
Which carbohydrates are good sources of energy?
You Need Complex Carbs
- Sweet Potatoes. Sweet potatoes have naturally occurring sugars and are full of dietary fiber and micronutrients. ...
- Yams. Nutritionally, yams resemble sweet potatoes. ...
- Oats. Oats are an amazing source of complex carbohydrates and protein that can help build more muscle and optimize body composition.
- Clean Carbs. ...
- Brown Rice. ...
- Quinoa. ...
Do carbohydrates or lipids provide more energy?
Lipids have a high proportion of hydrogen present in the fatty acid chains. When the molecule is metabolised, the chemical energy is released. Being so reduced and anhydrous, they are an economical way to store fuel reserves, and provide more than twice as much energy as the same quantity of carbohydrate.
Do fats give more energy than carbohydrates?
Fats contain more energy than carbohydrates because they need more oxygen for each carbon atom, which in turn produces more energy. This arises because there are more electrons surrounding each carbon atom in fat. While fat has a negative reputation, it is an important component of each person's diet, and intake should vary according to individual lifestyles.
Do starchy foods provide energy?
Starchy foods usually contain more nutrients, which can increase your energy levels and leave you feeling full longer than do simple sugars. Complex carbohydrates are made up of lots of sugars combined together. Sources of complex carbohydrates that will give you long-lasting energy include whole grains, fruits and vegetables.
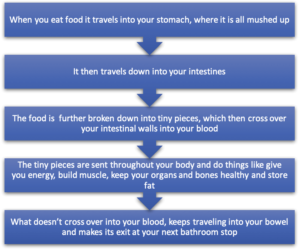
Do you need to eat carbs for energy?
The glucose from carbs is converted into the energy your brain and muscles need to function, Meyerowitz explains. Fats and protein are also necessary for energy, but they're more of a long-term fuel source, while carbohydrates fulfill the body's most immediate energy needs.
What happens if you don't eat carbs?
A sudden lack of carbs will make you lose weight. It's mostly water weight at first, though. This is mostly because cutting carbs also wipes out the glycogen stores in your muscles. Glycogen helps your body retain water.
Can a person survive without carbs?
Diets lacking in carbohydrate will utilize protein and fats as a source of energy. This can lead to long-term complications and increased mortality from diseases of the heart, kidney, gastrointestinal tract and certain types of cancer.
Does carbs make you have energy?
Carbohydrates serve several key functions in your body. They provide you with energy for daily tasks and are the primary fuel source for your brain's high energy demands.
What happens if I eat too little carbs?
If you eat too few carbs, you may experience some unpleasant side effects. According to Mayo Clinic, these may include dizziness, headaches, weakness, fatigue, nutrient deficiencies, nausea, diarrhea, mental fatigue and even bad breath.
Can not eating enough carbs make you tired?
You're Always Tired Carbs are converted to energy more efficiently than protein or fat, so you may start feeling a little sluggish throughout the day on a low-carb diet. Weakness and fatigue—sometimes called "keto flu"—are common side effects of a low-carb diet.
Why do I feel better without carbs?
Your body thinks it's starving. A very low-carb diet flips your metabolic switch from burning more carbs than fat, to more fat than carbs. This usually takes a few days in a process known as ketosis.
What can I replace carbs with for energy?
Lean Protein You should get about 50 percent of your calories from carbohydrates. If you have plenty of carbohydrates in your diet already, you can replace simple carbohydrates with protein. Lean beef, poultry, fish, pork and eggs are all foods that do not contain carbohydrate but are loaded with protein.
What happens if you eat no carbs for a week?
You may experience low-carb flu. Some of those side effects include fatigue, weakness, dizziness, headaches, irritability, and nausea and they can last anywhere between a few days and a few weeks.
What gives more energy carbs or protein?
“Protein takes more energy for you to digest than refined carbohydrates, and also gives your body a feeling of satiety,” says Dr. Hauser. Low-carb diets have been shown to help some people lose weight.
Do carbs give you energy or make you tired?
Carbohydrates are generally quickly digested/absorbed into glucose (or energy). This raises your blood sugar and thus, energy. However, because they are so quickly digested and absorbed, your blood sugar will also fall quickly leading you to potentially feel fatigued.
