What affects ocean currents?
San Diego researchers say warming ocean waters are gradually, but steadily, speeding up surface ocean currents and that could disrupt the ocean’s delicate food web. “We were surprised to see that surface currents speed up in more than three-fourths of ...
What are facts about ocean currents?
Oceanic currents are driven by three main factors:
- The rise and fall of the tides. Tides create a current in the oceans, which are strongest near the shore, and in bays and estuaries along the coast. ...
- Wind. Winds drive currents that are at or near the ocean's surface. ...
- Thermohaline circulation. ...
How do ocean currents affect climate?
Ocean currents act much like a conveyor belt, transporting warm water and precipitation from the equator toward the poles and cold water from the poles back to the tropics. Thus, ocean currents regulate global climate, helping to counteract the uneven distribution of solar radiation reaching Earth’s surface.
Which explains how ocean currents affect global?
Thus, ocean currents regulate global climate, helping to counteract the uneven distribution of solar radiation reaching Earth’s surface. Without currents in the ocean, regional temperatures would be more extreme—super hot at the equator and frigid toward the poles—and much less of Earth’s land would be habitable.

How are ocean currents changing?
Climate change is slowing down the conveyor belt of ocean currents that brings warm water from the tropics up to the North Atlantic. Our research, published today in Nature Climate Change, looks at the profound consequences to global climate if this Atlantic conveyor collapses entirely.
Do ocean currents change and explain why?
Winds, water density, and tides all drive ocean currents. Coastal and sea floor features influence their location, direction, and speed. Earth's rotation results in the Coriolis effect which also influences ocean currents.
What happens if ocean currents change?
Study warns of 'irreversible transition' in ocean currents that could rapidly freeze parts of North America. If the current system collapses, it would lead to dramatic changes in worldwide weather patterns. If this circulation shuts down, it could bring extreme cold to Europe and parts of North America.
Do ocean currents move?
Ocean water is constantly moving, and not only in the form of waves and tides. Ocean currents flow like vast rivers, sweeping along predictable paths. Some ocean currents flow at the surface; others flow deep within water.
Can surface currents change?
These surface currents do not depend on weather; they remain unchanged even in large storms because they depend on factors that do not change. Surface currents are created by three things: global wind patterns, the rotation of the Earth, and the shape of the ocean basins.
How fast do ocean currents move?
Horizontal movements are called currents, which range in magnitude from a few centimetres per second to as much as 4 metres (about 13 feet) per second. A characteristic surface speed is about 5 to 50 cm (about 2 to 20 inches) per second. Currents generally diminish in intensity with increasing depth.
Can ocean currents stop?
Water that is less dense will not be able to sink and flow through the deep ocean, which may disrupt or stop the pattern of ocean currents in the region. Scientists estimate that, given the current rate of change, these currents could stop within the next few decades.
What would happen if the Atlantic Ocean currents stopped?
If the circulation shuts down, it could bring extreme cold to Europe and parts of North America, raise sea levels along the U.S. East Coast and disrupt seasonal monsoons that provide water to much of the world.
What would happen if the Gulf Stream stopped?
Without the oceanic currents bringing warm water north, Europe and North America experience a sudden and catastrophic temperature drop.
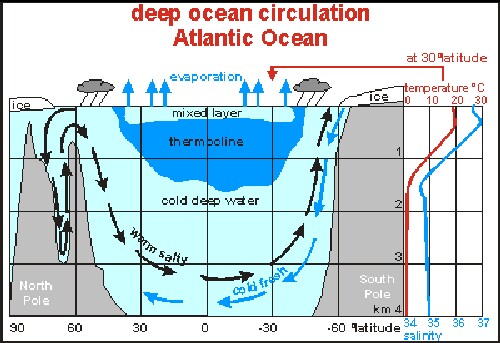
What controls deep ocean currents?
These deep-ocean currents are driven by differences in the water's density, which is controlled by temperature (thermo) and salinity (haline). This process is known as thermohaline circulation.
What causes deep ocean currents to move?
Deep currents are driven by temperature and water density/salinity. Of course, deep currents impact surface currents, which carry warm water to the poles. Surface currents are also driven by global wind systems fueled by energy from the sun. Factors like wind direction and the Coriolis effect play a role.
How many ocean currents are there in the world?
There are five major ocean-wide gyres—the North Atlantic, South Atlantic, North Pacific, South Pacific, and Indian Ocean gyres. Each is flanked by a strong and narrow “western boundary current,” and a weak and broad “eastern boundary current” (Ross, 1995).
What is ocean currents short answer?
Ocean currents are the continuous, predictable, directional movement of seawater driven by gravity, wind (Coriolis Effect), and water density. Ocean water moves in two directions: horizontally and vertically. Horizontal movements are referred to as currents, while vertical changes are called upwellings or downwellings.
