Stereoisomers that do not form mirror images of each other are termed as diastereomers. All have the same physical and chemical properties (except interaction with light). These have varying physical and chemical properties. They have the same molecular shape.
What are the physical properties of stereoisomers?
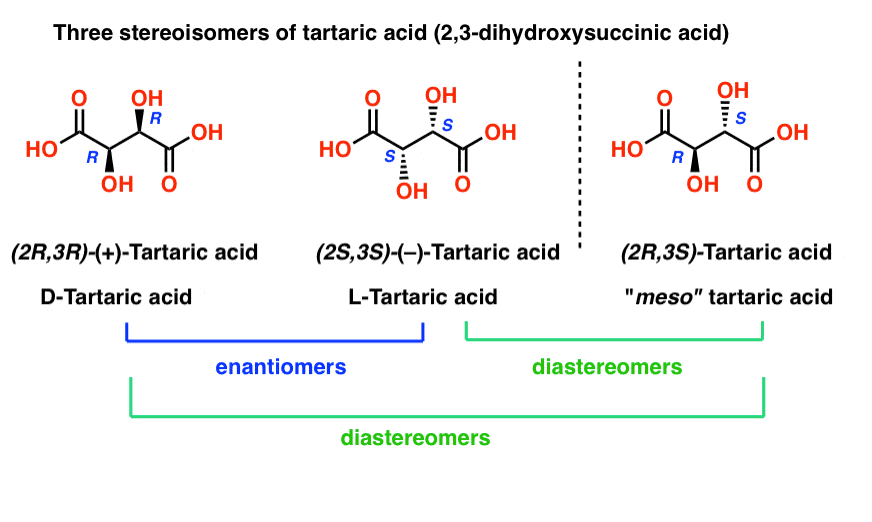
Physical Properties of Stereoisomers. If a molecule contains more than one chirality center and therefore consists of several pairs of enantiomers and diastereomers, the physical properties of each diastereomer must be noted. Tartaric acid, for instance, consists of three stereoisomers, a pair of enantiomers and a meso compound.
Do all optical isomers have the same properties?
Optical isomers have basically the same properties (melting points, boiling points, etc.) but there are a few exceptions (uses in biological mechanisms and optical activity). There are drugs, called enantiopure drugs, that have different effects based on whether the drug is a racemic mixture or purely one enantiomer.
What is the difference between enantiomers and diastereomers?
Enantiomers are equal in all their physical properties except for their optical rotation, as they rotate the plane of polarized light by equal amounts in opposite directions. In contrast, diastereomers are characteristically different in their physical properties, such as melting and boiling points, densities,...
What are the stereoisomers of tartaric acid?
Tartaric acid, for instance, consists of three stereoisomers, a pair of enantiomers and a meso compound. (+)- and (-)-tartaric acid represent a pair of entantiomers. They differ only in their direction of optical rotation.
Which stereoisomers have different physical properties?
Physical Properties of StereoisomersStereoisomerConfigurationDensity (g/ml)(+)-Tartaric acid(2R,3R)1.7598(-)-Tartaric acid(2S,3S)1.7598meso-Tartaric acid(2R,3S) / (2S,3R)1.6660Racemate of tartaric acid(2R,3R) and (2S,3S)1.7880
Do diastereomers have the same physical properties?
Diastereomers can have different physical properties and reactivity. They have different melting points and boiling points and different densities.
Are the physical properties of isomers the same?
They have the same formula but different structures. The word, "isomer", is from the Greek, meaning "same things", referring to their identical content. However, isomers often have very different physical and biological properties.
Do enantiomers have the same physical properties?
Enantiomers have identical chemical and physical properties and are indistinguishable from each other except for the direction of rotation of the plane of polarized light. They are described as optically active.
Why do enantiomers have identical physical properties?
they have the same melting point, the same solubility, and so on. Two compounds that are almost identical, but mirror images of each other, have exactly the same kinds of intermolecular attraction, so it may not be a surprise that their physical properties are identical.
Why do diastereomers have different physical properties?
1 Answer. Because they are different chemical compounds.
Why do isomers have the same chemical properties?
isomers. isomers Chemical compounds having the same molecular formula but different properties due to the different arrangement of atoms within the molecules.
What properties of isomers are same?
Isomers have the same number of atoms of each element in them and the same atomic weight but differ in other properties. For example, there are two compounds with the molecular formula C2H6O.
How do stereoisomers differ from one another?
