
Why do organic compounds have higher melting and boiling point than inorganic?
Organic compounds don't have higher melting and boiling point, inorganic compound have. It's because of the difference in chemical bonds. Inorganic compounds are mostly made of strong ionic bonds, which give them a very high melting and boiling point.
Why do ionic compounds have a high melting point?
Ionic compounds usually have high melting points because the electrostatic forces holding the ions (ion-ion interaction) are much stronger. In organic compounds the presence of polarity, or especially hydrogen bonding, generally leads to higher melting point. Consider the following examples.
What are the applications of melting point in organic chemistry?
The most important application of melting point is confirmation of synthesized organic compound, however now different spectral techniques are also available (like IR, NMR and Mass Spectroscopy) but melting point confirmation through reference melting point is an economical, easy and convenient way for confirming the synthesized compound.
Why do different substances have different melting points?
Different substances have different melting points due to their structure, composition, the force of attraction between the molecules of the organic compound, and the level of impure particles present in the compound. If the molecules' structure is tightly packed, then the heating range will be higher than for the loosely packed compounds.

Do organic or inorganic compounds have higher melting points?
Explanation: It's because of the difference in chemical bonds. Inorganic compounds are mostly made of strong ionic bonds, which give them a very high melting and boiling point. On the other hand, organic compounds are made of comparatively weak covalent bonds, which is the cause of their low melting and boiling point.
Are organic compounds low melting point?
Organic compounds have a low melting point because of weaker bond strength of bonds present in between the atoms of the compound.
Do inorganic compounds have high melting points?
Inorganic compounds are often ionic, and so have very high melting points.
How do melting points compare to organic compounds?
The force of Attraction- Another factor that influences the melting point is the force of attraction. If the force of attraction is strong among the molecules, then the organic compound's melting point will be higher.
Are organic compounds melting point?
Organic compounds can be gases, liquids, or solids at room temperature. Ionic compounds are all solids at room temperature with very high melting points. Organic compounds have relatively low melting points and boiling points.
What is melting point in organic chemistry?
Melting Points in Organic Chemistry The melting point of a compound is the temperature at which the solid phase transitions into the liquid phase at a standard pressure of 1 atmosphere.
How do inorganic and organic compounds differ?
The primary difference that lies between these organic compounds and inorganic compounds is that organic compounds always have a carbon atom while most of the inorganic compounds do not contain the carbon atom in them. Almost all the organic compounds contain the carbon-hydrogen or a simple C-H bond in them.
What is the main difference between organic and inorganic chemistry?
While organic chemistry is defined as the study of carbon-containing compounds, inorganic chemistry is the study of the remaining (i.e., not carbon-containing) subset of compounds. But there can be overlap between the two fields.
What are true about organic compounds?
organic compound, any of a large class of chemical compounds in which one or more atoms of carbon are covalently linked to atoms of other elements, most commonly hydrogen, oxygen, or nitrogen. The few carbon-containing compounds not classified as organic include carbides, carbonates, and cyanides.
Which compound has the highest melting point?
Tantalum carbide (TaC) and hafnium carbide (HfC) are of particular interest due to their high melting temperatures (>4000 K) which are the highest reported among all known inorganic materials1,2,3.
Which compound has a higher melting point?
Ionic compounds, as expected, usually have very high melting points due to the strength of ion-ion interactions (there are some ionic compounds, however, that are liquids at room temperature). The presence of polar and especially hydrogen-bonding groups on organic compounds generally leads to higher melting points.
What is the melting point of inorganic compounds?
Inorganic polymers with ionic and polar bonds have usually very high melting/boiling points irrespective to their molecular weight. As a classical textbook example, melting point for compounds with 1:1 composition, NaCl (800.7 °C), MgO (2825 °C), and AlN (2800 °C) may be offered.
Which compounds have lower melting points?
The chemical element with the lowest melting point is Helium and the element with the highest melting point is Carbon.
Which compound has a low melting and boiling point?
Covalent compoundsCovalent compounds have generally low melting and boiling points.