Are carbs or fat better for energy?
Fats are the slowest source of energy but the most energy-efficient form of food. Each gram of fat supplies the body with about 9 calories, more than twice that supplied by proteins or carbohydrates. Because fats are such an efficient form of energy, the body stores any excess energy as fat.
Why do carbs make you put on weight?
The fact is, carbs don't cause instant weight gain. However, starchy carbs do have a tendency to be calorie-dense. Consuming these extra calories is what causes weight gain. Even some complex carbs can be calorie-dense,4 however, so be mindful of your serving size if you wish to avoid weight gain.
Do carbs get converted to fat?
When high amounts of unhealthy carbohydrates are consumed, they're converted to triglycerides, a form of fat, and are stored in fat tissue, states the National Council on Strength & Fitness. The glucose-to-triglycerides pathway results in fat accumulation, which has fueled the low-carb craze.
What foods have no carbohydrates?
Meat, fish, seafood, fats and oils are the most common no-carb foods but the list doesn't end there. There are beverages, seasonings, condiments, sweeteners, and snacks that are also zero carb, but you have to know which ones.
Why does a teenager need carbohydrates?
Breads, grains and cereals are carbohydrates that provide energy for your brain and muscles. They're also an excellent source of fibre and B vitamins. Without enough carbohydrates you may feel tired and run down. Try to include some carbohydrates at each mealtime.
Understanding Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are a type of macronutrient found in many foods and beverages. Most carbohydrates occur naturally in plant-based foods, such as grain...
More Carbohydrate Terms: Net Carbs and Glycemic Index
Terms such as "low carb" or "net carbs" often appear on product labels. But the Food and Drug Administration doesn't regulate these terms, so there...
How Many Carbohydrates Do You Need?
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends that carbohydrates make up 45 to 65 percent of your total daily calories.So, if you get 2,000 calor...
Choose Your Carbohydrates Wisely
Carbohydrates are an essential part of a healthy diet, and provide many important nutrients. Still, not all carbs are created equal.Here's how to m...
What are the best carbs to eat?
21 Best Carbs to Eat. 1. Beetroot (Beets) Carb Content: 16 grams per cup. Beetroot is an excellent source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They’re also full of folate, manganese, magnesium, iron, copper, vitamin C, and potassium. Beets also contain nitrates, which get converted into nitric oxide and help reduce blood pressure – ...
How many carbs are in a potato?
Potatoes. Carb Content: 37 grams per medium-sized potato. There’s a reason potatoes have been a staple food for generations. Aside from being a carb powerhouse, they are full of vitamins and minerals such as iron, copper, manganese, vitamin C, magnesium, potassium, and B vitamins.
How many grams of carbs are in a mango?
Mangoes. Carb Content: 21 grams per cup (sliced) Mangoes are a tropical fruit known for their rich orange color and juicy flesh. They are packed with vitamins and an excellent source of carbohydrate. Mangoes are rich in potassium, magnesium, and vitamins A, C, K, and E.
How does glucose enter the body?
Carbohydrate is broken down into glucose (sugar) before being absorbed into the bloodstream. Glucose then enters the body's cells with the help of insulin. The glucose is used by your body for energy, fueling everything you do, be that running or simply breathing. If you're worried about which carbs you should be eating, ...
Why are blueberries considered a superfood?
You’ve probably heard blueberries referred to as a superfood because they are high in antioxidants.
Why should we eat fruits and vegetables?
Because fruits and vegetables are also carbohydrates (complex), and we need plenty of them in our diet to maintain optimal health. While we should avoid heavily processed foods, we should base our meals on starchy carbs, particularly the higher fibre varieties found in fruits and vegetables and whole grains.
Is fiber a carbohydrate?
And fiber is key here, because a generous percentage of carbohydrate in fruit and vegetables is fiber. Additionally, many of the best carbs to eat contain resistant starch, which comes with many health benefits. Resistant starch feeds the friendly bacteria in your gut and increases the production of short-chain fatty acids.
How many carbohydrates do you need?
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends that carbohydrates make up 45 to 65 percent of your total daily calories.
What does net carbs mean?
