
What foods to avoid if phosphorus is high?
What foods to avoid if phosphorus is high? Dairy foods. Beans. Lentils. Nuts. Bran cereals. Oatmeal. Colas and other drinks with phosphate additives. Some bottled ice tea. In respect to this, what foods are high in phosphorus? Chicken and Turkey. Share on Pinterest. Pork.
What are facts about phosphorus?
Facts About Phosphorus. Phosphorus is in Period 3 and Group 15 of the periodic table. It has 15 protons, so it has the atomic number 15. This also means it is the 15th element on the periodic table.
What are the signs of phosphorus deficiency?
These are some deficiency symptoms listed below:
- Red or purple blots on the leaf surfaces
- Loss of older leaves
- Plants stunted and the colour of leaves become dark green than normal
- Seed dormancy increases
- Premature fall of leaves and fruit
- Phosphatase enzyme activity increases
- Causes accumulation of carbohydrates in soybean plant
Is phosphate and phosphorus the same in fertilizer?
There should be no difference in P fertilizer sources, as long as nutrient analysis differences are taken into account. While there are certain situations where one product performs better, phosphorus fertilizer recommendations are the same regardless of the phosphate fertilizer source. Plus sign (+) if content is closed, 'X' if content is open.
See more
What does phosphorus do for potatoes?
Phosphorus is important for early root and shoot development, providing energy for plant processes such as ion uptake and transport.
Do potatoes need potassium or phosphorus?
Potatoes use more potassium than any other nutrient – including nitrogen. Potassium (K) is required for nutrient movement in the potato plant.
How much phosphate do potatoes need?
Table 1. Uptake of soil nutrients by potato vines and tubers as a function of tuber yield.NutrientNutrient uptake from vinesNutrient uptake tuber yield: 500 cwt/APhosphorus (P)11 lb/A28 lb/APotassium (K)75 lb/A240 lb/ACalcium (Ca)43 lb/A7.4 lb/AMagnesium (Mg)25 lb/A14.7 lb/A7 more rows
Do potatoes like phosphate?
Phosphorus is an important nutrient for both potato yield and tuber quality. Potatoes can remove a considerable amount of P compared to other crops; for example, a 400-500 cwt/A yield could remove 60-80 lb P2O5/A.
Whats the best fertilizer for potatoes?
The best fertilizer for growing potatoes is one that has relatively low Nitrogen (N) and is at least twice as high in Phosphorous (P) and Potash (K). A good example of a suitable potato fertilizer ratio would be a 5-10-10.
What fertilizer do potatoes need the most?
Season and NPK Ratio A month or two after they've been planted, potatoes need lots of nitrogen, so a fertilizer with an NPK of 34-0-0 is the best choice. An NPK of 12-12-17 or 14-7-21 is best for the last couple of months before harvest when the plants require more potassium.
How do you increase the yield of potatoes?
The two key yield components of potato are tuber numbers per unit area, and tuber size or weight. Increased yields come from achieving the optimum tuber numbers, maintaining a green leaf canopy, and increasing tuber size and weight.
When should I fertilize my potatoes?
General recommendations instruct gardeners to apply a pre-plant and then fertilize monthly starting two weeks after planting. However, many extension professionals recommend applying fertilizer to the soil before planting and waiting on other applications until after tuber formation.
Is superphosphate good for potatoes?
Potatoes do not like having waterlogged soils as they will rot. You will be able to purchase Dynamic Lifter and superphosphate from your local nursery or hardware store.
Is Epsom salt good for potatoes?
Is Epsom salt good for potatoes? Yes, Epsom salt can be helpful when added to the soil of potato plants. It provides the plants with a good boost of magnesium, which is beneficial in stimulating biochemical reactions. It also helps to build strong cell walls and supports the growth process.
What nutrients do growing potatoes need?
