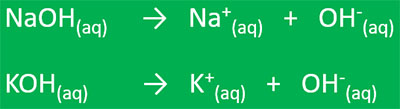
Generally all strong bases are soluble in water they completely dissociate when added in water. Complete step by step solution: Bases are defined as a substance which can neutralize the acid. For example NaOH
Sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na⁺ and hydroxide anions OH⁻. Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali that decomposes proteins at ordi…
Do strong bases dissolve in water?
Strong bases like strong acids dissociate 100% in water. As such all the strong bases are ionic compounds where OH- is one of the ions. Such compounds are called hydroxides. Not all hydroxides are strong bases since not all hydroxides are highly soluble.
Do bases form hydrogen ions when dissolved in water?
No , bases do not produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in water. Water in itself is ionised to an extent of 10^ (-14). There is an equilibrium between H+ and OH- ions which is maintained from pH 0 to 14 i.e. {The product of hydrogen ion concentration and hydroxl ion concentration in water is a constant} [H+] [OH-]=10^ (-14).
How do strong and weak bases dissociate or ionize?
How do you know if an electrolyte is strong or weak? Electrolytes are substances which, when dissolved in water, break up into cations (plus-charged ions) and anions (minus-charged ions). We say they ionize. Strong electrolytes ionize completely (100%), while weak electrolytes ionize only partially (usually on the order of 1–10%).
Why do strong acids dissociate completely in water?
Answers and Replies
- They are strong electrolytes.
- The hydrogen atom that is lost during dissociation is *not* strongly bound to the rest of the acid molecule.
- Therefore, the solvent (usually water) pulls at the H+ atom more strongly than the rest of the acid molecule.

Do strong bases dissociate completely or partially?
completelyStrong acids/bases dissociate completely whereas weak acids/bases dissociate partially.
Do weak bases dissociate completely in water?
Unlike strong acids/bases, weak acids and weak bases do not completely dissociate (separate into ions) at equilibrium in water, so calculating the pH of these solutions requires consideration of a unique ionization constant and equilibrium concentrations.
Do strong acids and strong bases dissociate 100% in water?
Strong Bases. A strong base (BOH) also completely dissociates and ionizes 100% in an aqueous solution. Moreover, strong bases are good proton acceptors, which cannot remain in aqueous solution. For instance, all O2- ions are converted to OH–, hydroxide ions, by accepting protons from H2O molecules.
Does strong acid dissociate completely?
Any acid that dissociates 100% into ions is called a strong acid. If it does not dissociate 100%, it is a weak acid.
Do strong bases dissociate only slightly in water?
Strong bases almost %100 dissociate into ions when dissolved in water. For example, NaOH is a strong base, and it dissociates almost 100% into ions in water. Strong bases almost %100 dissociate into ions when dissolved in water. For example, NaOH is a strong base, and it dissociates almost 100% into ions in water.
What happens to a strong base in water?
Strong bases (such as Group 1 and 2 metal hydroxides) dissociate completely in water to produce hydroxide ions.
Which of the following will 100% dissociate in water?
Sulfuric acid (H 2SO 4) dissociates 100 percent in water.
Why do strong acids not dissociate completely?
While there's lots of problems with estimating pKa lower then 0, in highly concentrated solutions strong acid simply can't be fully dissociated, because there's more acid then water. Levelling effect disappears and acid shows its real strength (not having much to do with pKa).
Do bases dissociate in water?
Arrhenius argued that bases are neutral compounds that either dissociate or ionize in water to give OH- ions and a positive ion. NaOH is an Arrhenius base because it dissociates in water to give the hydroxide (OH-) and sodium (Na+) ions.
What completely dissociates in water?
1 Answer. For all practical purposes, strong acids completely dissociate in water. That is the definition: A strong acid is an acid that completely dissociates in water.
Do strong bases ionize in water?
Summary. A strong base is a base that ionizes completely in an aqueous solution. A weak base is a base that ionizes only slightly in an aqueous solution.
Why strong acids dissociate completely in water?
