
What is a sea urchin pedicellaria?
Numerous pedicellariae (singular = pedicellaria) of several types are present on the body surface and some can be seen in the vicinity of the mouth. Sea urchin pedicellariae have three tiny jaws at the end of a pedicle . Pedicellariae have a skeleton consisting of three ossicles in the jaws and a long slender ossicle in the pedicle.
What is a pedicellaria?
Pedicellariae are compound ossicles that articulate with other ossicles and protrude from the aboral (upper) surface of some sea stars (and also the test of sea urchins). They usually have short fleshy stalks and either two or three moveable ossicles forming a set of pincer-like jaws.
What is a sea cucumber?
Sea cucumbers are echinoderms from the class Holothuroidea. They are marine animals with a leathery skin and an elongated body containing a single, branched gonad. Sea cucumbers are found on the sea floor worldwide.
What is the phylogeny of a sea cucumber?
Phylogeny and classification. In the sea cucumber the ossicles are only found in the dermis, making them a very supple organism. For most echinoderms, their ossicles are found in units making up a three dimensional structure. However, in sea cucumbers the ossicles are found in a two-dimensional network.

Do sea cucumbers have Ambulacra?
Like sea urchins, most sea cucumbers have five strip-like ambulacral areas running along the length of the body from the mouth to the anus. The three on the lower surface have numerous tube feet, often with suckers, that allow the animal to crawl along; they are called trivium.
Do echinoderms have pedicellariae?
A pedicellaria (plural: pedicellariae) is a small wrench- or claw-shaped appendage with movable jaws, called valves, commonly found on echinoderms (phylum Echinodermata), particularly in sea stars (class Asteroidea) and sea urchins (class Echinoidea).
What is the white thing that comes out of a sea cucumber?
Cuvierian tubules are clusters of fine tubes located at the base of the respiratory tree in some sea cucumbers in the genera Bohadschia, Holothuria and Pearsonothuria, all of which are included in the family Holothuriidae. The tubules can be discharged through the anus when the sea cucumber is stressed.
Do sea cucumbers have rays or spines?
Aptly named, sea cucumbers are the sluggish creatures that often cause new divers to ask, “What are those things on the sea floor that look like cucumbers?” They differ from other echinoderms in that they are more soft-bodied and their leathery skin lacks spines, but the skin of many species is covered with wart-like ...
Do all sea stars have pedicellariae?
Pedicellariae are found only in echinoderms, particularly sea stars and sea urchins. The type found on collector urchins are known as globiferous, meaning they have a three-pronged jaw and a venom sac at the end of a long stalk.
What features of the sea cucumber show it is an echinoderm?
Sea cucumbers are part of a larger animal group called echinoderms, which also contains starfish and sea urchins. Their body shape is similar to a cucumber, but they have small tentacle-like tube feet that are used for locomotion and feeding.
Is it okay to pick up a sea cucumber?
Although most sea cucumbers are harmless to humans, you should avoid picking them up as doing so may harm them or cause them to become disoriented. These creatures are benthic, which means that they live on the seafloor, but their young float in the currents and are considered planktonic animals.
What comes out of sea cucumbers?
When threatened, a sea cucumber contracts its body, tears a hole in an interior wall, and shoots a few of these noodles out its anus. The threads immediately stretch when they hit seawater, growing up to 20 times their original length before stiffening.
What happens when you squeeze a sea cucumber?
They violently contract their muscles and jettison some of their internal organs out of their anus. The missing body parts are quickly regenerated.
Can you touch a sea cucumber?
Sea cucumbers are extremely sensitive. They don't really like being touched. Even if you do see a sea cucumber, please refrain from touching.
Are sea cucumbers venomous?
All sea cucumbers possess an extremely potent poison, known as holothurin. This is concentrated in the socalled Cuvierian tubules, threadlike appendages in the end of the gut. In the event of a serious attack the sea cucumber expels these Cuvierian tubules through its anus towards the aggressor.
Do sea cucumbers have spiny skin?
The phylum Echinodermata , which contains about 7,000 species, gets its name from the Greek, literally meaning "spiny skin." Many echinoderms actually do have "spiny" skin, but others do not. This phylum exists exclusively in the sea, and cannot be found on land or in fresh water.
Do sea urchins have pedicellariae?
Sea urchins are part of the phylum Echinodermata which also includes starfish. Sea urchins have globular bodies covered by calcified spines. The spines are either rounded at the tip or hollow for envenomation. The also can have pedicellariae that can grasp and envenomate, typically with more venom than in the spines.
Is Offence and defense organ in echinoderms?
Answer: The pedicellariae is the offence and defense organ in echinoderms.
What is the function of the pedicellariae in a sea star?