Typically "net carbs" is used to mean the amount of carbohydrates in a product excluding fiber, or excluding both fiber and sugar alcohols. You probably have also heard talk about the glycemic index. The glycemic index classifies carbohydrate-containing foods according to their potential to raise your blood sugar level.
How many carbs are in a day?
That translates to between 225 and 325 grams of carbohydrates a day. You can find the carbohydrate content of packaged foods on the Nutrition Facts label. The label shows total carbohydrates — which includes starches, fiber, sugar alcohols, and naturally occurring and added sugars. The label might also list separately total fiber, ...
What is the best way to get fiber?
Choose whole grains. Whole grain s are better sources than refined grains of fiber and other important nutrients, such as B vitamins. Refined grains go through a process that strips out parts of the grain — along with some of the nutrients and fiber.
What are some good substitutes for meat?
Eat more legumes. Legumes — which include beans, peas and lentils — are among the most versatile and nutritious foods available. They are typically low in fat and high in folate, potassium, iron and magnesium, and they contain beneficial fats and fiber. Legumes are a good source of protein and can be a healthy substitute for meat, which has more saturated fat and cholesterol.
How many types of carbohydrates are there?
There are three main types of carbohydrates:
What is starch made of?
Starch. Starch is a complex carbohydrate, meaning it is made of many sugar units bonded together. Starch occurs naturally in vegetables, grains, and cooked dry beans and peas.
Why do athletes eat carbs?
In essence, the body enters a state of glycolysis (for glucose) or fructolysis (for fructose) that converts these simple sugars into energy. Excess calories from sugar that don’t get used immediately are stored in the liver as glycogen.
Why are carbohydrates and fats unhealthy?
Carbohydrates and fats are not inherently unhealthy. The main cause behind many of these problems is overconsumption without doing anything to convert the glucose and fatty acids into energy. To make those conversions, the body responds to stimuli.
How many calories does fat provide?
Every gram of dietary fat supplies the body with about 9 calories. To put things in perspective, protein and carbohydrates both supply 4 calories per gram. In the intestine, fats are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol. These fatty acid chains are converted into energy via a process called beta-oxidation.
How long does it take for sugar to be in your bloodstream?
Certain carbohydrates can be converted into sugars and be present in your bloodstream for use as soon as 60 seconds after you eat.
What percentage of the dry weight of a diet is carbohydrates?
To put things in perspective: Carbohydrates, proteins and fats comprise 90% of the dry weight of the diet and 100% of its energy.1. For all three of these, energy is measured in “calories.”. However, carbohydrates and fats stand apart from proteins. These two macronutrients are the subject of many misconceptions when it comes to health ...
What are the two main principles of nutrition?
Carbs and Fats For Energy. When it comes to nutrition, generally you want to adhere to two main principles: balance and quality. This means that you want to eat foods with good nutrient content, while also making sure that you get varied carbohydrate and fat intake.
What happens when you work out?
For example, if you work out, the body takes note of this and starts turning those calories into the energy you need to complete your workout. Without any use, the calories become the deposits of fat or the elevated levels of sugar in the blood that we associate with being unhealthy.
How much glucose is needed for ketosis?
What this table clearly demonstrates is that whether during a total fast or a ketogenic diet without carbohydrate containing foods, new or recycled gluconeogenic substrates provide for the generation of anywhere from 100–200 g/d of glucose. Add to this up to 50 g/d of dietary carbohydrate as part of a well-formulated ketogenic diet, and it becomes clear why nutritional ketosis is well tolerated under a variety of challenging conditions.
What does a keto diet do to the body?
A ketone-suppressing diet (i.e., any diet supplying >30% of energy from the combined intakes of carbohydrate and protein) essentially forces the brain to rely on glucose for fuel. It is true that some cells within the body do require glucose.
How long did Jeff Volek follow a keto diet?
We recruited 20 competitive ultra-runners, 10 of whom followed a traditional high carbohydrate diet and the other 10 had been following a ketogenic diet for at least 6 months (mean diet duration 22 months). The ketogenic diet group reported an average daily carbohydrate intake of 64 grams and had a mean fasting serum BOHB of 0.6 mM.
Why is ketone beta hydroxybutyrate important?
