
(Though lobotomies did still occur into the 1980’s in countries, like France.) Today, the lobotomy is viewed as a somewhat quirky, definitely grisly step on the road to scientific discovery. Thousands of people’s lives were affected by the procedure–in the US alone, it’s estimated over 40,000 people had a lobotomy.
Did lobotomies really work?
Did any lobotomies actually work? Surprisingly, yes . The modern lobotomy originated in the 1930s, when doctors realized that by severing fiber tracts connected to the frontal lobe, they could help patients overcome certain psychiatric problems, such as intractable depression and anxiety.
Why is lobotomy no longer used?
Why is lobotomy no longer used? In 1949, Egas Moniz won the Nobel Prize for inventing lobotomy, and the operation peaked in popularity around the same time. But from the mid-1950s, it rapidly fell out of favour, partly because of poor results and partly because of the introduction of the first wave of effective psychiatric drugs.
Are lobotomies still performed in the US?
Yes, lobotomies are still performed in the United States as they are worldwide, but they are not the crude psychosurgeries of the past.
Does lobotomy still happen?
Do lobotomies still happen? Lobotomy is rarely, if ever, performed today, and if it is, "it's a much more elegant procedure," Lerner said. "You're not going in with an ice pick and monkeying around." The removal of specific brain areas (psychosurgery) is only used to treat patients for whom all other treatments have failed.
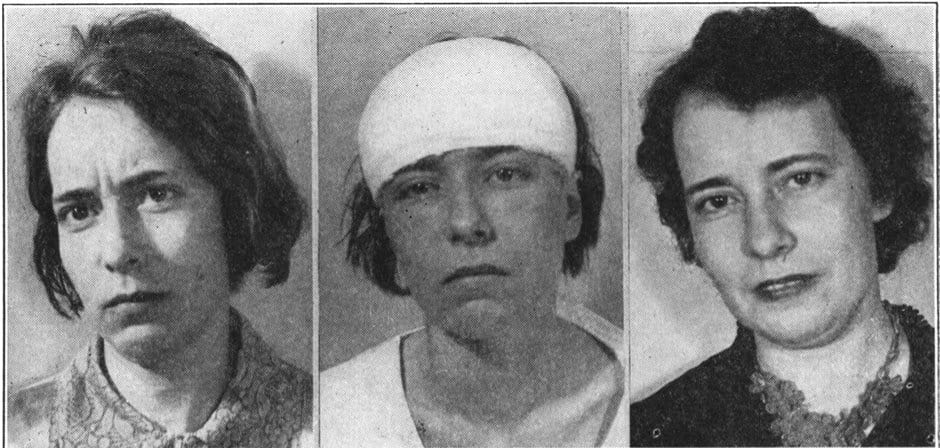
When was the last lobotomy performed in the US?
The last recorded lobotomy in the United States was performed by Dr. Walter Freeman in 1967 and ended in the death of the person on whom it was performed. In Europe, the Soviet Union banned lobotomies in 1950 , a year after inventor Dr. Egas Moniz won the Nobel Prize for medicine.
Are lobotomies performed anymore?
Lobotomy is rarely, if ever, performed today, and if it is, "it's a much more elegant procedure," Lerner said. "You're not going in with an ice pick and monkeying around." The removal of specific brain areas (psychosurgery) is reserved for treating patients for whom all other treatments have failed.
What does a lobotomy do to a person?
