Veins lack an internal and external elastic lamina The tunica externa is the thickest Have venous valves that prevent back flow of blood especially in limbs — faulty valves cause backflow and varicose veins
What is internal elastic lamina in histology?
Histology. It is very thin in veins and venules. In elastic arteries such as the aorta, which have very regular elastic laminae between layers of smooth muscle cells in their tunica media, the internal elastic lamina is approximately the same thickness as the other elastic laminae that are normally present.
What is the thickness of internal elastic lamina in arteries?
In elastic arteries such as the aorta, which have very regular elastic laminae between layers of smooth muscle cells in their tunica media, the internal elastic lamina is approximately the same thickness as the other elastic laminae that are normally present.
Why is elastic lamina absent in the medium vein?
An internal elastic lamina is characteristic of the muscular artery but are lacking in the medium vein. The lamina appears folded like “ribbon candy” due to postmortem shrinkage of the vessel.
Is there an external elastic lamina in the adventitia?
There is no external elastic lamina, and the adventitia consists of a thin layer of collagen and isolated elastic fibers. By the contraction of their muscle fibers, the arterioles generate the "peripheral resistance" that reduces the blood pressure at the periphery, and thereby protects the capillaries and venules.

Does vein have elastic lamina?
2:122:58Which blood vessels have elastic laminae? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd external elastic lamina an elastic artery as the name indicates the the artery has an excess ofMoreAnd external elastic lamina an elastic artery as the name indicates the the artery has an excess of elastic lamina. So the tunica media is predominantly occupied by elastic lamina. Therefore.
What vessels have external elastic lamina?
VESSELSTunica intimaTunica media1. Endothelial cell lining 2. Subendothelial layer 3. Internal elastic lamina1. Smooth muscle cells, collagen fibers, and ground substance 2. Elastin in the form of fenestrated elastic lamellae (esp elastic arteries) 3. External elastic lamina
Does vein have external elastic membrane?
Veins. An internal elastic membrane is absent. The tunica media is relatively thin. The tunica adventitia is the thickest tunic and there is no external elastic membrane.
Where is the external elastic lamina?
n. A layer of elastic connective tissue lying immediately outside the smooth muscle of the tunica media of an artery.
Do arteries have external elastic lamina?
There is no external elastic lamina, and the adventitia consists of a thin layer of collagen and isolated elastic fibers.
Which of the following is true about veins?
So, the correct answer is option C- 'They carry blood from organs towards heart'.
Do veins have elastic tissue?
But unlike the arteries, the venous pressure is low. Veins are thin-walled and are less elastic. This feature permits the veins to hold a very high percentage of the blood in circulation.
What is the internal elastic lamina?
The internal elastic lamina is a fenestrated sheet that forms the boundary between the intimal and medial layers, influencing both its mechanical and mass transport properties. The size and number of these fenestrae vary in the arterial system and change with maturation [100,118].
What is the difference between arteries and veins?
Arteries carry blood away from the heart, and veins carry blood towards the heart. With the exception of pulmonary blood vessels, arteries carry oxygenated blood and veins carry deoxygenated blood. Arteries have thick walls with muscle tissue. Veins have thinner walls and use valves to keep your blood flowing.
How do veins prevent backflow?
The regular opening and closing of valves prevents backflow (blood that is flowing in reverse — also called venous reflux or insufficiency). If backflow occurs, blood can begin to pool in the veins, potentially damaging them. Most common venous disorders are caused by the backflow or venous insufficiency.
Do venules have internal elastic lamina?
The vessels involved in microvasculitis are usually arterioles without an internal elastic lamina (i.e., <30 to 40 μm), microvessels, and venules.
Why does the aorta have elastic tissue?
Elastic arteries are those nearest the heart (aorta and pulmonary arteries) that contain much more elastic tissue in the tunica media than muscular arteries. This feature of the elastic arteries allows them to maintain a relatively constant pressure gradient despite the constant pumping action of the heart.
Do veins have elastic fibers?
But unlike the arteries, the venous pressure is low. Veins are thin-walled and are less elastic. This feature permits the veins to hold a very high percentage of the blood in circulation.
What are types of capillaries?
The 3 types of CapillariesContinuous capillaries. These are the most common types of capillaries. ... Fenestrated capillaries. Fenestrated capillaries are “leakier” than continuous capillaries. ... Sinusoid capillaries.
What is internal elastic lamina?
An internal elastic lamina is characteristic of the muscular artery but are lacking in the medium vein. The lamina appears folded like “ribbon candy” due to postmortem shrinkage of the vessel.
Which layer of the arteries is the predominate layer?
The tunica media is the predominate layer in arteries; tunica adventitia is the predominate layer in veins. 400x.
Which is more dominant, tunica adventitia or arteries?
The tunica adventitia is a much more dominant component in the wall of veins compared with arteries.
Which is thicker, veins or tunica media?
The tunica media is thicker in arteries than veins, which results in arteries being more patent (open in appearance in histological sections) than veins. In contrast, veins have a thicker tunica adventitia than arteries.
What are the layers of the arteries?
All blood vessels, arteries and veins, are comprised of three layers: Tunica intima.
How many layers of smooth muscle are in the tunica media?
