What are the five steps of meiosis?
What are the 8 parts of meiosis?
- prophase I. the chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase I. pairs of homologous chromosomes move to the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase I.
- Telophase I and Cytokinesis.
- Prophase II.
- Metaphase II.
- Anaphase II.
- Telophase II and Cytokinesis.
What causes nondisjunction during meiosis II?
Nondisjunction in meiosis I occurs when the tetrads fail to separate during anaphase I. Nondisjunction in meiosis II results from the failure of the sister chromatids to separate during anaphase II. Since meiosis I proceeded without error, 2 of the 4 daughter cells will have a normal complement of 23 chromosomes.
Did mitosis evolve first or meiosis and why?
Plants use meiosis and mitosis differently depending on their life cycle. For example, meiosis will be used to make spores and then those spores will use mitosis to replicate. So, which comes first depends on the life cycle of the organism. Mitosis evolved first.
What are the 4 types of chromosomal mutations?
What are the 5 chromosomal mutations?
- Non-Disjunction and Down’s Syndrome.
- Deletion.
- Duplication.
- Inversion of Genes.
- Translocation of Genes.
Do mutations happen in meiosis or mitosis?
Mutations can occur before, during, and after mitosis and meiosis.
What causes mutations during meiosis?
Mutations may also occur during mitosis and meiosis. A mutation caused by an environmental factor, or mutagen, is known as an induced mutation. Typical mutagens include chemicals, like those inhaled while smoking, and radiation, such as X-rays, ultraviolet light, and nuclear radiation.
During what process does mutations occur?
DNA replicationMutations can result from errors in DNA replication during cell division, exposure to mutagens or a viral infection. Germline mutations (that occur in eggs and sperm) can be passed on to offspring, while somatic mutations (that occur in body cells) are not passed on.
Why are mutations in meiosis often more damaging than mutations in mitosis?
Explanation: Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces gametes while mitosis is a type of cell division that produces somatic cells. If a somatic cell develops a mutation, it is most likely not harmful or does not change the organism in any way because only two cells are affected.
What are some chromosomal mutations that can occur during meiosis?
Examples of structural chromosome mutations include translocations, deletions, duplications, inversions, and isochromosomes. Abnormal chromosome numbers result from nondisjunction, or the failure of chromosomes to separate correctly during cell division.
Do mutations only occur during interphase?
Mutations can occur during many points of a cell's life cycle - during DNA replication, during Interphase as a result of some environmental factor, or during expression of DNA as cells make proteins.
What causes chromosome mutation?
Usually, a chromosomal mutation happens because of a change in chromosome structures, chromosomal rearrangement, or other chromosomal abnormalities such as a change in chromosome number or missing chromosome. As previously stated, these often take place because there are issues during crossing over or cell division.
Why does mutation occur?
Mutations result either from errors in DNA replication or from the damaging effects of mutagens, such as chemicals and radiation, which react with DNA and change the structures of individual nucleotides. All cells possess DNA-repair enzymes that attempt to minimize the number of mutations that occur (Section 14.2).
What is the cause of chromosomal mutation?
Usually, a chromosomal mutation happens because of a change in chromosome structures, chromosomal rearrangement, or other chromosomal abnormalities such as a change in chromosome number or missing chromosome. As previously stated, these often take place because there are issues during crossing over or cell division.
Does crossing over cause mutations?
We demonstrate that crossing over is an important source of new mutations and gBGC at recombination hotspots associated with DSB repair.
How do mutations happen in DNA replication?
Mutations result either from errors in DNA replication or from the damaging effects of mutagens, such as chemicals and radiation, which react with DNA and change the structures of individual nucleotides. All cells possess DNA-repair enzymes that attempt to minimize the number of mutations that occur (Section 14.2).
What is the result of a mutation during replication?
But some replication errors make it past these mechanisms, thus becoming permanent mutations. These altered nucleotide sequences can then be passed down from one cellular generation to the next, and if they occur in cells that give rise to gametes, they can even be transmitted to subsequent organismal generations.
How do chromosome mutations affect the cell?
Chromosome mutations can result in changes in the number of chromosomes in a cell or changes in the structure of a chromosome. Unlike a gene mutation which alters a single gene or larger segment of DNA on a chromosome, chromosome mutations change and impact the entire chromosome.
What is chromosome mutation?
Updated April 13, 2019. A chromosome mutation is an unpredictable change that occurs in a chromosome. These changes are most often brought on by problems that occur during meiosis (division process of gametes) or by mutagens (chemicals, radiation, etc.). Chromosome mutations can result in changes in the number of chromosomes in a cell ...
