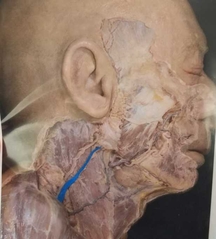
The Anatomy of Jugular Veins
- Anatomy The jugular veins are paired right and left. There are four main jugular veins, two internal and two external. ...
- Function Arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins carry blood toward the heart. All veins except those returning blood from the pulmonary system carry deoxygenated blood. ...
- Clinical Significance The internal and external jugular veins both have clinical significance. ...
What are the internal and external jugular veins?
There is a pair of internal jugular veins (right and left) and a pair of external jugular veins. They are the main path for deoxygenated blood returning from the cranium back to the heart.
What does it mean when your jugular vein is bulging?
The internal jugular vein and external jugular vein run down both sides of your neck. Bulging of these two jugular veins may be accompanied by pain or discomfort. Additional symptoms depend on the underlying condition causing JVD. JVD can occur for various reasons and may be a sign of a serious heart problem.
What is the largest pair of jugular veins?
The largest pair of jugular veins are the internal jugular veins. They exit the cranium through the jugular foramen (foramen is a fancy medical term for a hole). Each of the internal jugular veins runs on either side of the neck under the sternocleidomastoid muscle. They are difficult to locate without ultrasound to assist. 1
What happens to the jugular vein in heart failure?
For people with right-sided heart failure, the left side of the heart has usually already failed, so the right side is under much more pressure to pump blood. Over time, the right side is weakened and cannot work as well. Blood then accumulates in the veins and leads to a bulging jugular vein.

Is there a left and right jugular vein?
There is a pair of internal jugular veins (right and left) and a pair of external jugular veins. They are the main path for deoxygenated blood returning from the cranium back to the heart.
Is jugular vein only on one side?
There are two sets of jugular veins: external and internal. The left and right external jugular veins drain into the subclavian veins. The internal jugular veins join with the subclavian veins more medially to form the brachiocephalic veins.
What are the two big veins in your neck?
The jugular veins are a major part of your body's circulatory system. They run from your head, down through your neck and into your upper chest. There are two main pairs of jugular veins, the interior and exterior jugular veins, and jugular vein distention can happen in either.
Which side of your neck is your jugular vein?
Internal and external jugular veins run along the right and left sides of your neck. They bring blood from your head to the superior vena cava, which is the largest vein in the upper body.
What happens if the jugular vein is blocked?
The internal jugular vein is the largest vein in the neck that serves as the main source of blood flow down from the head. Obstruction of blood flow through the internal jugular vein can cause backflow of blood into the brain, increasing intracranial pressure, which can cause serious brain damage if left untreated.
Is the jugular vein the same as the carotid artery?
The main difference between jugular vein and carotid artery is that jugular vein drains deoxygenated blood from the head and face whereas carotid artery supplies oxygenated blood to the head and face. Both jugular vein and carotid artery are located on each side of the trachea.
Which neck vein goes to the brain?
the internal jugular veinThe function of the internal jugular vein is to collect blood from the skull, brain, superficial parts of the face, and the majority of the neck.
What are the warning signs of a blocked carotid artery?
Carotid Artery Blockage SymptomsBlurred vision or vision loss.Confusion.Memory loss.Numbness or weakness in part of your body or one side of your body.Problems with thinking, reasoning, memory and speech.
Why is my left neck vein popping out?
Jugular vein distention (JVD) occurs when the pressure inside the vena cava, a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood back to the heart, causes a bulging neck vein. The internal jugular vein and external jugular vein run down both sides of your neck.
Is the jugular bigger on one side?
The internal jugular vein (IJV) is a major vein collecting blood from the head and neck and is also a clinically important vein. The right IJV is known empirically to be larger than the left IJV.
How do you check for jugular veins?
With the patient supine and the head slightly elevated on a pillow, locate the right external jugular vein. If the vein is not easily seen, apply digital pressure at the region where the vein normally enters the thorax at the clavicle. This will reveal the vein in many patients. Release the pressure.
Why does it feel like the veins in my neck hurt?
Carotidynia is a pain that you feel in your neck or face. It is linked with physical changes that can happen in a carotid artery in your neck. Your neck may feel tender in the area of the artery. The pain often goes up the neck to the jaw, ear, or forehead.
Is the jugular bigger on one side?
The internal jugular vein (IJV) is a major vein collecting blood from the head and neck and is also a clinically important vein. The right IJV is known empirically to be larger than the left IJV.
Where are the jugular veins located?
jugular vein, any of several veins of the neck that drain blood from the brain, face, and neck, returning it to the heart via the superior vena cava. The main vessels are the external jugular vein and the interior jugular vein.
Are jugular veins symmetrical?
The Internal jugular veins are asymmetric.
Why is JVP on right side?
Causes of a raised JVP Right-sided heart failure: commonly caused by left-sided heart failure. Pulmonary hypertension is another cause of right-sided heart failure, often occurring due to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or interstitial lung disease.