All potatoes need nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to grow well. These are the three main numbers you'll see on bags of fertilizer (e.g., 10-10-10). Nitrogen is necessary for foliage growth, phosphorus encourages root development, and potassium helps the plant resist disease and pests.
Are coffee grounds good for potatoes?
Using coffee grounds on your potatoes work absolutely fine. Adding coffee grounds to your potato plants helps in giving them a considerable growth. You can add the grounds in form of a coffee compost blend and you can as well mix coffee compost with leafmold.
Can a person with kidney disease eat potatoes?
Objective(s): Despite the nutritional benefits of potato tuber, patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) should limit the consumption because of its high potassium content.
Does boiling potatoes remove potassium?
What's the best way to reduce potassium in potatoes? For the most effective potassium removal, potatoes must be cut into small pieces, sliced thin or grated. If boiled at least 10 minutes in a large pot of water, potassium is reduced by at least half the original amount.
Are potatoes OK for renal diet?
The National Kidney Foundation classifies potato, white and sweet, as a food with high potassium content (more than 200 g per portion) and recommends a limited intake, although culinary techniques for minimizing potassium content are applied. A potassium-restricted diet typically allows about 2,000 mg per day.
How long do you have to soak potatoes to get potassium out of them?
Leaching method: Peel and dice potatoes. Place in a large pot of warm tap water and soak for 2 to 4 hours.
What is the role of phosphorus in potato production?
Phosphorus is important for early root and shoot development, providing energy for plant processes such as ion uptake and transport.
What is the role of phosphorus in starch?
Following tuber initiation, phosphorus is an essential component for starch synthesis, transport and storage. Under situations of high phosphorus tie-up e.g. volcanic soils or low organic matter, low P, sandy soils, it is important that fertilizer-P is placed close to the seed piece.
Why band phosphorus fertilizer?
Because phosphorus is relatively immobile in the soil, banding the fertilizer usually works better than broadcasting.
Is foliar phosphate good for tuber growth?
However, foliar phosphate is not a substitute for soil applied phosphate. Without adequate soil phosphate early season growth is sub-optimal .
Does phosphorus affect starch quality?
Phosphorus and starch viscosity. Phosphate fertilizer use can influence starch quality. By increasing the tuber P content, the viscosity of the gelatinized starch is also increased and the gelatinization temperature decreased.
How to get calcium in potatoes?
The best way of having adequate calcium in the soil is to apply lime to bring the pH to acceptable levels.
Why is pH important in fertilizer?
pH. pH is an important factor in any fertilizer program and in controlling common scab. As pH increases to near 6.0 plant nutrients also increase and toxic elements become less available, thereby providing optimal growing conditions from the standpoint of nutrients.
What causes salt in fertilizer?
The carriers of nitrogen and potassium are the primary fertilizer components that create salt problems. Salts are a factor when high concentrations of fertilizers are applied in bands, as they are in potato production, and applied under optimal soil moisture conditions and then conditions turn dry. The salts in the fertilizer bands move with the soil moisture to the surface and concentrate causing root "burn" thereby retarding emergence and subsequent growth. The potential for salt injury is greatest in sandy soils and when fertilizer is placed close to seed pieces.
Does gypsum change pH?
Gypsum suppli es calci um without changing the soil pH. (An application of 1400 lbs of gypsum will supply approximately 300 lbs calcium/A.) Foliar applications of calcium and sidedress applications of calcium nitrate (at rates commonly applied in the Northeast) do little to provide adequate calcium for plant nutrition.
Do potatoes need magnesium?
Potatoes have a relatively high demand for magnesium. If a soil is at least 5.0 or magnesium levels are greater than 100 lbs/A, magnesium is not needed in fertilizer bands. At pH levels below 5.0 or when soil magnesium are less 100 lbs/A, 30 lbs/A of elemental magnesium (50 lbs of MgO/A) are recommended.