What are ocean currents explain any three effects of ocean current?
The following are the three effects of ocean currents: It keeps the temperature high and makes the area more heated than the surrounding areas. The warm ocean currents led to rainfall. It shares minerals & pollution attached to it becomes profoundly adulterated & later negligible.
Which explains how ocean currents affect climate?
Ocean currents act much like a conveyor belt, transporting warm water and precipitation from the equator toward the poles and cold water from the poles back to the tropics. Thus, ocean currents regulate global climate, helping to counteract the uneven distribution of solar radiation reaching Earth's surface.
What causes ocean currents quizlet?
A directional movement of ocean water; surface currents result from steady winds over the ocean surface; deep ocean currents result from density variations due to temperature and salinity differences.
How does ocean current affect climate?
The movement of this heat through local and global ocean currents affects the regulation of local weather conditions and temperature extremes, stabilization of global climate patterns, cycling of gases, and delivery of nutrients and larva to marine ecosystems. Ocean currents are located at the ocean surface and in deep water below 300 meters ...
What is the importance of ocean currents?
Ocean Currents and Climate. Background Info. Fast Facts. Vocabulary. Mass flows of water, or currents, are essential to understanding how heat energy moves between the Earth’s water bodies, landmasses, and atmosphere. The ocean covers 71 percent of the planet and holds 97 percent of its water, making the ocean a key factor in ...
How does the density of ocean water affect the water?
Water density is affected by the temperature, salinity (saltiness), and depth of the water. The colder and saltier the ocean water, the denser it is. The greater the density differences between different layers in the water column, the greater the mixing and circulation. Density differences in ocean water contribute to a global-scale circulation system, also called the global conveyor belt.
What would happen if the ocean conveyor belt was stopped?
Climate change leading to increases in ocean temperatures, evaporation of seawater, and glacial and sea ice melting could create an influx of warm freshwater onto the ocean surface. This would further block the formation of sea ice and disrupt the sinking of denser cold, salty water. These events could slow or even stop the ocean conveyor belt, which would result in global climate changes that could include drastic decreases in Europe’s temperatures due to a disruption of the Gulf Stream.
What are the forces that affect ocean currents?
The topography and shape of ocean basins and nearby landmasses also influence ocean currents. These forces and physical characteristics affect the size, shape, speed, ...
What are tidal currents?
They are also influenced by coastal topography. Tidal currents are the only type of currents that change regularly and can be easily predicted.
Which direction do storms swirl?
the result of Earth's rotation on weather patterns and ocean currents. The Coriolis effect makes storms swirl clockwise in the Southern hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere. current. Noun. steady, predictable flow of fluid within a larger body of that fluid. density.
What causes ocean currents?
Deep ocean currents. Differences in water density, resulting from the variability of water temperature ( thermo) and salinity ( haline ), also cause ocean currents. This process is known as thermohaline circulation. In cold regions, such as the North Atlantic Ocean, ocean water loses heat to the atmosphere and becomes cold and dense.
How does the Earth's rotation affect ocean currents?
Coastal and sea floor features influence their location, direction, and speed. Earth’s rotation results in the Coriolis effect which also influences ocean currents. Similar to a person trying to walk in a straight line across a spinning merry-go-round, winds and ocean waters get deflected from a straight line path as they travel across ...
How do ocean currents affect the food web?
Ocean currents are an important abiotic factor that significantly influences food webs and reproduction of marine organisms and the marine ecosystems that they inhabit. Many species with limited mobility are dependent on this "liquid wind" to bring food and nutrients to them and to distribute larvae and reproductive cells. Even fish and mammals living in the ocean may have their destinations and food supply affected by currents.
How can ocean currents be used in education?
Educators can use ocean currents to help students learn and appreciate the interaction of Earth's systems and how scientists study these processes with drifting buoys, sound monitors, and other methods. The lesson plans, labs, and other resources in this collection can help students understand how distant abiotic factors, ...
What are the effects of ocean currents on fish?
Even fish and mammals living in the ocean may have their destinations and food supply affected by currents. Upwelling currents bring cold nutrient-rich waters from the ocean bottom to the surface, supporting many of the most important fisheries and ecosystems in the world.
What happens when the ocean freezes?
In cold regions, such as the North Atlantic Ocean, ocean water loses heat to the atmosphere and becomes cold and dense. When ocean water freezes, forming sea ice, salt is left behind causing surrounding seawater to become saltier and denser. Dense-cold-salty water sinks to the ocean bottom.
What are the things that scientists use to monitor the ocean?
Drifters, buoys, Argo floats and more help scientists monitor the global ocean, including areas that are difficult to travel to via research ship.
What is ocean current?
Ocean Currents. Encyclopedic Entry. Vocabulary. Ocean water is constantly moving, and not only in the form of waves and tides. Ocean currents flow like vast rivers, sweeping along predictable paths. Some ocean currents flow at the surface; others flow deep within water. Some currents flow for short distances; others cross entire ocean basins ...