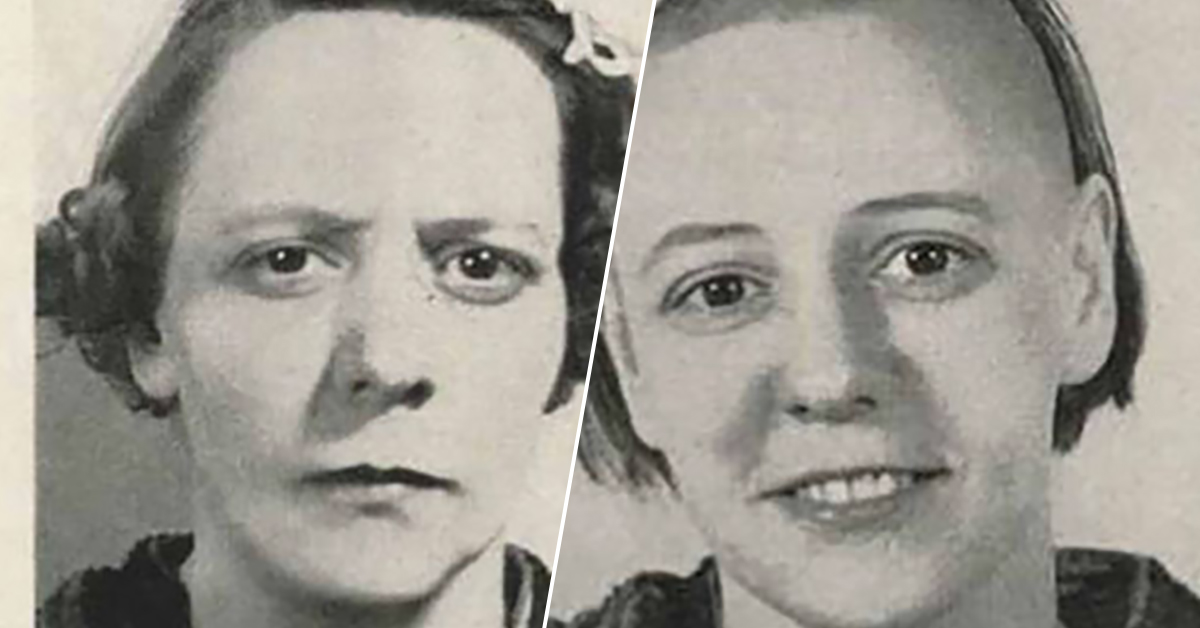
The lobotomy procedure could have severe negative effects on a patient's personality and ability to function independently. Lobotomy patients often show a marked reduction in initiative and inhibition.
Is lobotomy banned?
But the U.S., and much of western Europe, never banned lobotomy. And the procedure was still performed in these places throughout the 1980s. Today, lobotomies are rarely performed, although they're technically still legal. Surgeons occasionally use a more refined type of psychosurgery called a cingulotomy in its place.
What is the craziest surgery?
Unusual Plastic Surgery ProceduresPalm Line Surgery. People who believe in palm reading but aren't happy with their own lines now have a way to cheat fate. ... “Pokertox” ... Ear Cropping. ... Umbilicoplasty. ... Foot Fillers. ... Dimpleplasty. ... Tongue Splitting.
What does it feel like to be lobotomized?
Freeman believed that cutting certain nerves in the brain could eliminate excess emotion and stabilize a personality. Indeed, many people who received the transorbital lobotomy seemed to lose their ability to feel intense emotions, appearing childlike and less prone to worry.
Do they still do lobotomies UK?
In the UK this surgery is only used - as a last resort - in cases of severe depression or obsessive compulsive disorder. It's likely Zavaroni fought hard to have the op. Unlike all other psychiatric treatments, lobotomies cannot be given without the consent of the patient in this country.
How much does a lobotomy cost?
Psychiatric institutions were overcrowded and underfunded. Sternburg writes, “Lobotomy kept costs down; the upkeep of an insane patient cost the state $35,000 a year while a lobotomy cost $250, after which the patient could be discharged.”
How is an ice pick lobotomy performed?
1945: American surgeon Walter Freeman develops the 'ice pick' lobotomy. Performed under local anaesthetic, it takes only a few minutes and involves driving the pick through the thin bone of the eye socket, then manipulating it to damage the prefrontal lobes.
Why was lobotomy discontinued?
In 1949, Egas Moniz won the Nobel Prize for inventing lobotomy, and the operation peaked in popularity around the same time. But from the mid-1950s, it rapidly fell out of favour, partly because of poor results and partly because of the introduction of the first wave of effective psychiatric drugs.