Strong acids and strong bases dissociate completely in aqueous solution, due to which they give more number of H+ or OH-ions. What ion does a strong acid have? When a strong acid is added into water, it ionizes completely to form hydrogen ion, H+ (aq). That is the same for every strong acid.
Why do weak bases not dissociate completely?
according to ostwald dilution law, there is relationship between dissociation constant and degree of dissociation of weak electrolyte. Since, weak acids have very small dissociation constant ('k' value ) , so they do not donate all of its hydrogen ion (H+). That's why , they do not dissociate completely.
What does a weak base do in water?
Weak bases partially ionize in water to produce hydroxide ions. Because the ionization is not complete, the concentration of OH⁻ in a weak base solution is typically much less than the initial base concentration.
What does a weak base do when dissolved in water?
A weak base is a base that, upon dissolution in water, does not dissociate completely, so that the resulting aqueous solution contains only a small proportion of hydroxide ions and the concerned basic radical, and a large proportion of undissociated molecules of the base.
What dissociates completely in water?
1 Answer. For all practical purposes, strong acids completely dissociate in water. That is the definition: A strong acid is an acid that completely dissociates in water.
What is bond dissociation energy?
From Atkins (9th Ed 10.4): "bond dissociation energy, $D_o$, the energy required to separate the atoms to infinity or by the well depth $D_e$." - What is meant here by wellis a potential well– for now just think of that as the 2D box talked about in physics.
What is a chemistry stack exchange?
Chemistry Stack Exchange is a question and answer site for scientists, academics, teachers, and students in the field of chemistry. It only takes a minute to sign up.
Is there a direct relationship between bond dissociation energy and bond enthalpy?
It actually works out that there is a direct relationship to bond dissociation energy and bond enthalpy; which makes sense. It is elegantly related by:
Is the rule of a strong or weak conjugate rule?
The rule is not "weak/strong conjugate rule" . The strength of an acid is expressed by its acidity constant, Ka. The higher the value of the constant, the stronger the acid. Likewise, the strength of a base is expressed by its basicity constant, Kb. For a conjugate acid-base pair, in water, it is Ka .
Which acid dissociates completely in water?
Today we studied about Strong and weak acids. It says Strong acid like HCl is the one which dissociates completely in Water but we know that in HCl there are strong attractive forces due to high electronegtavity difference btween Cl and H So how come HCl dissociate easily? Similar is the case with HF... if anyone can explain plzz
What causes complete dissociation?
This behavior (complete dissociation) is caused by the relative difference between the energy holding the reactants together ( enthalpy of dissolution?) and the energy holding the products together (enthalpy of formation?). If the energy holding the products together is higher, than the reaction favors the products and the compound will dissociate.
What is a strong acid?
A strong acid is DEFINED as one which will completely dissociate in the medium (solvent) under discussion. (So, while water is the "normal" solvent considered, it could be something else; like ethanol (anhydrous), gasoline, or even a solid or a gasseous "solvent") (Confusingly, some will call the acid "strong" if it is strong in water, ...
What is the dielectric constant of water?
First of all, dielectric constant of water is a property of a bulk liquid, with randomly oriented molecules. When it comes to solvation water molecules become ordered, so in the microscale the local dielectric constant has a different value. Plus, ordering these molecules means strong entropic and enthalpic effects.
Why do acids disassociate?
Strong acids disassociate completely not necessarily because their components are held "more tightly" in compounds with the solvent particles, but rather because the compounds they form with the solvent particles (or the formation of solvated ions) is much more stable than their acidic compound form.
Why do H+ atoms dissolve?
We're told that they dissolve completely because. They are strong electrolytes. The hydrogen atom that is lost during dissociation is *not* strongly bound to the rest of the acid molecule. Therefore, the solvent (usually water) pulls at the H+ atom more strongly than the rest of the acid molecule.
Which ions have stronger holds on their protons?
And more, strong acids have weaker holds on their protons (H+ ions), while weak acids have stronger holds on their protons.