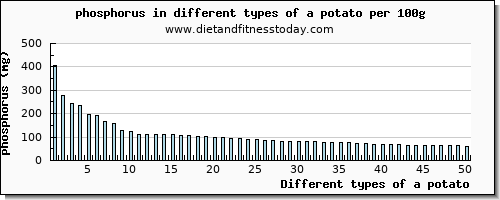
How much phosphorus is in a potato?
Welcome to the nutritional phosphorus content in 67 different types of potatoes, ranging from 404 mg to 22 mg per 100g. The basic type of potatoes is Potatoes, raw, skin, where the amount of phosphorus in 100g is 38 mg.
What is the lowest amount of phosphorus in 100g of potatoes?
The lowest amount of phosphorus in 100g is in Potatoes, canned, solids and liquids which contains 22 mg. This gives as percentage of the recommended daily allowance 2 % of the RDA. For this 100g serving the amount of Calories is 44 kcal, the amount of Protein is 1.2 g, the amount of Fat is 0.11 g, the amount of Carbohydrate is 9.89 g. ...
What is the highest amount of phosphorus in food?
The highest amount of phosphorus from the 4 raw items is in Potatoes, white, flesh and skin, raw where the content is 62 mg per 100g. The number of food items which are cooked are 12 items. The highest amount of phosphorus from the 12 cooked items is in Potatoes, microwaved, cooked in skin, flesh, without salt where the amount is 109 mg per 100g.
How many grams of phosphorus are in 100 calories?
100 calories of potatoes, raw, skin is a serving size of 1.72 g, and the amount of Phosphorus is 65.52 mg (6.9% RDA). Other important and related nutrients and macronutrients such as Fat, in 100 Calories are as follows; Protein 4.43 g (8.62% RDA), Fat 0.17 g (0% RDA), Carbohydrate 21.45 g (17.24% RDA).
How much phosphorus is in a potato?
A medium baked Russet potato provides you with 123 milligrams of phosphorus, which is about 18 percent of the recommended dietary allowance for adults of 700 milligrams per day. Red-skinned and white potatoes have similar phosphorus levels, but sweet potatoes have slightly lower phosphorus levels with 97 milligrams in a potato of the same size.
Which potatoes have the lowest phosphorus?
Red-skinned and white potatoes have similar phosphorus levels, but sweet potatoes have slightly lower phosphorus levels with 97 milligrams in a potato of the same size.
Why is phosphorus important for bones?
Phosphorus is also important for keeping your bones and teeth healthy as well as getting rid of waste products in your kidneys, forming DNA, repairing any damaged cells and keeping your muscles from getting really sore after a workout. Without phosphorus your nerves, muscles and heart wouldn't work properly.
What are the symptoms of not getting enough phosphorus?
Not getting enough phosphorus can cause symptoms including fatigue, anxiety, fragile bones, numbness, irritability, loss of appetite, stiff joints and irregular breathing. Alcoholism, diabetes, celiac disease, Crohn's disease and certain types of medications can make this type of deficiency more likely. Potatoes, one of the most commonly eaten ...
What is the best source of phosphorus?
Potatoes, one of the most commonly eaten vegetables in the United States, are a good source of phosphorus and can help you meet your recommended phosphorus intake.
Is potato fattening?
While some people may consider potatoes fattening, they are actually low in calories and quite nutritious, providing you with a number of essential vitamins and minerals, including potassium and vitamin C.
Do beans absorb phosphorus?
Just keep in mind that your body doesn 't absorb the phosphorus in beans as well as that found in animal products due to the way it is stored in the beans. Only about half of the phosphorus in beans, whole grains, nuts and seeds is available for absorption.
Why is it important to feed potatoes while growing?
The most important thing about potato feed while growing is ensuring they get the correct nutrition during their growth stage. This can lead to producing better yields than usual.
How do potatoes grow?
The soil composition also affects how well potatoes grow. Potatoes enjoy good drainage and plenty of organic matter, such as compost or peat moss. In particular, the soil should be well-drained so that the plants do not get too wet when it rains or it snows.
