
What kind of gas do you put in a plasma cutter?
If your Plasma Cutter uses other gases like oxygen, nitrogen, etc. as a plasma gas then you need a cylinder containing compressed oxygen or nitrogen. Can a plasma cutter cut wood?
Do I need a compressor for my plasma cutter?
If your Plasma Cutter uses compressed air as the plasma gas and your Plasma Cutter does not have a built-in compressor, then you need a compressor. If your Plasma Cutter uses other gases like oxygen, nitrogen, etc. as a plasma gas then you need a cylinder containing compressed oxygen or nitrogen.
What can I cut with a plasma cutter?
Your Plasma Cutter can cut any electrically conductive material, however, the melting point of some materials makes it difficult to get good a cutting edge. The plasma gas in your machine can attain temperatures up to 27000ºC and the cutting is faster and cheaper than other thermal cutting processes.
Can you cut aluminum with oxygen plasma gas?
(Plasma cutting aluminum plate or stainless plate with oxygen plasma gas is not recommended). Oxygen plasma gas reacts with carbon steel to produce a finer spray of molten metal, each droplet having a lower surface tension. This molten spray is more easily ejected from the kerf.
What type of gas is used for plasma cutters?
What is the best mixture for plasma cutting?
What metals are plasma cutters made of?
What is a primeweld plasma cutter?
What is the energy produced by plasma gas?
What factors are factored into plasma cutter gas selection?
What is plasma cutting?
See 2 more

Which gas is used for plasma cutting?
Compressed air, nitrogen, argon, hydrogen and oxygen, or blends of two or three of these components are the most popular plasma gases for plasma cutting.
What is needed for plasma cutting?
Plasma cutting requires two basic elements — air and electricity — so the next question to ask is what type of input power is available. Several 30-amp plasma cutters, such as the Spectrum® 375 X-TREME™, operate using 120- or 240-volt power.
Can you run a plasma cutter without air?
1:555:55Plasma Cutting With No Air - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo don't do. This. Guys see the heat coming off there guys absolutely boiling hot we've got no airMoreSo don't do. This. Guys see the heat coming off there guys absolutely boiling hot we've got no air there to cool it down we've got nowhere to make the plasma. It's putting a strain on your machine.
How big of an air compressor do I need to run a plasma cutter?
As a good rule of thumb, select a compressor that has a flow rate capacity of at least 1.5 times the consumption rate of the plasma cutter.
Is a plasma cutter better than a torch?
Plasma does not require the metal to be preheated before cutting, which saves time, and plasma cutters also outperform oxy-fuel torches when cutting stacked metals. Faster speeds can be achieved on thinner metals with plasma, with minimal or no metal distortion.
How does a gasless plasma cutter work?
0:011:23How Does a Plasma Cutter Work? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo how plasma cutting systems work is they utilize compressed air or compressed gases such asMoreSo how plasma cutting systems work is they utilize compressed air or compressed gases such as nitrogen to ionize to create plasma typically. These gases are fed through the back of the machine.
Do all plasma cutters need air compressor?
First, the arc heats the metal until it's semi-gaseous. Second, the plasma is forced by blasts of air to finish the cut. Therefore, all plasma cutters need an air compressor to generate enough air pressure for the task. If you buy a plasma cutter without a built-in source of air, you'll need a separate air compressor.
How do you set up a plasma cutting machine?
How to Use a Plasma CutterStep 1: Choose Work Location. ... Step 2: Plug in Unit. ... Step 3: Connect the Air. ... Step 4: Turn the Air On. ... Step 5: Attach the Ground Clamp. ... Step 6: Turn on the Machine. ... Step 7: Set the Current. ... Step 8: Cut the Metal.More items...
What are the two types of plasma cutting?
Types of Plasma Cutting Nearly all plasma cutting systems fall under two categories: Conventional and Precision plasma systems. Conventional Plasma Systems - Typically use shop air as the plasma gas, and the shape of the arc is determined by the nozzle on the torch.
What are the two types of plasma cutters?
Two types of plasma cutters — manual and automatic — are common to shops that fabricate sheet metal and piping. Some of the differences between the two types of plasma cutters are portability, productivity and ease of use.