Pedicellariae attach and articulate to small granules on the surface of the test. In life the pedicellariae are in constant motion. The valves that form the head can open and close and the primary function of the pedicellariae is to keep the surface of the test free of debris and small parasites.
Which type of forceps like pedicellariae are present in starfish?
two-valved pedicellariae comprise the order Forcipulata—the “forceps carriers.” The pedicellariae have protective and, sometimes, food-taking functions. In most species the arms are long and rounded, and the disk is small.
What do sea cucumbers eat?
They feed primarily on tiny pieces of algae and marine creatures, which get broken down into smaller and smaller pieces, similar to how earthworms break down organic matter in gardens, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).The sand that the sea cucumbers ingest passes straight through their system and comes out the other end in the form of a sandy poop log.
How do sea cucumbers reproduce?
Most species of sea cucumbers reproduce sexual ly via external fertilization, according to National Geographic. This means that the males release their sperm into the water and females release their eggs into the water, and hopefully a few egg and sperm run into each other.
How do sea cucumber larvae drift?
The sea cucumber larvae drift with the currents until they grow large enough to latch onto the ocean floor.
Where are sea cucumbers exported?
Most of the animals that are harvested are exported to Asian markets, where sea cucumbers are considered a delicacy. In some areas, such as Papua New Guinea, overfishing of sea cucumbers has completely decimated the local population, Cool Green Science reported.
What is the respiratory system of sea cucumbers?
A sea cucumber's respiratory system is made up of two respiratory trees on either side of the digestive tract, according to the University of Alaska Southeast. Water flows into the body through the base of the two Y-shaped trees at the anus, and oxygen is transferred across a thin membrane into the body cavity.
What phylum is sand dollars?
This class falls under the Echinodermata phylum, which also includes many other well-known marine invertebrates, such as sea stars, sea urchins and sand dollars, according to National Geographic.
Do sea cucumbers have bones?
Although sea cucumbers don't have bones, many species of the animal have a rudimentary skeleton made of microscopic plates of calcium carbonate that lie loosely scattered underneath the skin, according to UCMP. Some species can align their skeletal plates when threatened so that their bodies become rigid, according to the University of Alaska Southeast .
What is the class of sea cucumbers?
The class Holothruoidea is better known by as the sea cucumbers. Sea cucumbers are cylindrical echinoderm animals with feathery tentacles at the mouth end of their bodies. They are often mistakenly called worms. Some species resembles fat pickles a few centimeters long (Fig. 3.94 A). Others are like thin tubes over a meter long (Fig. 3.94 B). These animals are common residents of reefs and rocky shorelines worldwide. A few species swim constantly in the water, seldom touching the bottom; they are the only members of this phylum to do so. Some Pacific islanders collect sea cucumbers, remove their intestines, and dry the muscular body wall, making a food eaten in many countries.
How many rows of tube feet are there in a sea cucumber?
Fig. 3.85. ( D) Most species of sea cucumber have five rows of tube feet running along the length of their cylindrical bodies. The sea cucumber Pseudocolochirus violaceus is better known by its common name, the sea apple.
What are the two surfaces of the echinoderm?
In the echinoderms there are two surfaces. One is the oral surface , where the mouth is and the tube feet project. The tube feet on the oral surface are limited to distinct regions called the ambulacral regions. The other surface is the aboral, which typically contains the anal opening of the digestive system.
How do echinoderms move?
An echinoderm moves by using many tube feet. Tube feet are small, delicate projections attached along the side of a water-filled tube called a radial canal. Figure 3.85 shows some examples of echinoderm tube feet. Tube feet extend through the small holes in the skeleton to the outside.
What are sea urchins?
Sea urchins belong to the class Echinoidea, named for the movable spines projecting from their body like a hedgehog’s spines (from the Greek word echinoid meaning like a hedgehog ). Sea urchins (Fig. 3.83 A) are common around the world, from the ocean’s shoreline to great depths and from tropical waters to polar waters. Sea urchins are relatively small; most species could fit in the palm of your hand. The spines are adaptations that protect the urchins from predators. Spines and tube feet help urchins move and get food. The long, thin, sharp spines of some sea urchins easily penetrate flesh and in some species, toxic chemicals on the tissue covering the sharp spines make its stab extremely painful (Fig. 3.87 A and B). Other species, with short, thick, or blunt spines are safe to handle (Fig. 3.87 C and D). A few species that have adapted to live in the wave surge zone of rocky coastlines have flattened spines (Fig. 3.87 D). Flat, broad plate spines give these urchins a low profile and prevent them from getting swept away by powerful waves. Sand dollars have fine velvet-textured spines that help these animals burrow into sand (Fig. 3.87 E). Pedicellariae are small jaw-like pincher appendages found on many species of sea urchins and sea stars (Fig. 3.88). They are typically attached to the echinoderm body at the base of the spines. The name pedicellaria comes from the Latin root words ped - meaning foot and - icellus meaning little. A pedicellaria snaps open if something touches its outer surface; it snaps shut if it is touched on its inner surface. Some pedicellariae are toxic, containing a small poison gland. Others have powerful jaws that can crush small organisms.