Are lobotomies still performed in Australia?
In most Australia states, the use of deep brain stimulation to treat psychiatric illnesses is defined as a form of psychosurgery. That means it falls under the restrictions of state-based mental health legislation and as such is banned in NSW.
Did the FDA approve lobotomies?
He and Watts had recorded 625 surgical lobotomies altogether; Freeman performed 2,400 transorbital lobotomies by 1957. With FDA approval for chlorpromazine to treat mental illness in 1954, admissions to mental hospitals declined as did the need for lobotomies. Dr.
Who was the first person to have lobotomy?
Neurologist Egas Moniz performed the first brain surgery to treat mental illness in Portugal in 1935. The procedure, which Moniz called a "leucotomy," involved drilling holes in the patient's skull to get to the brain. Freeman brought the operation to America and gave it a new name: the lobotomy.
Who was the doctor who performed lobotomies in the 1950s?
Wolfhard Baumgartel was a staff physician at the Athens State Hospital in Ohio in the 1950s, where he observed Dr. Walter Freeman perform a series of lobotomies. Patricia Moen was lobotomized by Walter Freeman in 1962 at the age of 36. Their oral histories about their experiences are below.
Who performed the first transorbital lobotomy?
All Things Considered. On Jan. 17, 1946, a psychiatrist named Walter Freeman launched a radical new era in the treatment of mental illness in this country. On that day, he performed the first-ever transorbital or "ice-pick" lobotomy in his Washington, D.C., office.
Is icepick lobotomy still performed?
Ye olde "icepick lobotomies" are no longer performed, to the best of my knowledge. However, it seems that psychosurgery in general is still used in some parts of the world (a bit too often, by the looks of it, esp. in the treatment of addiction in countries such as China) and, in extreme cases, in North America and Europe.
Is lobotomy still used in epilepsy?
Psychosurgery, at least currently and in the past, still seems a bit like trying to carve an egg with dynamite. Lobotomy still seems to be used in the treatment of highly drug resistant epilepsy ( Temporal lobotomy in the surgical management of...
What is lobotomy in medical terms?
Lobotomy was an umbrella term for a series of different operations that purposely damaged brain tissue in order to treat mental illness , said Dr. Barron Lerner, a medical historian and professor at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York. "The behaviors [doctors] were trying to fix, they thought, were set down in neurological connections," Lerner ...
Who developed the lobotomy technique?
Italian and American doctors were early adopters of the lobotomy. The American neurosurgeons Walter Freeman and James Watts adapted Moniz's technique to create the "Freeman-Watts technique" or the "Freeman-Watts standard prefrontal lobotomy," according to Encyclopaedia Britannica.
What is the procedure called when you sever a connection in the prefrontal lobe?
Lobotomy , also known as leucotomy, is a neurosurgical operation that involves severing connections in the brain's prefrontal lobe, according to Encyclopaedia Britannica.
What was the first procedure to destroy the fibers that connected the frontal lobe to other parts of the brain
The first procedures involved cutting a hole in the skull and injecting ethanol into the brain to destroy the fibers that connected the frontal lobe to other parts of the brain. Later, Moniz introduced a surgical instrument called a leucotome, which contains a loop of wire that, when rotated, creates a circular lesion in the brain.
What was the role of mental institutions in the prevalence of lobotomy?
At the time, there were hundreds of thousands of mental institutions, which were overcrowded and chaotic. By giving unruly patients lobotomies, doctors could maintain control over the institution, Lerner said.
Who developed the transorbital lobotomy?
The Italian psychiatrist Amarro Fiamberti first developed a procedure that involved accessing the frontal lobes through the eye sockets, which would inspire Freeman to develop the transorbital lobotomy in 1945, a method that would not require a traditional surgeon and operating room.
Does lobotomy affect personality?
While a small percentage of people supposedly got better or stayed the same, for many people, lobotomy had negative effects on a patient's personality, initiative, inhibitions, empathy and ability to function on their own. "The main long-term side effect was mental dullness," Lerner said.
Why are lobotomies not used in prison?