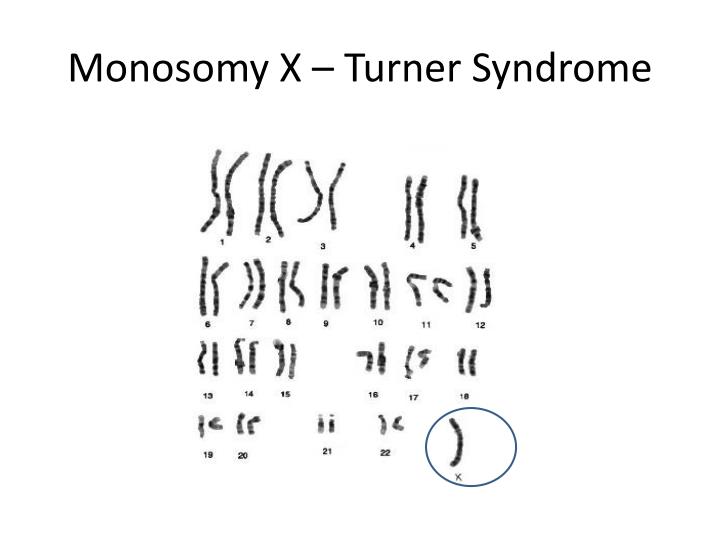
What is the term for a condition that occurs due to nondisjunction in autosomal cells?
Down syndrome is an example of a condition that occurs due to nondisjunction in autosomal (non-sex) cells. Individuals with Down syndrome have an extra chromosome on autosomal chromosome 21. A chromosome mutation that results in individuals with more than one haploid set of chromosomes in a cell is termed polyploidy.
What causes chromosome number changes?
Chromosome Number Changes. Down syndrome is caused by a chromosomal anomaly: the 21st set having three rather than the normal two chromosomes. Kateryna Kon/Science Photo Library/Getty Images. A chromosome mutation that causes individuals to have an abnormal number of chromosomes is termed aneuploidy.
Why do aneuploid cells occur?
Aneuploid cells occur as a result of chromosome breakage or nondisjunction errors that happen during meiosis or mit osis. Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes to separate properly during cell division. It produces individuals with either extra or missing chromosomes.
Why are chromosome numbers abnormal?
Abnormal chromosome numbers result from nondisjunction, or the failure of chromosomes to separate correctly during cell division.
How are identical copies of chromosomes produced?
An identical copy of each chromosome is therefore produced through DNA replication. Each duplicated chromosome is comprised of two identical chromosomes called sister chromatids that are connected at the centromere region. Sister chromatids separate prior to the completion of cell division.
When Do Gene Mutations Occur?
Mutations frequently occur just before the process of mitosis when DNA is being replicated in the cell nucleus. During mitosis or meiosis, mishaps can occur when chromosomes are not lined up correctly or fail to separate properly. Chromosomal mutations in the germ cells can be inherited and passed along to the next generation.
What is genetic mutation?
Genetic mutations are slight alterations of DNA or RNA nucleotides, genes or chromosomes that may occur during replication or cell division. Random, uncorrected errors may be beneficial or harmful in relationship to evolution. Some effects of gene mutation go unnoticed.
What is frameshift mutation?
Frameshift mutations: These are point mutations that result when a nucleotide pair is added or omitted in a gene sequence that shifts how codons are read. Such mutations often result in different amino acids being added to the protein being synthesized. An example is beta thalassemia, a blood disorder caused by mutations to the HBB gene.
What are some examples of mutations in germline cells?
Defective genes on chromosomes are passed on, as well as too many or too few chromosomes per cell when these mutations happen in germline cells. Gene mutation examples include severe genetic disorders, cell overgrowth, tumor formation and heightened risk of breast cancer.
What is a mutation that changes the number of nucleotides?
Changes in the number or type of nucleotides are called point mutations . The effects of point mutation can range from harmless to life threatening. Mispairing or reordering of nucleotide bases are considered silent mutations when the change doesn’t affect cell functioning.
What type of mutation occurs when one nucleotide is replaced with another?
The new amino acid may even perform the same functions as the one it replaced. The following are types of point mutations that can occur: Missense mutation: This happens when one nucleotide is replaced with another. Substitutions of bases can interfere with normal protein syntheses and functioning.
How do spontaneous mutations affect DNA replication?
Most of the time, errors in DNA replication or segregation are quickly repaired by enzymes or the cell is destroyed before they can cause lasting damage. When DNA repair attempts fail, spontaneous mutations stay within the DNA. Benign spontaneous mutations increase the genetic variance and biodiversity of a population.