Why are ocean currents important?
Ocean currents are also critically important to sea life. They carry nutrients and food to organisms that live permanently attached in one place, and carry reproductive cells and ocean life to new places. Rivers flow because of gravity.
How do tides affect ocean currents?
Tides contribute to coastal currents that travel short distances. Major surface ocean currents in the open ocean, however, are set in motion by the wind, which drags on the surface of the water as it blows. The water starts flowing in the same direction as the wind. But currents do not simply track the wind.
How long does it take for a conveyor belt to move water around the globe?
These currents circulate around the globe in a thousand-year cycle.
What causes deep ocean currents?
In contrast to wind-driven surface currents, deep-ocean currents are caused by differences in water density. The process that creates deep currents is called thermohaline circulation —“thermo” referring to temperature and “haline” to saltiness.
What forces pull water with them?
The winds pull surface water with them, creating currents. As these currents flow westward, the Coriolis effect —a force that results from the rotation of the Earth—deflects them. The currents then bend to the right, heading north.
Which direction do storms swirl?
the result of Earth's rotation on weather patterns and ocean currents. The Coriolis effect makes storms swirl clockwise in the Southern hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere. steady, predictable flow of fluid within a larger body of that fluid.
Why is the ocean current in the Arctic so turbulent?
A major ocean current in the Arctic is faster and more turbulent as a result of rapid sea ice melt, a new study from NASA shows. The current is part of a delicate Arctic environment that is now flooded with fresh water, an effect of human-caused climate change.
What is the Atlantic current?
This important current is called the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation and helps regulate the planet's climate by carrying heat from the tropically-warmed water to northern latitudes like Europe and North America. If slowed enough, it could negatively impact marine life and the communities that depend it.
What would happen if the wind direction of the Beaufort Gyre changed?
If the direction were to change, the wind would reverse the current, pulling it counterclockwise and releasing the water it has accumulated all at once.
How does melting ice affect the ocean?
The melting ice could, in turn, lead to changes in how nutrients and organic material in the ocean are mixed, significantly affecting the food chain and wildlife in the Arctic . The results reveal a delicate balance between wind and ocean as the sea ice pack recedes under climate change.
What is the current that moves water from the Arctic to the tropics called?
This important current is called the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation and helps regulate the planet's climate by carrying heat ...
What would happen if the Arctic Ocean was released to the North Atlantic?
Fresh water released from the Arctic Ocean to the North Atlantic can change the density of surface waters.
Which direction does the current go in the Arctic?
Persistent westerly winds have also dragged the current in one direction for over 20 years, increasing the speed and size of the clockwise current and preventing the fresh water from leaving the Arctic Ocean.
How Do Ocean Currents Affect Climate?
For instance, water from the tropical Atlantic moves northwards through Atlantic in a Gulf Stream suffusing the Western Europe’s shores thus producing a mild climate. The mild climate raises the temperatures of the region higher than the regions across the Atlantic but on the same latitude. The Gulf Stream explains why Canada 's east coast is locked in ice while England is not especially during winter. The current cooling events being experienced in Western Europe is attributed to the Gulf Stream slowing down as a result of the global warming which has caused the polar ice cap to melt and slowing down the Great Ocean Conveyor Belt.
What causes ocean currents?
The movement of the ocean water is caused by forces acting on the water including the breaking waves, salinity differences, Coriolis effects, the wind, temperatures, and cabbeling.
How does surface cooling affect the ocean?
The surface cooling during winter makes the surrounding water become denser. After the surface water has become thicker than the underlying water, a process called convective overturning takes place where the dense water mixing downwards extending to the bottom. The dense mixed water spreads out at the bottom of the ocean. When this mixing takes place in higher latitude, a circulation pattern is created where warm water moves pole-wards from the tropics thus surrendering heat to the atmosphere resulting in the transportation of heat pole-wards. The cycle repeats itself over and over influencing the transfer of heat from the equator to the highlands.
How are ocean currents formed?
Cold currents are formed when the air circulating the eastern side of the subtropical high is blown over cold water mass and are then dragged toward the equator. Warm currents are masses of warm water with higher temperatures moving away from the equator. Warm currents are formed when the cold saline water becomes dense and sinks allowing the light warm water to flow in the opposite direction, usually far from the equator.
What causes ocean water to move?
The movement of the ocean water is caused by forces acting on the water including the breaking waves, salinity differences, Coriolis effects, the wind, temperatures, and cabbeling. The current direction is influenced by the shoreline, other currents, and the depth of the contours. The ocean currents can flow for thousands ...
What is the term for the mass of warm water with higher temperatures moving away from the equator?