There are no longer any forced lobotomies for prisoners or mental ward patients done against the person's will in an attempt to make the person more compliant or docile. Prior to World War II, there were some controversial uses of lobotomy for treatment of severe mental disorder.
Why are neurosurgeons reluctant to operate on both frontal lobes?
In fact, neurosurgeons are reluctant to operate on both frontal lobes even where there are intrinsic brain tumors (ie gliomas) which infiltrate and replace portions of each, because of the greatly reduced quality of life after removal or damage to both frontal lobes.
Is lobotomy surgery elective?
People would want to understand why you wanted a lobotomy and how you thought it would help you. Lobotomies are not elective surgery. They don’t get handed out like facelifts and tummy tucks. In fact, it sounds like it is nearly impossible for any reputable physician to recommend a lobotomy as appropriate treatment.
Can lobotomy be performed on epilepsy?
As far as I know, surgery that may resemble a lobotomy is only performed when necessitated by severe epilepsy or tumour, where the alternative is clearly worse. It’s then performed in a very different way to the way that guy with his ice picks did it, and far more carefully.
Can lobotomies be performed outright?
Probably in rare cases where damaged tissue would compromise the health of remaining tissue. Lobotomies haven't been performed outright, in the sense of lobotomies, in decades.
What did lobotomy patients become like?
In a 1942 presentation at the New York Academy of Medicine, the scientists reported that after lobotomy, patients did sometimes become "indolent " or "outspoken.". They were like "children," and loving families could simply dismiss their lack of social graces because now they were so much happier.
Why is lobotomy so popular?
That's because it's actually an excellent way to treat extreme cases of epilepsy, as well as other seizure disorders.
What did Burckhardt think of the frontal lobe?
Though Burckhardt was derided by his colleagues, some of whom thought his work was barbarous, Moniz and Freeman were intrigued by the idea that the frontal lobe could be somehow separated from the rest of the brain. This would leave incurably schizophrenic patients relieved of their emotional distress, they believed.
When did lobotomy become standard practice?
Though many of Moniz and Freeman's patients became essentially catatonic, while others were unaffected, enough seemed "cured" that the lobotomy became standard practice in mental institutions in the 1940s and early 50s.
What part of the brain was cut by hollow needles?
Later surgeries involved "coring" several regions in the frontal cortex with hollow needles -- literally sucking out parts of the brain to sever neural connections. All these surgeries were done blind, which is to say they rarely opened up a person's skull to see where they were cutting.
Who was the popularizer of lobotomies in the 1940s?
That’s exactly how Walter Freeman, a popularizer of lobotomies in the 1940s, performed thousands of operations. In the mid-20th century, the lobotomy was such a popular “cure” ] Save this story for later. Save this story for later. If you thought that scene in Sucker Punch where the doctor gave lobotomies with an ice pick was artistic ...
Who invented the lobotomy?
Invention of the Lobotomy. Moniz and Freemen are usually credited with inventing the lobotomy in the 1930s, though in truth their work was based on many other people's research going back to the mid-19th century.
When did lobotomy fall out of favor?
After initial signs of improvement, some patients’ symptoms would return. Others were left struggling to perform basic everyday activities. By the 1950’s, bad results and the arrival of the first psychiatric drugs meant the lobotomy had fallen out of favor.
When was the lobotomy first used?
Humans have long believed that drilling holes into the skull and/or brain could relieve various physical and mental ailments–it used to be called trepanation, and the practice goes all the way back to 6500 BCE. The lobotomy was comparatively sophisticated, but still nothing you’d want to endure unless you had to.
Who invented the lobotomy?
The lobotomy was comparatively sophisticated, but still nothing you’d want to endure unless you had to. In 1935, Portuguese physician Egas Moniz developed the first modern lobotomy, then called a “leucectomy,” to treat patients with obsessive behavior. Dr.
What happens when Jack Nicholson gets one?
When Jack Nicholson’s character gets one at the end of One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest, it annihilates his entire personality and renders him non-verbal. In reality, many patients did report positive results–aggressive patients did sometimes become more docile after having them, for example.