What are true about organic compounds?
organic compound, any of a large class of chemical compounds in which one or more atoms of carbon are covalently linked to atoms of other elements, most commonly hydrogen, oxygen, or nitrogen. The few carbon-containing compounds not classified as organic include carbides, carbonates, and cyanides.
What are the characteristics of organic compounds?
The general characteristics of Organic Compounds include:Can be isolated as well as prepared in laboratory.Comprise almost 90% of all known compounds.Mostly built up of only three elements- carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. ... Possess complex structures and high molecular weights.More items...
Why does melting point depend on the shape of the molecules?
Aside from the intermolecular interactions , however, the melting point depends also on how the molecules are packed or arranged in the solid form. The more symmetrical they are, the better they pack and form a perfect crystal lattice which results in a higher melting point. So, as the molecules fit tighter, more energy is required to break the lattice and melt them apart.
Which isomer has a higher melting point?
For example, despite being nonpolar, the trans isomer of 1,2-dichloroethane has a higher melting point (−50 o C) than the cis isomer (−80 o C) because of higher symmetry which allows for compact packing in the solid phase. In contrast, the cis isomer is a polar molecule with a higher boiling ...
Why is the cis isomer polar?
In contrast, the cis isomer is a polar molecule with a higher boiling point (60 o C vs 48 o C ) because of the net molecular dipole moment and intermolecular dipole-dipole interactions.
What factors influence the boiling point of a molecule?
The larger this surface, the stronger the intermolecular interactions, and thus, the higher the boiling point. This can be seen by comparing the boiling points of pentane, 2-methylbutane, and 2,2-dimethylpropane:
Why does the boiling point of propylamine increase?
Notice that the boiling point increases as we are going from the tertiary to the primary amine as a result of increasing the number of hydrogen bonding per nitrogen. Propylamine has two hydrogens connected to the nitrogen and each can make a hydrogen bond with a neighboring nitrogen atom from another molecule.
How does hydrogen bonding affect physical properties?
As expected, hydrogen bonding affects the physical properties which we can see, for example, by comparing the boiling point of ethanol shown above and dimethyl ether. These two are constitutional isomers meaning they have the same chemical formula and therefore, molecular mass.
What type of interaction occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to an electronegative atom?
You can check the previous post for more details about the hydrogen bonding. In short, it is another type of intermolecular electrostatic interaction that occurs between a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom such as O, N, or F, is attracted to a lone pair of electrons on an atom in another molecule.
How do inorganic compounds melt?
For inorganic compound to melt, the ions have to move past each other. That requires enough energy to overcome the ionic bonds between the ions. For organic compounds to melt, the molecules have to move past each other. That requires enough energy to overcome the intermolecular forces between the molecules.
Which compounds have lower melting points?
Most carbon compounds are molecular, and molecular compounds always have lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds, or network covalent compounds like silicon carbide. That’s because ionic and covalent bonds are much stronger than the forces between neutral molecules such as methane or naphthalene. 712 views.
Why are ionic compounds always stable?
Another thing is ionic compounds always exist as crystals formed of numerous molecules. This makes ionic compounds very stable to heat and they tend to have very high melting and boiling points.
What is the melting point of ta4hfc5?
Under ordinary conditions the ceramic Ta4HfC5 tantalum hafnium carbide is reported to have a melting point of 4215 °C. Under very high pressures (by which I mean ludicrously high pressures, such as deep in the Earth’s core), many materials are kept in the solid state at much higher temperatures than at one atmosphere.
What temperature does a solid change to?
What it can do is melt, which happens at about 0 degrees Celsius (at standard pressure. If pressure changes, the melting point will change.) But a solid CAN change directly to a gas, without melting and spending time as a liquid. This process is called sublimation.
Why do crystals grow?
Crystals grow when water in the atmosphere changes directly to a solid. By the way, under normal conditions both these processes happen slowly, which is why it takes a while for food to develop “freezer burn”. Related Answer. Robert Weber. Answered 4 years ago · Author has 124 answers and 143.7K answer views.
Is the attraction between the molecules weaker than the intermolecular forces?
That requires enough energy to overcome the intermolecular forces between the molecules. These are not the covalent bonds between the atoms. They are the attraction between the molecules. Intermolecular forces of attraction are weaker than ionic bonds.