What Are the Factors That Affect Potato Growth?
Many factors affect potato growth, and many of these are external to the potato itself. The amount of light available is critical for potatoes. If enough light is not t available, they will grow spindly.
How Can Gardeners Increase Potato Yields?
Potatoes have high water with nutrient requirements, and the crop can be susceptible to diseases. As a result, potato growers need to take care of their crops all year round. This means frequent inspections and the use of pesticides. Because of these problems, gardeners are looking for better ways to grow potatoes without the risk of disease or pests.
How Deep Should I Plant Potato Seeds To Increase Yields?
Some gardeners have had bad potato growth experiences, and they don’t know why. They might be planting potatoes too deep or putting them in the ground too early, but the best way to ensure your yields are good is to plant them at the correct depth and wait until the soil warms up.
What is the best way to increase potato yield?
Potato feed for increased yields includes everything from fertilizer, fertilizer application techniques, and irrigation practices to plant spacing . Using a combination of these methods, gardeners can increase yield potential through better potato cultivation practices.
Why are potatoes grown in colder zones?
Potato plants are often grown in colder zones due to their lower water needs and generally shorter growing season. In warmer zones, people recommend that you grow potatoes as a cover crop.
What nutrients are needed for potatoes to grow?
Calcium is a vital nutrient for potatoes and most aspects of tuber quality can be improved by having a sufficient supply of calcium during growth.
How to achieve high potato yields?
To achieve high potato yields it is important to prolong the potato bulking stage by extending the green leaf canopy duration.
What are the two elements that are used in plant growth?
Nitrogen and Potassium - early growth and dry matter#N#Phosphate - more tubers, growth and dry matter#N#Magnesium - for plant development#N#Zinc and Manganese - Powdery and Common Scab control#N#Sulphur - Common and Powdery Scab and tuber numbers
What is a liquid micronutrient fertiliser?
A flowable liquid micronutrient fertiliser containing 500 g/l of manganese for application as a foliar spray or seed treatment to a wide range of crops. A liquid fertiliser containing a high concentration of phosphate together with potash and magnesium for foliar application to potatoes and other crops.
What are the nutrients in potatoes?
High-Yield Potatoes Have High Nitrogen and Potassium Needs. Potatoes are grown in nearly every state in the U.S., with sales in excess of $3 billion. Yield, tuber size and specific gravity (dry-matter content) influence quality factors such as frying properties and flavor.
How much nitrogen is in russet potatoes?
Don Horneck of Oregon State University. The total amount of nitrogen (353 pounds N) and potassium oxide (618 pounds K₂O) he found contained in the vines and tubers was very large. Nutrients removed from the field by the tubers was 214 lbs/a of N and 288 lbs/a of K₂O. Phosphorus (P₂O₅) requirements totaled 92 lbs/a of P₂O₅ with nearly three-quarters leaving the field in the tubers. Accumulation of magnesium ( Mg) and sulfur (S) was 40 and 35 lbs/a, respectively. The high requirement for both N and K suggests that their application be timed with plant growth stage and needs to achieve optimum crop-use efficiency and nutrient effectiveness.
What is the P fertilizer for plants?
Factors to consider in P nutrient management are the relatively shallow root system and cool soils at planting time. Since P moves little even in sandy soils, placement within the primary root zone is desirable. Growers select a particular P fertilizer source, such as monoammonium phosphate (MAP) or diam monium phosphate (DAP), by preference and compatibility with their equipment.
What is the maturity class of potato?
According to Dr. Rob Mikkelsen, the maturity class or growing-season length is a primary factor determining potato nutrient requirements.¹ Short-season varieties generally demand intensive nutrients during the vegetative and tuber initiation stages of growth.
What factors are important for P nutrient management?
Factors to consider in P nutrient management are the relatively shallow root system and cool soils at planting time. Since P moves little even in sandy soils, placement within the primary root zone is desirable.