Why do sea stars have spines?
Some sea stars have spines extending from the ossicles, to help defend them from predators. Sea stars have a water vascular system and tube feet much like those of the sea urchins. Ambulacral grooves (from the Latin root ambul meaning walk) are narrow channels in the oral surface of a sea star filled with tube feet.
What is the water vascular system of sea urchins?
Water vascular system of sea urchin. Image by Byron Inouye. The water vascular system is a complex series of canals running through an echinoderm’s body (Fig. 3.84). It is a hydraulic pressure system that aids in movement.
How to remove pedicellariae?
Remove several pedicellariaewith your fine forceps and place them in a drop of bleach on a microscope slide. Wait a few minutes for the organic tissue to be oxidized and then place a coverslip over the drop. Examine it with the compound microscope and look for the jaw-like ossicles. These pedicellariae contain three ossicles. One is a short basal piece in the stalk, whereas the other two support the two jaws. Tiny muscles extend between these ossicles to operate the jaws but these will have been removed by the bleach.
What is excretion in echinoderms?
Excretion in echinoderms is by simple diffusion of metabolic wastes (ammonia) across thin permeable regions of the body wall. A variety of gas exchange structures, including the tube feet, is found in various echinoderms. A hemal system is present but its role in transport is still poorly understood and the chief transport system is the circulating fluid of the various coelomic compartments. The hemal system may be a transport system that delivers nutrients from the gut to the coelomic compartments for local distribution. The nervous system consists of two central nerve rings with radial nerves to the periphery. Echinoderms are dioecious and fertilization is usually external.
Where are sea stars found?
The sea star, Asterias forbesi, is common in shallow water along the Atlantic Coast of North America from the Gulf of Maine to the Gulf of Mexico.
Is an echinoderm a marine organism?
The adult radial symmetry is pentamerous, with body parts occurring in fives or multiples of five. All echinoderms are marine and benthic. About 6000 extant species are known, but the fossil record includes about 13,000 extinct species.
Is bipinnaria a starfish?
With age, the bipinnaria becomes a juvenile starfish. These juveniles are not on the composite slide. The juvenile starfish has five pairs of ciliated (for swimming) larval arms. It is the will settle out of the plankton onto a (hopefully) suitable substrate and metamorphose into the pentaradial adult.
What is the purpose of pedicellariae?
They may be scattered over the surface or may be grouped around spines. Their function is to pick off debris so as to keep the surface clean and to prevent larvae of other invertebrates from settling and growing there.
What are the ossicles of sea stars?
Paxillae are small pillar-shaped ossicles with flat tops sometimes found covering the aboral surface of sea stars such as Luidia, Astropecten and Goniaster that live underneath sediment. Their stalks emerge from the body wall and their tops, each fringed with short spines, and abut each other to form a protective external false skin. Beneath this is a water-filled cavity which contains the madreporite and delicate gill structures known as papillae.
How are sea urchins tested?
Sea urchins are covered with plates which are usually fused together to give a rigid test, but in the order Echinothurioida, the test is leathery because the plates are separate. The test is divided into five segments that extend from the apex to the mouth. Each contains two ambulacral rows of plates alternating with two interambulacral rows. The ambulacral plates are each pierced by a pair of pores through which the active tube feet are connected to the water vascular system. Ossicles in the form of spines connect to tubercles on some of the plates. Sea urchins have several types of pedicellariae, some of which are toxic. A ring of specialised plates surround the aboral pole consisting of five genital plates, one of which is the madreporite, and five smaller ocular plates. Other large specialist plates surround the mouth in a set of jaws known as Aristotle's lantern.
How are ossicles made?
Ossicles are created intracellularly by specialised secretory cells known as sclerocytes in the dermis of the body wall of echinoderms. Each ossicle is composed of microcrystals of calcite arranged in a three-dimensional lattice known as a stereom. Under polarized light the ossicle behaves as if it were a single crystal because the axes of all the crystals are parallel. The space between the crystals is known as the stroma and allows entry to sclerocytes for enlargement and repair. The honeycomb structure is light but tough and collagenous ligaments connect the ossicles together. The ossicles are embedded in a tough connective tissue which is also part of the endoskeleton. When an ossicle becomes redundant, specialised cells known as phagocytes are able to reabsorb the calcareous material. All the ossicles, even those that protrude from the body wall, are covered by a thin layer of epidermis but functionally they act more like an exoskeleton than an endoskeleton.
What are the different types of osseicle?
Ossicles have a variety of forms including flat plates, spines, rods and crosses, and specialised compound structures including pedicellariae and paxillae.