What kind of gas do you use with a plasma cutter?
work by sending an electric arc through a gas that is passing through a constricted opening. The gas can be shop air, nitrogen, argon, oxygen.
4 Gases Used in Plasma Cutter & How to Choose - Weld Guru
Leaves an oxidized cut area affecting weldability ; Oxidation and nitriding of the cut surface can occur, which can cause porosity in welds. You can combat this by using high-quality weld wire with denitrifiers and deoxidizers.
Gas selection guide - plasma cutting aluminum, mild/stainless steel
The best gas to use depends, mainly on three considerations: cut quality, productivity, and economy. For mild steel, use an oxygen plasma gas and air shield gas for the best, clean cut quality, lowest dross levels, minimal rework, excellent weldability and highest cutting speed/productivity.
What gas is used for cutting steel?
If you want fast speeds with lower power levels when using your plasma cutting machines, then oxygen is the plasma gas for you. Ideal for cutting structura- low carbon and low alloy steel, it can be used for cutting materials with a variety of different thicknesses.
Why is hydrogen plasma gas considered environmentally friendly?
Hydrogen plasma gas is classed as environmentally friendly as it reduces the emission of Co2. This gas contributes to increased productivity due to its high-speed cutting.
What is the fastest way to cut metal?
Plasma cutting is one of the fastest, most efficient ways to cut metals such as carbon steel, stainless steel and aluminium, allowing you to cut through materials up to 6 inches thick.
How many phases are there in plasma gas?
As well as the five named plasma gases above, plasma gas can also be further categorised into three different phases:
Is argon a good gas?
For materials that are greater than ½ an inch thick, argon is good to use. Argon does not react with metals when cutting, which is why it is classified as an inert gas.
Why use different gas in plasma?
Different gases are used, depending on material type and thickness, in order to achieve the best balance of cut quality, parts life, productivity, and overall cost of operation. Most plasma system manuals tend to overwhelm the operator with a confusing array of cut charts and gas choices. The intent of this article is to provide a brief overview ...
What is the best plasma gas?
Air. Air is the most versatile plasma gas; it produces good cut quality and speed on mild steel, stainless, and aluminum. Air also lowers the cost of operation because it is not necessary to purchase gases. However air is not free. Shop air must be cleaned to remove contamination such as particulate, oil mist, and moisture.
What gas is used for cutting aluminum?
Argon hydrogen. Argon hydrogen is the gas of choice for thick stainless and aluminum cutting (> 1/2") The mixture typically used is 35% hydrogen: 65% argon (H-35). Argon hydrogen is the hottest burning plasma gas and provides the maximum cutting capability. (Argon hydrogen is used in water injection torches up to 1000 amps for cutting up ...
What gas is used in multi gas torches?
In multi-gas torches, Argon hydrogen provides a straight cut and a very smooth almost polished surface on stainless steel. Some jagged dross may occur along the bottom edge. Nitrogen is typically used as the shield gas with argon hydrogen . The disadvantage of this combination is its expense.
What gas is used to cut mild steel?
Oxygen. Oxygen has become the industry standard for cutting mild steel because it provides the best, clean cut quality and fastest cutting speed of any plasma gas. (Plasma cutting aluminum plate or stainless plate with oxygen plasma gas is not recommended). Oxygen plasma gas reacts with carbon steel to produce a finer spray of molten metal, ...
What is the best cut quality for stainless steel?
For best cut quality on stainless and aluminum under 1/2" use nitrogen plasma and air secondary for a good balance of cut quality and affordability. For a slightly better and faster cut, use CO 2 as the secondary. If your system allows, water shield will provide the best edge quality.
What is the disadvantage of oxygen plasma?
This molten spray is more easily ejected from the kerf. The disadvantage of oxygen is the cost of the gas and the consumable parts life.
What is Plasma Cutting?
You are all aware that the matter around us has three states, solid, liquid, and gas. Take the example of water, it has three states, ice, water, and steam and they are differentiated by their energy levels; water relatively has more energy than ice, and so on.
How does plasma cut plate?
As more current flows from the electrode to the workpiece the plasma becomes sufficiently hot to melt the targeted workpiece area and the high-velocity plasma takes away the molten chips. The shield gas restricts the plasma to the cutting area, cools the nozzle, and protects the cut. This is how the plasma of your machine cuts the plate. Your Plasma Cutter may have a separate arrangement for cooling the nozzle.