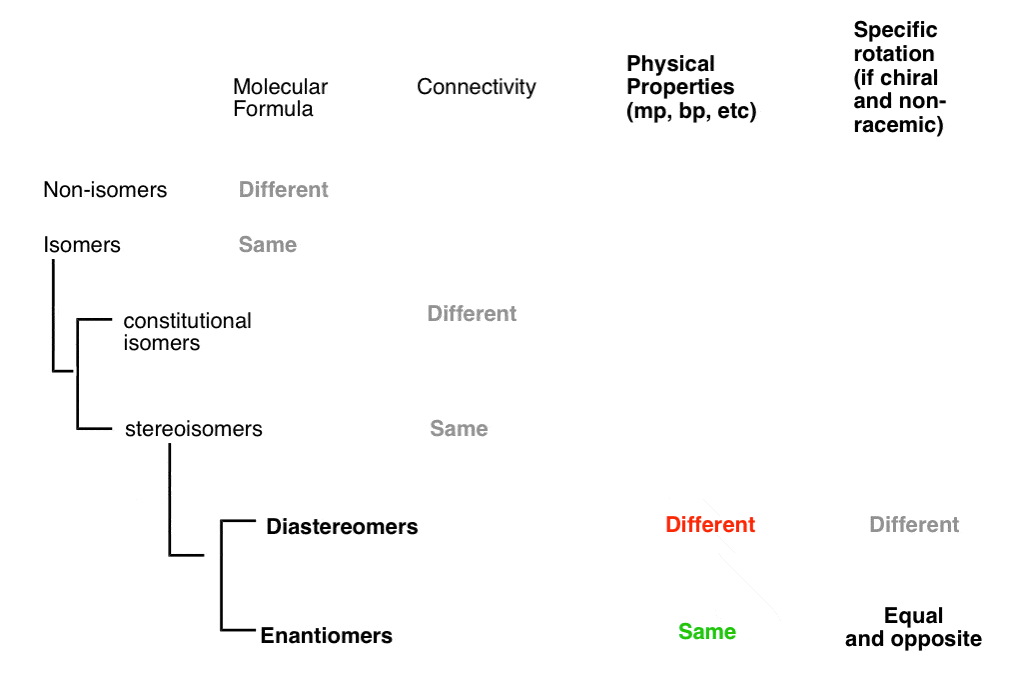
Stereoisomers have identical molecular formulas and arrangements of atoms. They differ from each other only in the spatial orientation of groups in the molecule. For organic chemistry, there are several types of stereoisomers: enantiomers, diasteriomers, geometric isomers, and conformers.
What is the difference between stereoisomers and enantiomers?
Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. Enantiomers are mirror images of each other which are known as stereoisomers. Diastereomers are also non-superimposable but are not mirror images of each other. Diastereomers are not mirrored images of each other which are known as stereoisomers.
Do diastereomers have same chemical properties?
Properties of Enantiomers and Diastereomers Enantiomers have identical chemical and physical properties, except for their optical rotation. In comparison, the diastereomers have different physical properties and sometimes different chemical properties also.
What two properties of enantiomers are different from each other?
Enantiomers differ only in the properties that are chiral: ➢ direction of rotation of plane polarized light, ➢ their rate of reaction with chiral reagents, ➢ biological activity and taste.
What are the properties of diastereomers?
Diastereomers have different physical properties such as melting points, boiling points, densities, solubilities, refractive indices, dielectric constants and specific rotations. Enantiomers have similar physical properties except the opposite sign of specific rotation.
What is the difference between enantiomers and diastereomers?
Enantiomers are a pair of molecules that exist in two forms that are mirror images of one another but cannot be superimposed one upon the other. Diastereomers are defined as compounds with the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded elements but are non-superimposable non-mirror images.
How do you identify diastereomers?
Among molecules with the same connectivity: Molecules that are mirror images but non-superimposable are enantiomers. If they aren't superimposable, and they aren't mirror images, then they're diastereomers.
Can diastereomers be the same molecule?
The definition of diastereomers is simple: if two molecules are stereoisomers (same molecular formula, same connectivity, different arrangement of atoms in space) but are not enantiomers, then they are diastereomers by default.
What is the difference between optical isomers and enantiomers?
Optical isomers, or enantiomers, have the same sequence of atoms and bonds but are different in their 3D shape. Two enantiomers are nonsuperimposible mirror images of one another (i.e., chiral ), with the most common cited example being our hands.
Why does a mixture of both, a racemic mixture (or racemic modification ), not rotate light?
He also observed that a mixture of both, a racemic mixture (or racemic modification ), did not rotate light because the optical activity of one molecule canceled the effects of the other molecule. Pasteur was the first to show the existence of chiral molecules.
What is the overall rotation of polarized light?
In a racemic mixture, both dextrorotary and levorotary enantiomers are present in equal amounts, so the overall rotation of polarized light is zero. The clockwise rotation is canceled by the counterclockwise rotation.
Do optical isomers have symmetry?
Optical isomers also have no axis of symmetry, which means that there is no line that bisects the compound such that the left half is a mirror image of the right half. Optical isomers have basically the same properties (melting points, boiling points, etc.) but there are a few exceptions (uses in biological mechanisms and optical activity).
What are the physical properties of enantiomers?
In contrast, diastereomers are characteristically different in their physical properties, such as melting and boiling points, densities, solubilities, heats of formation, and Gibbs free energies. If a molecule contains more than one chirality center and therefore consists of several pairs of enantiomers and diastereomers, the physical properties of each diastereomer must be noted. Tartaric acid, for instance, consists of three stereoisomers, a pair of enantiomers and a meso compound.
Is Meso Tartaric acid a pure compound?
Meso-tartaric acid, which is diastereomeric to (+)- and (-)-tartaric acid and shows no mirror-image relationship to them, thus has different physical properties. The racemic mixture of (+)- and (-)-tartaric acid behaves like a pure compound. It shows, for instance, a definite melting point. Nevertheless, its physical properties differ from ...