In addition to the fact that ketones are a cleaner-burning fuel (i.e., producing fewer free-radicals) than glucose when used by the brain and other organs, the primary ketone beta-hydroxybutyrate can also function as a signal to activate genes that regulate our defenses against oxidative stress and inflammation ³.
When discussing carbohydrate restriction, two fallacious arguments related to the energy needs of the brain and the sustainability of?
When discussing carbohydrate restriction, two fallacious arguments related to the energy needs of the brain and the sustainability of a ketogenic diet are often levied against the use of a well-formulated ketogenic diet in practical therapeutic medicine:
Is fiber good for keto?
We need more dietary fiber than is possible on a ketogenic diet. In addition to promoting colon health, there is now strong evidence that short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) produced from colonic fermentation of fiber also improves brain health. And it is indeed true that the combination of a very high fiber intake plus adequate carbohydrate restriction to sustain nutritional ketosis is difficult to achieve without the use of purified fiber supplements. But what we point out in our blog post on fiber is that the production of beta-hydroxybutyrate can provide many-fold more SCFAs to the brain than a very high fiber diet combined with an optimized microbiome. Thus, the moderate level of fiber that one can achieve with a real-food well-formulated ketogenic diet should be more than adequate to maintain organ health throughout the body.
Is ketosis a sign of thyroid dysfunction?
Thyroid dysfunction secondary to nutritional ketosis. In the context of the common observation of impaired energy and exercise tolerance when nutritional ketosis is combined with inadequate intakes of electrolytes, it is tempting to blame this on impaired thyroid function. However, this common conclusion does not stand up to basic scientific scrutiny. Yes, the blood level of the active thyroid hormone T3 typically falls by 30–40% in the first few weeks of a well-formulated ketogenic diet, but this is not accompanied by any signs or symptoms of clinical hypothyroidism. As discussed in our prior blog post Does Your Thyroid Need Dietary Carbohydrates?, this change is due to a marked reduction in thyroid hormone resistance (similar to the concurrent improved insulin resistance) during nutritional ketosis. Therefore, this is a healthy response and not a sign of endocrine dysfunction.
How long can you stay on a low carb diet?
The article posted on the gym’s website also claims that “ very few people can maintain a low-carb diet beyond 3-6 months, without negative side effects “. A recent peer-reviewed study led by Dr Sarah Hallberg published in Diabetes Review, [3] demonstrated long term adherence to a low-carb diet that included healthy, satiating fats.
Why do we not need carbohydrates?
The key point is that you do not need to consume carbohydrates because your body can synthesise all the glucose your body needs to carry out the biological process of growth and metabolism. Our liver is able to perform this function in a process known as gluconeogenesis.
Why do we not need to eat carbs?
The key point is that you do not need to consume carbohydrates because your body can synthesise all the glucose your body needs to carry out the biological process of growth and metabolism. Our liver is able to perform this function in a process known as gluconeogenesis.
Why are legumes bad for you?
The big problem with legumes and wholegrains is the fact that they can cause serious damage to our digestion, which can lead to mineral deficiencies in our body . As discussed in the reference from the Weston A. Price Foundation [19] phytic acid in grains, nuts, seeds and beans represents a serious problem in our diets.
What are the substances that are not digested by humans?
The term includes cellulose, gums, mucilages, pectins and lignins. Humans cannot digest fibre, but these substances are said to contribute to the health of the digestive tract. Rather than focusing entirely on fibre, we should look at the intestines as a complex ecosystem.
What is the role of fibre in bowel function?
One of the points discussed was the role of fibre in bowel function. For years, modern gastroenterology has put its whole emphasis on the fibre theory of bowel function which, briefly stated, is the theory that those who consume lots of fibre will have healthy bowel function.
Can your brain stop working if you don't eat enough carbs?
I myself have been following a LCHF approach to nutrition for six years and it is easy. What I find frustrating is when we are constantly told by so-called experts that our brains are going to stop working if we don’t eat enough carbs. The truth is that on low carb diets once we become “fat burners” instead of “carb burners”, our brains can also use ketones (a byproduct of fat metabolism) as a supplementary fuel source.
What macro nutrients are needed for anaerobic exercise?
We require a certain percentage of all macro nutrients for basal metabolic functions, but the role of glycolysis becomes even more important with an absence of oxygen availability. Carbohydrates may be the most critical of all the macro nutrients for the performance of anaerobic exercises.