What is the nozzle of a plasma cutter?
Plasma torch or cutter nozzle: This is an important part of your Plasma Cutter. The nozzle of your machine is generally made of copper, and the electrode is made of copper with a tungsten insert at the point of arc formation. Copper is used for its electrical conductivity and tungsten for its high melting point, however, tungsten faces the problem of burning in the presence of oxygen. Because of this, when you use oxygen or air as a gas in the plasma cutter, you have to use an alternative to tungsten (like Hafnium) as an electrode insert.
What happens when plasma blows away molten chips?
The high velocity ionized gas plunging on the workpiece forms a conductive path between the electrode and the workpiece. The plasma cutting system of your machine senses this situation and stops the arc between the electrode and the nozzle and facilitates the flow of current from the electrode to the workpiece; the arc formed between the electrode and the workpiece makes the plasma hot enough to melt the workpiece material and cutting happens when the high-velocity plasma blows away the molten chips.
What is the power source for a plasma cutter?
The electrode and the workpiece of your Plasma Cutter are connected to a DC power source.
Why does a plasma cutter emit radiation?
The plasma arc used in your Plasma Cutter emits radiations due to very high temperature and there can be unpleasant fumes during cutting; hence, following safety precautions are necessary.
How thick can a plasma torch cut?
You can use your handheld plasma torch to cut material up to 1.5 inches thickness and for higher thickness material cutting (up to 6 inches thick) a regular machine is preferred. The output current and the power (kilowatts) rating of the plasma cutter indicate the maximum cutting thickness and speed of cutting.
What is the safety of plasma cutters?
Safety is paramount when using a plasma cutter. Looking directly into the flame can permanently damage your eyes and the flame will also very quickly cut through skin, muscle and bone. It’s vital for you to select the appropriate PPE for the workplace, which can include helmets, safety footwear, gloves, eye protection and respiratory protective equipment to ensure the safety of workers.
Why is my plasma cutter not cutting?
The only times a plasma cutter will struggle to perform is if there is any water or moisture in the machine’s air compressor and if the air pressure is incorrect. If there is too much air the plasma can potentially blow out of the machine, however, if there is too little you will have trouble cutting. To find out what the right amount of air pressure is for your machine, check the guidelines on your plasma torch.
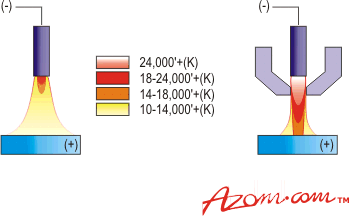
How hot does a Plasma Cutter get?
The heat of a plasma cutter can reach an impressive temperature of 25,000 degrees Celsius . To put this into perspective, it is hotter than the surface of the sun which sits at a comfortable 5,505 degrees Celsius.
What metals will a Plasma Cutter cut?
A plasma cutter can only be used for metals and alloys that are conductive. These include:
What is the best plasma cutting material for cutting stainless steel?
Argon is ideal for cutting thick stainless steel and aluminium as it’s the hottest burning plasma.
How much does a plasma cutter cost?
There are many inexpensive plasma cutters on the market, which start as low as £130, however, while these machines may make some impressive cuts it won’t be long before you need a replacement. Established names who are leading manufacturers of welding and cutting supplies are much more reliable, which will reflect in the plasma cutter’s abilities.
When was plasma cutting invented?
Plasma cutting is a process that was developed from plasma welding in the 1950s, and was designed to precisely cut both thin and thick materials. However, plasma cutting was not accepted by manufacturers and fabricators until the 1970s due to the cost of the system and the gases required, and the lack of knowledge surrounding the process.
How much air flow does a plasma cutter need?
For example, a Miller Spectrum 375 requires 4.5 cfm at 60psi, while the 625 requires 6 cfm at 75 psi.
Can you run a compressor off of a bottle of nitrogen?
You can run it off of bottled nitrogen, but, by the time you buy the bottle and go through a few refills, you will be very near the cost of a decent small compressor.
Is nitrogen as expensive as compressed air?