Why is lobotomy not effective?
Mainly because there was no medication or therapy effective enough to treat people who suffered from various mental illness. And with electroshock therapy being already in use, this invasive operation didnx5ct shock people. However, the misinformation and active campaigning for the effectiveness of lobotomy had a significant impact too.
How many lobotomies did Moniz perform?
From the year 1945 to 1947 there were around 2,000 lobotomies performed. However, the numbers skyrocketed to 18,000 after Moniz was awarded the Nobel Prize Medicine for his discovery in 1949.
Who was the first doctor to stab a patient's brain with an icepick?
A physician, Walter Freeman, helped popularize this procedure in the US. With no surgical training, Freeman decided to change the operation, and instead of drilling holes in the skull, he stabbed patientsx5c brains with an icepick through the eye socket.

Overview
A lobotomy, or leucotomy, is a form of psychosurgery, a neurosurgical treatment of a mental disorder that involves severing connections in the brain's prefrontal cortex. The surgery causes most of the connections to and from the prefrontal cortex, the anterior part of the frontal lobes of the brain, to be severed.
In the past, the surgery was used for treating mental disorders and occasionally other conditions …
Effects
Historically, patients of lobotomy were, immediately following surgery, often stuporous, confused, and incontinent. Some developed an enormous appetite and gained considerable weight. Seizures were another common complication of surgery. Emphasis was put on the training of patients in the weeks and months following surgery.
The purpose of the operation was to reduce the symptoms of mental disorders, and it was recog…
History
In the early 20th century, the number of patients residing in mental hospitals increased significantly while little in the way of effective medical treatment was available. Lobotomy was one of a series of radical and invasive physical therapies developed in Europe at this time that signaled a break with a psychiatric culture of therapeutic nihilism that had prevailed since the late nineteenth-century. The new "heroic" physical therapies devised during this experimental era, inc…
Reception
Moniz rapidly disseminated his results through articles in the medical press and a monograph in 1936. Initially, however, the medical community appeared hostile to the new procedure. On 26 July 1936, one of his assistants, Diogo Furtado, gave a presentation at the Parisian meeting of the Société Médico-Psychologique on the results of the second cohort of patients leucotomised by Lima. Sobral Cid, who had supplied Moniz with the first set of patients for leucotomy from his o…
Prevalence
In the United States, approximately 40,000 people were lobotomized. In England, 17,000 lobotomies were performed, and the three Nordic countries of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden had a combined figure of approximately 9,300 lobotomies. Scandinavian hospitals lobotomized 2.5 times as many people per capita as hospitals in the US. Sweden lobotomized at least 4,500 people between 1944 and 1966, mainly women. This figure includes young children. In Norway, t…
Criticism
As early as 1944, an author in the Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease remarked: "The history of prefrontal lobotomy has been brief and stormy. Its course has been dotted with both violent opposition and with slavish, unquestioning acceptance." Beginning in 1947 Swedish psychiatrist Snorre Wohlfahrt evaluated early trials, reporting that it is "distinctly hazardous to leucotomize schizophrenics" and that lobotomy was "still too imperfect to enable us, with its aid, to venture o…
Notable cases
• Rosemary Kennedy, sister of US President John F. Kennedy, underwent a lobotomy in 1941 that left her incapacitated and institutionalized for the rest of her life.
• Howard Dully wrote a memoir of his late-life discovery that he had been lobotomized in 1960 at age 12.
• New Zealand author and poet Janet Frame received a literary award in 1951 the day before a scheduled lobotomy was to take place, and it was never performed.
Literary and cinematic portrayals
Lobotomies have been featured in several literary and cinematic presentations that both reflected society's attitude towards the procedure and, at times, changed it. Writers and film-makers have played a pivotal role in turning public sentiment against the procedure.
• Robert Penn Warren's 1946 novel All the King's Men describes a lobotomy as making "a Comanche brave look like a tyro with a scalping knife", and portrays the surgeon as a repressed man who c…