Warm currents are masses of warm water with higher temperatures moving away from the equator. Warm currents are formed when the cold saline water becomes dense and sinks allowing the light warm water to flow in the opposite direction, usually far from the equator.
How long can ocean currents flow?
The ocean currents can flow for thousands of kilometers and create a global conveyer belt which is important in determining the climate of different regions of the earth. Ocean currents are either on the surface of the ocean or in the deep waters below 300 meters.
How does slowing ocean circulation affect sea levels?
One of the main impacts of the slowing ocean circulation is on sea levels, especially those of the US East Coast. "The northward surface flow of the AMOC leads to a deflection of water masses to the right, away from the US East Coast. This is due to Earth's rotation that diverts moving objects such as currents to the right in ...
Why is the ocean circulation slowing down?
The slowdown of ocean circulation is directly caused by warming global temperatures and has been predicted by climate scientists.
What is the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation?
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) transports water across the planet's oceans, including the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian. The region contributing to the slowdown is the North Atlantic, according to the research. Read More.
Why does warm water turn back south?
As warm water currents move north, they typically turn back south as it gets cooler and heavier. Added freshwater from the melting ice is causing this turn to be slower because of reduced salinity.
Why are hurricanes closer to the coast?
An increase in heat waves across Europe and stronger hurricanes closer to the US coastline because of warmer water drifting closer to the coast can be linked to the ocean circulation , Rahmstorf said.
What are the impacts of slowing ocean circulation?
One of the main impacts of the slowing ocean circulation is on sea levels, especially those of the US East Coast.
How much has the water level risen in the past 140 years?
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), water levels have risen by 8 to 9 inches on average within the past 140 years. The rate at which these waters are rising has also increased in recent years.
How do ocean currents affect climate?
Some currents take warm water away from the equator, influencing coastal climates near the poles. Others take colder water from the poles or the deep ocean and move it towards the equator, creating cooler coastal climates.
Why do ocean currents help the Earth?
Ocean currents bring warm water and rain from the equator to the poles and cold water from the poles toward the equator. These ocean currents help to counteract the high levels of solar radiation that the Earth’s equator receive. Without these currents, it would be much hotter at the equator and much colder at the poles, ...
How does the ocean influence climate?
The movement of the ocean currents has an especially significant factor in the development of the planet’s climate.
How does increasing CO2 affect the Atlantic current?
Manabe and Stouffer concluded that as CO2 concentrations increase, the Atlantic convective currents significantly decrease. With a four-fold increase in CO2, it was predicted that the current would begin to slow, and eventually stop over a period of 100 to 200 years. This would cause the climate of much of Western Europe to change, and would impact billions of people worldwide.
How does photosynthesis affect the climate?
Plant life absorbs carbon dioxide and produces oxygen, which means that atmospheric CO2 concentrations will increase as a result of desertification and deforestation. Since carbon dioxide is the most plentiful greenhouse gas, this has an impact on global climate.
How much of the Earth's surface is covered by oceans?
But since oceans cover over 70 percent of the Earth’s surface, their influence on climate is even more pervasive. In fact, areas fit for habitation by human beings, plants and animals could be severely restricted if the influence of the ocean currents were nullified. While the earth’s climates are controlled by a number of factors, ...
Why do oceans help climate?
Because they absorb and emit heat more steadily than land, oceans help moderate temperatures in coastal areas, making winters warmer and summers cooler.
How long does it take for ocean currents to change?
In the deep ocean (water over 300 metres of depth) the currents are usually in a reasonably steady state, changing slowly over several weeks. Some areas are more dynamic, such as the Gulf Stream east of Cape Hatteras, and the Kuroshio Current in east Asia. Even in their most volatile states, these currents only change slowly from day-to-day, a feature amply illustrated in the video below from NASA which shows how the deep ocean currents change around the world, over a two year period (note the timeline top-right).
How do currents affect sailing?
Whatever craft you sail, currents can have a significant effect on your transit times across an ocean, particularly where the major ocean currents such as the Kuroshio and Gulf Stream flow. However, the beginning and end of most ocean crossings transit coastal waters, where there can be strong tides. Understanding how and why each type of current forms and where they occur increases the likelihood of a successful passage - whether it be a 'just-in-time' arrival on a ship or a podium finish in a yacht race.
What causes tidal currents?
Tidal currents, caused by astronomical forces , are usually the dominant force on the continental shelf, although wind-driven currents also play a part. The degree to which one or other dominates depends on factors such as the size and shape of the shelf locally and the speed and direction of winds blowing across the sea surface. The frequency at which tidal currents change depends on where you are in the world - simplistically, shelf seas in the Atlantic Ocean experience two high and two low tides a day (semi-diurnal frequency) and in the Pacific Ocean one high and one low tide a day (diurnal frequency). Elsewhere a mixture of the two is seen. As tidal currents are inherently predictable, we can have a high degree of confidence in their speed and direction in advance.