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?
Ionic compounds usually have high melting points because the electrostatic forces holding the ions (ion-ion interaction) are much stronger. In organic compounds the presence of polarity, or especially hydrogen bonding, generally leads to higher melting point. Consider the following examples.
What is the melting point of a compound?
The melting point is an important physical property of a compound. The melting point can be used to identify a substance and as an indication of its purity. The melting point of solid is defined as the temperature at which the solid exists in equilibrium with its liquid under an external pressure of one atmosphere.
Why is the melting point of butyric acid higher than that of butyric acid?
The melting point of sodium butanoate is higher than that of butyric acid because the attractive force in sodium butanoate is strong ionic interation.
What is the effect of the force of attraction between the molecules on the melting point of a compound?
2. Force of attraction between the molecules. The force of attraction between the molecules affects the melting point of a compound. Stronger intermolecular interactions result in higher melting points. Ionic compounds usually have high melting points because the electrostatic forces holding the ions (ion-ion interaction) are much stronger.
What happens when two materials have the same melting point?
If two materials have the same melting point, then they may (not necessarily) have the same structure. Consider the isomers n-butanol and t-butanol. Both have the same molecular formula (C 4 H 10 O), but differ in their structure. 2. Force of attraction between the molecules. The force of attraction between the molecules affects ...
What temperature does a compound melt?
A pure crystalline compound usually possesses a sharp melting point and it melts completely over a narrow range of temperature of not more that 0.5-1 o C. The presence of even small amount of impurities usually produces a depression in the freezing points and shows a marked increase in the width of the melting point range.
What does it mean when a molecule has a different melting point?
Melting point is also used for the identification and characterisation of a compound. If the melting point of two pure samples shows a clear difference in melting points, it indicates that the two compounds must have different structural arrangements. or they must have different arrangements of atoms or configurations.
What is the melting point of organic compounds?
The melting point determination of organic compounds helps people understand the physical and chemical properties of the substance. Many different factors affect the melting point of any substance, such as the force of attraction, impurities present in the substance, and the molecules' size and structure.
What is the method used to determine the melting point of organic compounds?
A small experiment can be conducted to determine the melting point determination of organic compounds. One such is given below. Thiele tube method – for this experiment, a tube known as Thiele tube is used, which is designed to contain oil and experiment with heat. A capillary, a thermometer, and a bunsen burner are required to complete ...
What is the melting range of an impure substance?
An extremely pure substance will have a melting range of one or two degrees. Impure substances have a much higher range and tend to depress and broaden the melting range, which is higher and smaller for the original, impure one. The melting occurs at a certain temperature change, but it depends on the structure of the molecule.
How to determine melting point of a substance?
There are various experiments through which the melting point of a certain substance can be determined; one such method is the capillary method. The capillary method uses similar equipment like the Thiele melting point method, such as a thermometer, a capillary tube, Bunsen burner, and eyepiece through which it is observed. While the experiment is going, the heat needs to be controlled at proper intervals, and the sample or the substance is observed through the eyepiece. Record the temperature on the thermometer when the sample starts to melt and record.
What is the role of the size of the molecule in the melting point determination of organic compounds?
The Size of the Molecule- Melting point determination of organic compounds helps to identify the organic compound properties, both physical and chemical. The structure of the molecule has a big role to play. The tighter the molecules are packed, the higher will be the melting point. If the structure of the molecules is loose, then the melting point would be lower.
Why do different substances have different melting points?
Different substances have different melting points due to their structure , composition , the force of attraction between the molecules of the organic compound, and the level of impure particles present in the compound. If the molecules' structure is tightly packed, then the heating range will be higher than for the loosely packed compounds.
Why is a pure crystal impure?
However, the crystals are impure when they occur in a mixture of two different organic molecules because they don't fit together well. Thus, It takes more heat to melt the pure structure.