What fossils have ossicles?
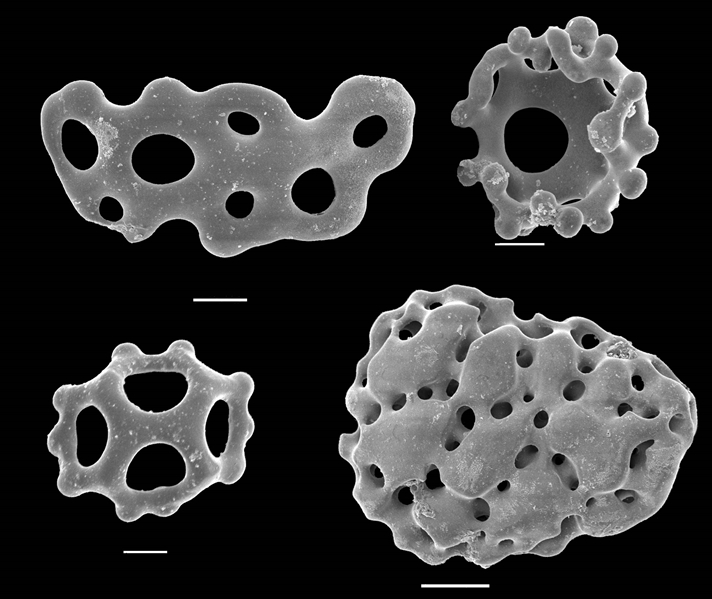
Crinoid fossils from the Jurassic showing ossicles. Several types of small ossicles are found in the body wall of sea cucumbers. Baskets are cup-shaped and usually have four projections. Buttons are disc-shaped and pierced by four holes and may be smooth or knobbed.
Where are ossicles found?
They are found in different forms and arrangements in sea urchins, starfish, brittle stars, sea cucumbers, and crinoids. The ossicles and spines (which are specialised sharp ossicles) are the only parts of the animal likely to be fossilized after an echinoderm dies.
Summary
Sea cucumbers are echinoderms from the class Holothuroidea . They are marine animals with a leathery skin and an elongated body containing a single, branched gonad. Sea cucumbers are found on the sea floor worldwide. The number of holothurian (/ˌhɒləˈθjʊəri.ən, ˌhoʊ-/) species worldwide is about 1,717, with the greatest number being in the Asia-Pacific region. Many of these …
Overview
Most sea cucumbers, as their name suggests, have a soft and cylindrical body, more or less lengthened, rounded off and occasionally fat in the extremities, and generally without solid appendages. Their shape ranges from almost spherical for "sea apples" (genus Pseudocolochirus) to serpent-like for Apodida or the classic sausage-shape, while others resemble caterpillars. The mouth is surro…
Anatomy
Sea cucumbers are typically 10 to 30 cm (4 to 12 in) in length, although the smallest known species are just 3 mm (0.12 in) long, and the largest can reach 3 meters (10 ft). The body ranges from almost spherical to worm-like, and lacks the arms found in many other echinoderms, such as starfish. The anterior end of the animal, containing the mouth, corresponds to the oral pole of other echino…
Life history and behaviour
Sea cucumbers can be found in great numbers on the deep seafloor, where they often make up the majority of the animal biomass. At depths deeper than 8.9 km (5.5 mi), sea cucumbers comprise 90% of the total mass of the macrofauna. Sea cucumbers form large herds that move across the bathygraphic features of the ocean, hunting food. The body of some deep water holothurians, such as E…
Phylogeny and classification
Holothuroidea (sea cucumbers) are one of five extant classes that make up the phylum Echinodermata. This is one of the most distinctive and diverse phyla, ranging from starfish to urchins to sea cucumbers and many other organisms. The echinoderms are mainly distinguished from other phyla by their body plan and organization. While the organisms in this phylum may not all look the sam…
Relation to humans
To supply the markets of Southern China, Makassar trepangers traded with the Indigenous Australians of Arnhem Land from at least the 18th century and probably earlier. This is the first recorded example of trade between the inhabitants of the Australian continent and their Asian neighbours.
There are many commercially important species of sea cucumber that are har…
Procurement
Sea cucumbers are harvested from the environment, both legally and illegally, and are increasingly farmed via aquaculture. The harvested animals are normally dried for resale. In 2016, prices on Alibaba ranged up to $1,000/kg.
In recent years, the sea cucumber industry in Alaska has increased due to increased demand for the skins and muscles to China. Wild sea cucumbers are caught by divers. Wild Alaskan sea cuc…
Conservation
In 2020, the Indian government created the world's first sea cucumber conservation area, the Dr KK Mohammed Koya Sea Cucumber Conservation Reserve, to protect the sea cucumber species. In India, the commercial harvesting and transportation of sea cucumbers is banned.