What is the energy system of anaerobic exercise?
This pathway gains its energy quickly, but cannot last for long periods of time. For the body to utilize this energy pathway properly, carbohydrates are critical. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is responsible for delivering energy to the body for functions. For different types of exercise, certain muscles are recruited and ATP is utilized towards those muscles being used. There are three different energy systems used during physical activity; the phosphagen system (creatine phosphate), lactic acid system (glycolic), and aerobic (or oxidative) system. Depending on which of these energy systems are being used, macro nutrients will have different roles.
What is anaerobic exercise?
The American Council on Exercise describes anaerobic exercise as it pertains to ventilatory threshold. Higher intensity intervals that load the cardio-respiratory system recruiting the second ventilatory threshold where lactate is rapidly increasing with intensity (ACE, 2010). Typically, in this threshold we will also see the use of fast twitch muscle fibers, as they have a capacity for anaerobic glycolysis. These muscle fibers are utilized primarily for any rapid, powerful movements such as jumping or sprinting (ACE, 2010 p. 82). A person who claims to have a lack of endurance, but ability to move quickly for short periods, is better at recruiting the use of these fast twitch muscle fibers. Where as a person who moves much more slowly, but can last for long periods of time are better at recruiting their slow twitch muscle fibers.
How to determine fuel utilization of macro nutrients?
To determine the fuel utilization of macro nutrients, the respiratory exchange ratio must be determined during aerobic exercise. This provides the ratio of carbon dioxide produced to the amount of oxygen consumed, allowing us to see which macro nutrient is most efficient in producing energy.
Is fat oxidation an energy source?
In conclusion, the utilization of fats versus carbohydrates as an energy source is dependent on the activity conducted. During those activities which are anaerobic, where the creatine phosphate or lactic acid system is in use carbohydrates are the most fuel-efficient energy source. During aerobic exercise or physical activity, fat oxidation is abundant in its stores as glycogen stores are limited. Athletes should look to incorporate a certain percentage of each macro nutrient in their diet, paying attention to timing. Carbohydrates closer to exercise are best as they can provide immediate glucose, versus fats which take longer to metabolize.
Do carbohydrates require oxygen?
Carbohydrates require use of an amount of oxygen equal to amount of carbon dioxide produced for higher RER. Oxidation of fat requires larger consumption of oxygen to CO2 produced. A case study conducted showed during low HR activities, the energy provided was through fat oxidation, and a smaller percent from carbohydrates. In the study as the participant began to increase his HR, the amount of energy provided through fat oxidation decreased, and carbohydrate oxidation increased along with the total energy expenditure.
What About Carbo-Loading?
You can boost your energy by topping off your carb stores 24 to 36 hours before a big effort, but that doesn’t mean you need to eat an entire package of pasta. Instead, adjust the balance of your macros within meals. Begin to prioritize carbohydrates while slightly lowering fat, protein, and fiber. Too much fat and fiber may cause GI distress, and dropping calories from fat and protein allows you to increase your carb intake without overeating and feeling uncomfortably full on race day. Most importantly, make sure that carbs are the center of your meal. “My teammates know that during a stage race, we institute a salad ban,” says Nedescu. For easy-to-digest calories, Nedescu will eat rice with eggs and some maple syrup, and Lis recommends making a carb-heavy fruit smoothie to sip throughout the day prerace.
How to boost energy with pasta?
You can boost your energy by topping off your carb stores 24 to 36 hours before a big effort, but that doesn’t mean you need to eat an entire package of pasta. Instead, adjust the balance of your macros within meals. Begin to prioritize carbohydrates while slightly lowering fat, protein, and fiber.
Why do we need carbohydrates?
Our muscles require glycogen, which we get from carbs, to power our bodies through miles of running, biking, skiing, or paddling. “We need carbohydrates, especially to fuel hard efforts,” says Lori Nedescu, a registered dietitian and professional cyclist.
Is cutting carbs good for athletes?
Cutting carbs gets really trendy about once a decade, according to Dana Lis, director of performance nutrition at the University of California at Davis. This time around, it’s in the form of the high-fat ketogenic diet, which has no demonstrable performance benefits for athletes.