Nitrogen isn't as expensive as other compressed gases , what with the atmosphere being 78% nitrogen, but I've not bought it to know the exact difference. Costco fills all their tires with nitrogen, so you know they wouldn't do it if it was significantly more expensive than compressing air.
What type of gas is used for plasma cutters?
The most commonly used plasma cutter gas type is air. Highly versatile and inexpensive, compressed air works well for lower current cutting and on most metals—mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum--from gauge sizes to one-inch thickness.
What is the best mixture for plasma cutting?
Argon-hydrogen mixtures. Because they have contrasting properties, combining hydrogen and argon creates an outstanding plasma-cutting flame. With a standard mix of 65% argon and 35% hydrogen, it produces the hottest plasma cutting flame and some of the cleanest cuts.
What metals are plasma cutters made of?
Of course, the material must be conductive, meaning a plasma cutter works on carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, brass, and cast iron. The dense stream slices through these metals, and the gas is also directed around the perimeter of the cutting area to shield the cut from contamination.
What is a primeweld plasma cutter?
PrimeWeld's CUT50DP plasma cutter uses an electrical current and non-hazardous compressed air to cut through stainless steel, alloy steel, mild steel, copper, and aluminum. A pilot arc improves the plasma arc's ability to transfer to the workpiece, allowing it to cut through rough, painted, rusty surfaces efficiently while producing minimal slag.
What is the energy produced by plasma gas?
The energy produced from the plasma gas splits the torch's water into its two components--hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen isolates the cutting zone from contamination, leaving a clean cut free of dross and oxides. Since it is converted into its essential components, the water does not require disposal.
What factors are factored into plasma cutter gas selection?
In addition to the metal's thickness, its chemical characteristics and the cut's dimensions will factor into the plasma cutter gas selection process.
What is plasma cutting?
Plasma cutting is a powerful yet simple process during which an electric arc is sent through a gas passing through a copper nozzle's constricted opening. The extreme heat that is created elevates the gas's temperature, converting it to the fourth state of matter called plasma. The plasma's electrical conductivity causes the arc to transfer to ...
Compressed Air
Oxygen
- Oxygen has become the go-to gas for cutting mild steel because it offers clean cuts and faster cutting speeds on carbon steels up to a 1 ¼" thickness. While it isn't recommended for cutting stainless steel or aluminum, you can count on high-quality cuts with a smooth face and dross (mineral waste formed on the surface of molten metal) that's easy to remove from the kerf (the sl…
Argon
- Argon is a rare, inert gas, making it relatively expensive but unreactive with the metals it's cutting. Using argon gasimproves the stability of the arc and prevents atmospheric contamination of welding pools. While its high kinetic energy makes it an effective gas for plasma cutting, it can't work alone because of its low conductivity. As a result, argon must be paired with an appropriat…
Hydrogen
- Along with being an excellent thermal conductor, hydrogen has the properties needed to quickly cool hot metal surfaces. For these reasons, hydrogen is ideal for cutting aluminum and stainless steel. However, although it has excellent conductivity, its low atomic weight prevents it from having high kinetic energy. Just like argon, it must combine with other gases to produce a high-i…
Argon-Hydrogen Mixtures
- Because they have contrasting properties, combining hydrogen and argon creates an outstanding plasma-cutting flame. With a standard mix of 65% argon and 35% hydrogen, it produces the hottest plasma cutting flame and some of the cleanest cuts. Typically used for cutting stainless steel and aluminum, the argon-hydrogen mixture is required for cutting material over 3" thick. It i…
Nitrogen-Water Combination
- The nitrogen-water plasma cutter gas mixture uses nitrogen as the main gas and water as the secondary (shield) gas. The energy produced from the plasma gas splits the torch's water into its two components--hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen isolates the cutting zone from contamination, leaving a clean cut free of dross and oxides. Since it is converted into its essenti…
Primeweld Plasma Cutters and Multi-Process Welders
- PrimeWeld's top-of-the-line CUT60 Dual Voltage Plasma Cutteris a versatile machine appropriate for industrial settings or in a home workshop. At the same time, the CT-520DP Pilot Arc Plasma Cutter Combo and CT-520D Plasma Cutter/Stick Welder Combofeature a high-quality plasma cutter teamed up with a TIG and stick welder. And our plasma cutters work with a variety of gas…