Arterioles have all three layers but the tunica media is comprised of 1-3 layers of smooth muscle fibers. Arteries have more than 3 layers of smooth muscle in the tunica media. This diagram compares the three layers: tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica adventitia in an elastic artery, muscular artery, and arteriole. CC by OpenStax.
What is the tunica adventitia?
The tunica adventitia is the layer beyond the tunica media. In large blood vessels, this region can also contain: vasa vasorum- blood vessels within blood vessels, provides nourishment to outermost layers of the blood vessel and nervi vasorum- nerves within blood vessels, innervates blood vessels
How many types of arteries are there?
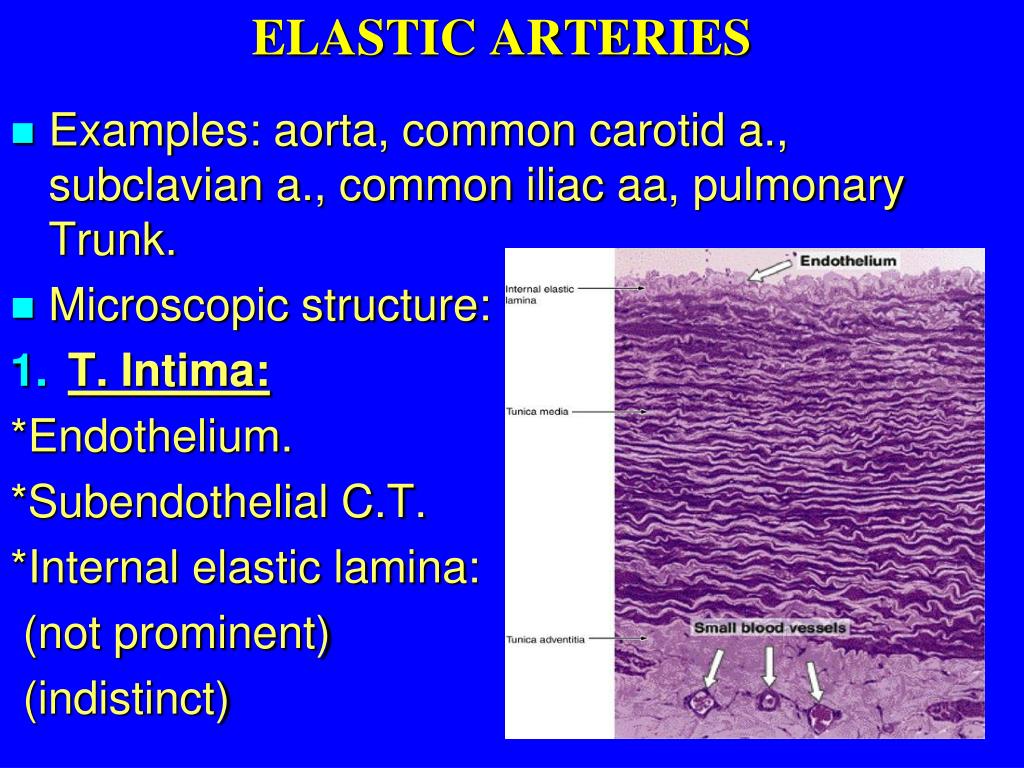
Types of arteries. Arteries are generally classified into three types: In the tunica media of elastic arteries, there is one elastic lamina for each layer of smooth muscle fibers so it is a 1:1 ratio of elastic lamina to smooth muscle.
What does sympathetic stimulation do to the nervi vasorum?
Sympathetic stimulation increases amount of catecholamines, such as epinephrine and norepinephrine reaching the nervi vasorum. Sympathetic stimulation will result in vasoconstriction (wall of blood vessel contracts), which results in increased blood pressure.
Which artery contains vasa vasorum?
The tunica adventitia of elastic arteries contains vasa vasorum and nervi vasorum. The primary elastic artery is the aorta. In the tunica media of muscular arteries, there is one elastic lamina for 2-3 layers of smooth muscle fibers so it is a 1:2-3 ratio for elastic lamina vs. smooth muscle.
Which arteries have elastic laminae?
In elastic arteries such as the aorta, which have very regular elastic laminae between layers of smooth muscle cells in their tunica media, the internal elastic lamina is approximately the same thickness as the other elastic laminae that are normally present.
Where is the elastic lamina found?
It is very thin in veins and venules. In elastic arteries such as the aorta, which have very regular elastic laminae between layers of smooth muscle cells in their tunica media, the internal elastic lamina is approximately the same thickness as the other elastic laminae that are normally present.
What causes narrowing of the lumen and downstream ischemia?
In chronic allograft nephropathy, disruption or reduplication of internal elastic lamina can be observed, which causes narrowing of the lumen and downstream ischemia. In fungal rhinosinusitis, the organism has predilection for internal elastic lamina during phase of spread.
Why is my elastic lamina reduplicated?
Reduplication of internal elastic lamina can be seen in elderly individuals due to intimal fibroplasia, which is part of the aging process.
What is the H&E stain?
H&E stain. The internal elastic lamina or internal elastic lamella is a layer of elastic tissue that forms the outermost part of the tunica intima of blood vessels. It separates tunica intima from tunica media .