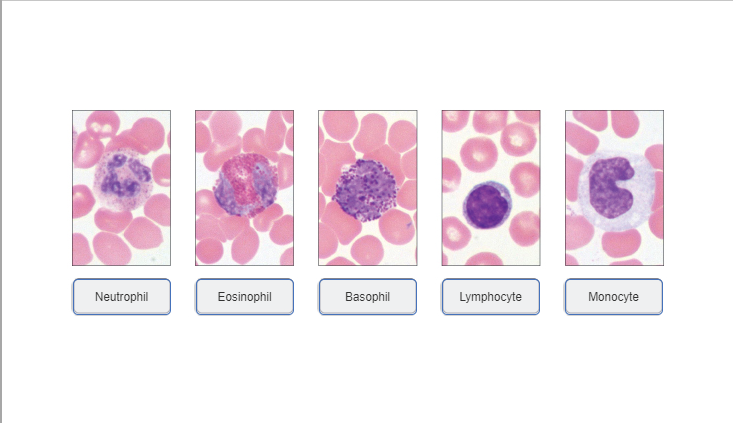
An elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is considered a prognostic indicator for patients with cancer. Neutrophils are no longer regarded as innate immune cells with a single function, let alone bystanders in the pathological process of cancer. Their diversity and plasticity are being increasingly recognized.
Can high neutrophils indicate cancer?
No, high neutrophils are not a reliable indicator of cancer. Diagnosing cancer requires a combination of blood tests, imaging, and tests on organ tissue . Was this page helpful?
What would cause low lymphocytes and high neutrophils?
Low lymphocytes may be caused by chemotherapy, leukemia, radiation therapy or sepsis, and high neutrophils may be caused by stress, infection, gout or rheumatoid arthritis, according to MedlinePlus. Both lymphocytes and neutrophils are types of white blood cells and are collected in a blood differential test.
What do neutrophils tell us about cancer treatment?
Tumor-associated neutrophils promote tumor angiogenesis by the release of both conventional and non-conventional pro-angiogenic factors. Therefore, neutrophil-mediated tumor angiogenesis should be taken into consideration in the design of novel anti-cancer therapy.
What would cause elevated neutrophils?
The most common cause of an increased number of neutrophils is In many instances, the increased number of neutrophils is a necessary reaction by the body, as it tries to heal or ward off an invading microorganism or foreign substance. Infections by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites may all increase the number of neutrophils in the blood.
What cancers are associated with high neutrophils?
Neutrophils can also influence the migration potential of cancer cells. In several types of cancer it has been shown that neutrophils promote metastasis. These tumors include skin squamous cell carcinoma [135], melanoma [136], adenocarcinomas [137], HNSCC [83], and breast cancer [138].
When should I be concerned about high neutrophils?
A normal (absolute) neutrophil count is between 2500 and 6000 neutrophils per microliter of blood. 2 A high neutrophil count may be due to infections, a leukemia cancer, or physical or emotional stress.
What diseases cause high neutrophils?
What causes neutrophilia?Chronic myelogenous leukemia. This blood cancer affects your white blood cells.Essential thrombocytosis (ET). This is a rare disorder where your body produces too many platelets.Polycythemia vera. ... Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML). ... Chronic neutrophilic leukemia.
Why would a neutrophil count be high?
A high neutrophil count may be due to many physiological conditions and diseases. In most cases, a high neutrophil count is commonly associated with an active bacterial infection in the body. In rare cases, the high neutrophil count may also result from blood cancer or leukemia.
What is the treatment for high neutrophils?
If you have chronic conditions that disrupt your neutrophil production, you may need to take drugs that allow the body to increase neutrophil production, such as : colony-stimulating factors. corticosteroids. bone marrow or stem cell transplantation.
Can anxiety cause high neutrophils?
In any acute inflammation, an increase in neutrophils is often seen. Increases may be seen after a heart attack (or other infarct) and necrosis. Heavy exercise, smoking, anxiety, and other stressors can elevate the neutrophil count. 7.
How high are neutrophils in leukemia?
hemoglobin count lower than normal range but not lower than 7. no blasts present. platelet count over 100,000, but less than the normal range of 150,000. neutrophil count over 1,000.
Can stress affect neutrophils?
Psychological stress or life events might significantly decrease neutrophil function in elderly individuals and lead to infectious diseases.
What causes high white blood cell count and high neutrophils?
Leukocytosis is most commonly caused by infection or inflammation. Other high white blood cell count causes may include: Excessive physical or emotional stress (such as fever, injury or surgery).
Does Covid cause high neutrophils?
Conclusion. The clinical syndrome of severe COVID-19 has several unique features, including, unusually for a viral infection, an increased neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio.
What is a normal range for neutrophils?
The most important infection-fighting WBC is the neutrophil . The number doctors look at is called your absolute neutrophil count (ANC). A healthy person has an ANC between 2,500 and 6,000.
What happens if neutrophils count is high?
Neutrophilia: Neutrophilia, also known as neutrophilic leukocytosis, occurs when your neutrophil count is too high, which is often the result of a bacterial infection. To combat the infection, immature neutrophils leave your bone marrow too soon and enter into your bloodstream.