How many jugular veins are there?
Anatomy. The jugular veins are paired right and left. There are four main jugular veins, two internal and two external. There is also a pair of anterior jugular veins.
Why is the right internal jugular vein considered preferable?
Access to the right internal jugular vein is considered preferable due to its length and straighter route. 1 . The external jugular veins can be used for peripheral intravenous (IV) access in emergency situations when other peripheral IV sites are unavailable.
What is the role of the jugular veins in the body?
3 . The jugular veins are responsible for returning deoxygenated blood from the cranium, face, and brain.
How long is the right internal jugular vein?
The internal jugular veins join with the subclavian veins to form the brachiocephalic veins. The right internal jugular vein is about 63 millimeters (mm) long while the left internal jugular vein averages about 53 mm long.
Why are external jugular veins distended?
Due to the superficial placement of the external jugular veins, they are useful indicators of systemic venous obstruction. When blood flow is obstructed by something like congestive heart failure, tension pneumothorax, or cardiac tamponade, distended external jugular veins could be a symptom. 2
Which layer of the jugular vein is the outermost?
Tunica adventitia (tunica externa) is the outermost layer of the jugular vein and connects it to surrounding tissues. At the distal (downstream) ends, external and internal jugular veins have one-way valves that prevent blood from flowing backward.
Where do the jugular veins exit?
They exit the cranium through the jugular foramen (foramen is a fancy medical term for a hole). Each of the internal jugular veins runs on either side of the neck under the sternocleidomastoid muscle. They are difficult to locate without ultrasound to assist. 1 .
What is the internal jugular vein?
The internal jugular vein is a major blood vessel that drains blood from important body organs and parts, such as the brain, face, and neck.
Why is the jugular vein important?
The vein plays an important role in assessing jugular vein pressure, especially among people with heart disorders. Measurements of jugular vein pressure are used to evaluate central venous pressure, which indicates how much blood is returning to the heart and how well the heart is pumping blood back into the arteries.
Why is the internal jugular vein so vulnerable to injury?
Because of its superficial location (near the outside of the body), the internal jugular vein is quite susceptible to injury, trauma, or damage. It also lacks protection from strong structures, like bones or cartilages. When blood flow to the vein is impeded or affected, shock or death will ultimately occur. Last medically reviewed on January 21, ...
Which vein is smaller, the left or right?
Generally, the left vein is somewhat smaller and thinner than the right, but both contain valves that assist with blood transport. The vein appears dilated (wider) at two points, and these distinct parts are called the superior bulb and the inferior bulb.
Where are the left and right veins located?
They each rest beside the thyroid gland at the center of the neck, just above the collarbone and near the trachea, or windpipe. These veins functions to carry oxygen-depleted blood from the brain, face, and neck, and transport it to the heart through the superior vena cava. Generally, the left vein is somewhat smaller and thinner than the right, ...
Do you need your jugular vein?
When the jugular veins are blocked, the pressure in the brain rises." The best way to unblock a jugular vein is with a needle-based infusion called a catheter. These tubes are usually made of plastic or stainless steel and are inserted into the vein through either the neck or the chest. They can be used to give medications or other substances directly to the heart via the bloodstream.
Can you live without a jugular vein?
The removal of a single jugular vein typically results in minimal or no complications. There are several additional veins in the neck via which blood might return. However, these veins usually connect with the internal jugular vein near its source in the anterior chest wall. They include the sternal, suprascapular, and infraclavicular veins.
What are the symptoms of jugular veins?
Blood then accumulates in the veins and leads to a bulging jugular vein. Symptoms can include shortness of breath, edema, and fatigue.
What does it mean when your jugular veins are distended?
It's a sign that something is causing the pressure in your veins to rise.
What is the cause of a vena cava obstruction?
This obstruction can cause distention in the axillary veins (paired veins of the upper limb), subclavian veins (paired veins responsible for draining blood from the upper extremities), and jugular veins. Superior vena cava obstruction is rare, but it's serious and often caused by dire conditions like cancer or an infection.
What is the name of the vein that carries blood back to the heart?
Jugular vein distention (JVD) occurs when the pressure inside the vena cava, a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood back to the heart, causes a bulging neck vein.
What is the main vein in the body?
The superior vena cava is one of the main veins in the body. It transports blood from your arms, chest, neck, and head to your heart. The jugular vein is one of several veins of the neck that connect to the superior vena cava. When there is an obstruction in the superior vena cava, it becomes compressed or blocked.
Why does my jugular vein bulge?
JVD is caused by increased pressure in the jugular veins. As pressure increases , the jugular vein will bulge. This increased pressure can be due to a number of conditions affecting the heart and lungs.
What causes jugular vein distention?
Tension pneumothoraces occur when air accumulates between the chest wall and the lung and increases pressure in the chest, reducing the amount of blood returned to the heart. It can cause jugular vein distention. A tension pneumothorax is a life-threatening condition that needs to be treated as soon as possible.