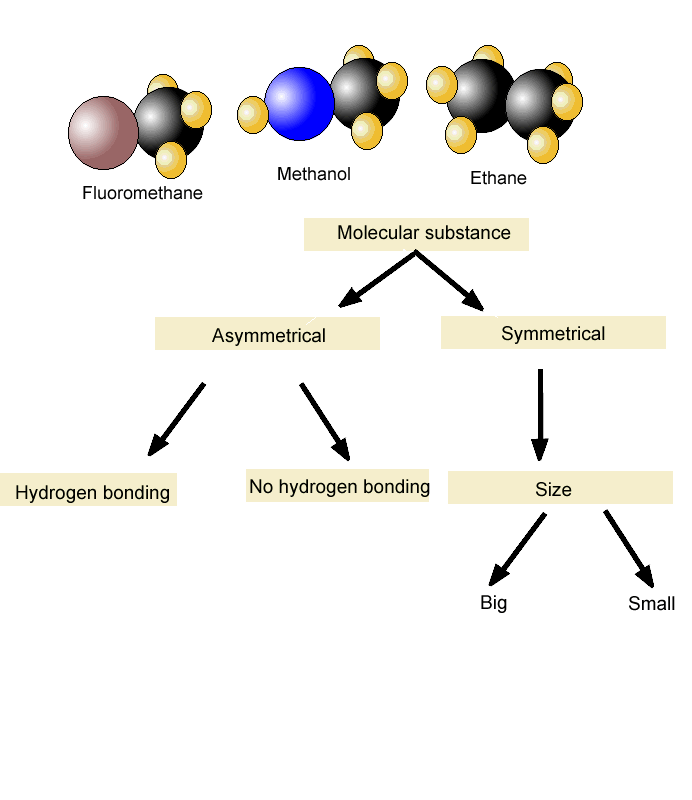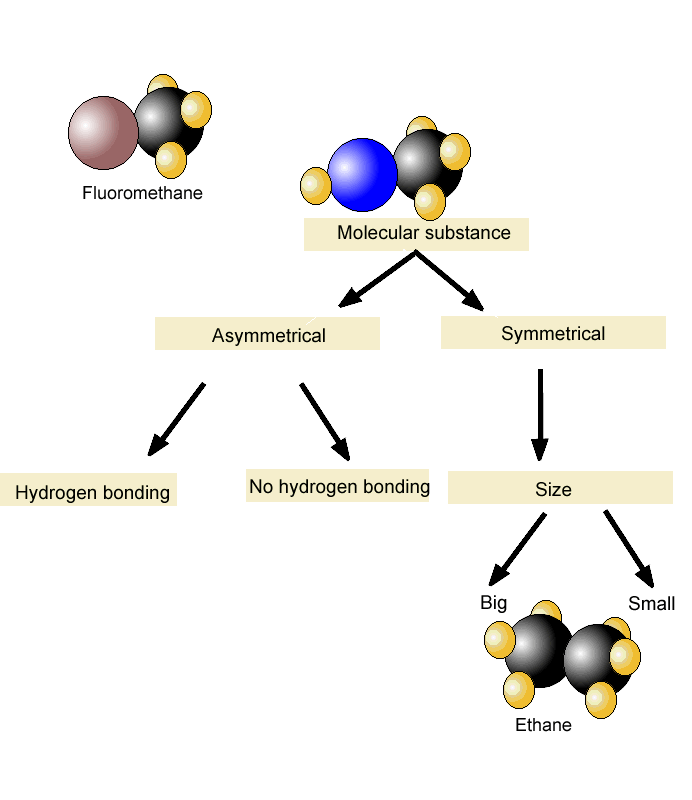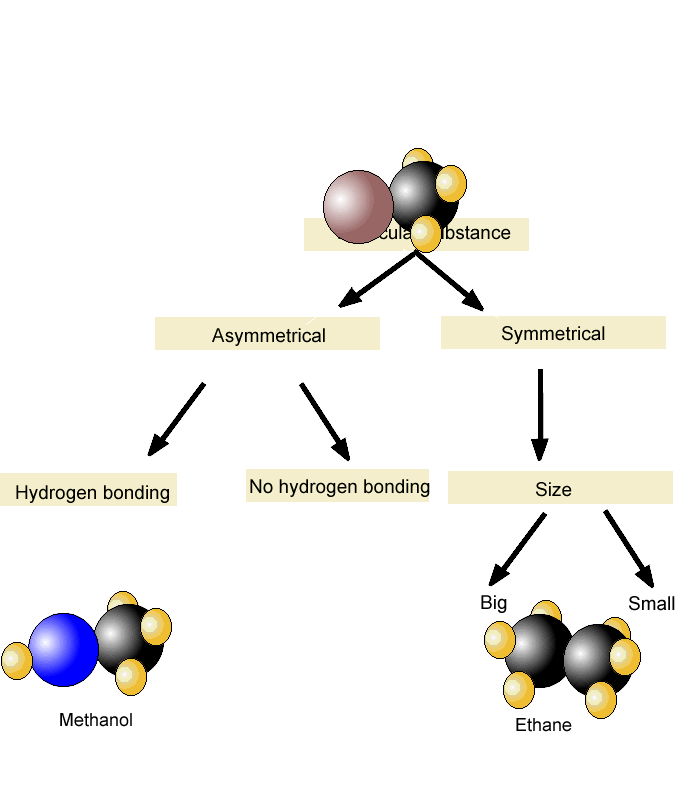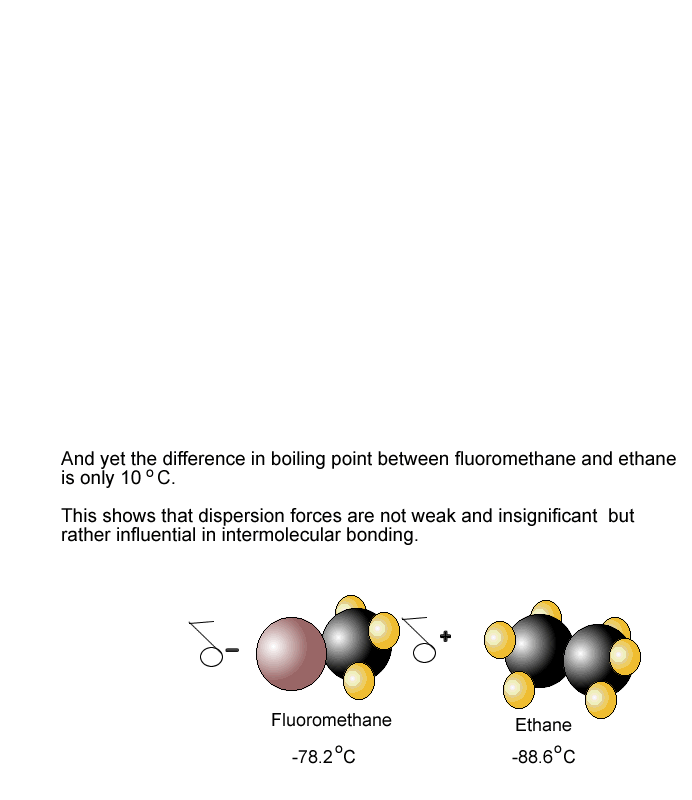
Boiling Point and Dipole-Dipole Interactions
Boiling Point and Hydrogen Bonding
- You can check the previous post for more details about the hydrogen bonding. In short, it is another type of intermolecular electrostatic interaction that occursbetween a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom such as O, N, or F, is attracted to alone pair of electrons on an atom inanother molecule. As expected, hydrogen bonding affects the physical properties which …
London Or Van Der Waals Forces
- Another factor that influences the boiling point is the surface of the molecule. The larger this surface, the stronger the intermolecular interactions, and thus, the higher the boiling point. This can be seen by comparing the boiling points of pentane, 2-methylbutane, and 2,2-dimethylpropane: Again, all three are constitutional isomers and have identical molecular weight…
Melting Points
- Just like we simplified the boiling point to explain the effect of intermolecular interactions on it, let’s formulate that the melting point of a compound is the temperature at which it is converted from the solid to the liquid phase. In general, the melting point of compounds with similar molecular weight increases with stronger intermolecular interactions. For example, pentane has …
Symmetry and Melting Point
- Aside from the intermolecular interactions, however,the melting point depends also on how the molecules are packed or arranged in the solid form. The more symmetrical they are, the better they pack and form a perfect crystal lattice which results in a higher melting point. So, as the molecules fit tighter, more energy is required to break the latti...