How high are neutrophils in leukemia?
hemoglobin count lower than normal range but not lower than 7. no blasts present. platelet count over 100,000, but less than the normal range of 150,000. neutrophil count over 1,000.
Is neutrophils 60% high?
Normal Results. The different types of white blood cells are given as a percentage: Neutrophils: 40% to 60%
What causes high white blood cell count and high neutrophils?
Infections by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites may all increase the number of neutrophils in the blood. , can cause an increase in the number and activity of neutrophils. Some drugs, such as corticosteroids, also lead to an increased number of neutrophils in the blood.
Why is my neutrophil count high?
A high neutrophil count may be due to many physiological conditions and diseases. In most cases, high neutrophils count is commonly associated with an active bacterial infection in the body. In rare cases, the high neutrophil count may also result from blood cancer or leukemia.
What are neutrophils?
Neutrophils comprise most of the white blood cells. They make up about 56% of the total white blood cells. Neutrophils are the soldiers that fight infections. They recognize the foreign proteins over an infectious particle and cover up the particle. They may either eat the infectious particle or release chemicals that kill the particle.
Why do neutrophils get in the blood?
An increased concentration of cortisol and adrenaline hormones and the ingestion of some drugs, such as prednisone, can cause more neutrophils to enter the bloodstream. Neutrophilia may be observed because of malignancy, such as leukemia.
What causes a decrease in neutrophils?
Autoimmune diseases, such as Crohn’s disease, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis, cause a decrease in the count of neutrophils as well. Neutrophilia and neutropenia need a meticulous clinical examination followed by relevant investigations so that appropriate treatment can be instituted.
How long do neutrophils live?
They migrate into the tissues, where they have a life span of only a few days after which the spleen destroys them. Neutrophils have a short lifespan.
What causes neutrophilia?
True neutrophilia: True neutrophilia is usually related to bacterial infections. Abscess, boils, pneumonia, cough, and fevers can cause neutrophilia by stimulating the bone marrow.
Where are neutrophils produced?
New neutrophils are then produced continuously in the bone marrow. The number of neutrophils in the blood might differ with each individual because it is affected by various factors, such as age and environment. However, the following is considered to the normal range of neutrophil count. In terms of cell count:
Why is neutrophil count checked?
During cancer treatment, the absolute neutrophil count is routinely checked to determine how the immune system is responding to the pressure of radiation or chemotherapy. Neutropenia is relatively common in these circumstances and can be classified as:
What do neutrophils do?
As a defensive immune cell, neutrophils have high motility (meaning the ability to move spontaneously) and are able to surround an infective agent to neutralize it. In addition to ingesting the pathogen, neutrophils can release cytotoxic (cell-killing) substances that directly destroy a foreign organism.
What is the ANC of neutropenia?
Moderate neutropenia (ANC between 1,000 and 500 cells/μL), which poses a moderate risk of infection. Severe neutropenia (ANC under 500 cells/μL), which poses a severe risk of infection.
How do neutrophils find their prey?
Neutrophils are able to find their prey through a process called chemotaxis wherein they recognize the chemicals released by a cut or scrape and move toward that "scent" automatically. This is unlike second-line adaptive immunity, which produces cells tailored to kill a specific pathogen and that pathogen alone.
What is the role of neutrophils in the immune system?
As part of our innate immune defense, neutrophils act as the first-line responders to infection, attacking bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens.
Why is neutropenia low?
By contrast, a low count, known as neutropenia, may be caused by sepsis, chemotherapy, radiation treatment, and certain autoimmune disorders. In some people, neutropenia can be chronic (ongoing and persistent), while for others it will be transient (usually in response to a disease or drug exposure). 5
Where are neutrophils produced?
They are produced in the bone marrow and account for around 50 to 70 percent of your total white blood cells.
Overview
Neutrophilia happens when your body produces too many neutrophils. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell. Your white blood cell count normally consists of five types of white blood cells, with neutrophils accounting for most of your white blood cells. Neutrophils help you fight infection.
Symptoms and Causes
Neutrophilia is your body’s reaction to an assortment of problems, from serious blood disorders to an everyday infection to a stressful day at work. Neutrophilia causes are classified as primary and secondary.
Diagnosis and Tests
Because neutrophilia can be a sign of underlying medical conditions, healthcare providers typically do a physical examination, looking for signs of infection, inflammation or blood disorders. Tests might include a complete blood count (CBC).
Management and Treatment
Neutrophilia isn’t a condition that can be treated. It’s a sign of underlying conditions, such as infection and inflammation. Neutrophilia may also be a sign of more serious conditions like blood disorders and blood cancer. Sometimes, neutrophilia is your body’s reaction to medication or stress.
Prevention
Generally speaking, neutrophilia can’t be prevented. You can be born with neutrophilia or develop it because you have another medical condition. If you don’t have a serious underlying condition, you can reduce your risk by taking care of your body. For example:
Living With
Neutrophilia is a sign of underlying problems. Once you know what’s causing your neutrophilia, you can take steps to manage the underlying condition.