
How to know if you tore your ACL or meniscus?
- You are now experiencing pain in the knee joint· Swelling
- facing difficulties in catching or locking of the knee joint
- Feeling it difficult to fully extend or bend the knee joint
- Limping
What happens if you leave a torn meniscus untreated?
The following are some of the things that can develop if your torn meniscus is left untreated: –Pieces of your meniscus can become loose and enter your knee joint, potentially causing excruciating pain or limiting your range of motion. –Pain, swelling, and inflammation can increase over time.
How long does it take to recover from meniscus surgery?
Though the surgery to repair a meniscus tear alone is not terribly long, the recovery time can last anywhere from three weeks to six months for a full return to activity.
Can you walk with a torn ACL and meniscus?
You can or can’t walk with a torn acl and meniscus basically its depends on the situation of injuries. Mri is the best study to diagnose an acl injury. The difference between medial and lateral meniscus tears simply comes down to location.

What ligaments attach to the medial meniscus?
In addition, the medial meniscus is adherent to the deep portion of the medial collateral ligament and may attach to the lateral meniscus via the transverse intermeniscal ligament. The lateral meniscus occasionally attaches posteriorly by the ligaments of Humphry and Wrisberg to the femur (see Fig. 23-14).
What does medial meniscus attach to?
Anatomy and attachment The posterior horn of the medial meniscus is firmly attached to the posterior aspect of the periphery to the joint capsule. At its midpoint, the meniscus is firmly attached to the femur and tibia through a condensation in the joint capsule known as the deep medial ligament.
Does the ACL attach to the lateral meniscus?
The attachments of the tibial side of ACL consisted of attachments to the bone (102.6 ± 27.5 mm2), articular cartilage (40.9 ± 13.6 mm2), and lateral meniscus (6.5 ± 4.6 mm2), suggesting that the ACL has close structural relationships with the articular cartilage and lateral meniscus.
Is the ACL part of the meniscus?
The meniscus functions as a shock absorber and helps distribute weight between the upper and lower legs. Meanwhile, the ACL is a band of tissue that runs through the middle of your knee and provides structural support for the knee during twisting and intense activities.
Which meniscus is torn with ACL?
Lateral meniscus tears are the most common type of meniscus tears seen at ACL reconstruction.
Why is the medial meniscus more likely to be injured?
The medial meniscus is more vulnerable to injury to due to its intimate attachment to the medial collateral ligament. The moveable lateral meniscus is less prone to tear except when the ACL is injured.
Can a medial meniscus tear heal on its own?
In the case of meniscus tears, some people think the injury will heal over time on its own. But the truth is that there are different types of meniscus tears — and some tears won't heal without treatment. If your tear is on the outer one-third of the meniscus, it may heal on its own or be repaired surgically.
What does ACL attach to?
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the ligaments in the knee joint. A ligament is a tough, flexible band of tissue that holds bones and cartilage together. The ACL connects the bottom of the thighbone (femur) to the top of the shinbone (tibia). The ACL helps keep the knee stable.
How can you tell the difference between an ACL tear and a torn meniscus?
Many ACL tears we see only have problems ascending stairs, jogging, or walking downhill but can walk up hills and on flat roads without an increase in pain. A meniscus tear, on the other hand, will cause fairly severe pain even just standing on it.
What happens if you tear your ACL and meniscus?
Recovery depends on the type and severity of your tear. Meniscus tears generally heal in approximately three months or sooner (with and without surgery), while ACL tears take longer. If you don't need surgery, recover takes about three to six months. Recovering from ACL surgery can take six months to a year.
Is an ACL tear worse than a meniscus tear?
While not always the case, an ACL tear is in most cases going to be the more severe injury. It is considered worse than tearing the MCL because ACL tears are in general more complex to treat and require a longer recovery time after surgery.
Can you tear meniscus and not ACL?
ACL Tears and Meniscus Injuries can occur together. Often when someone tears their ACL, the medial meniscus is also torn or sprained. These two injuries are addressed in the same surgery. The meniscus can be repaired or debrided.
Which is worse lateral or medial meniscus tear?
Is the lateral meniscus tear worse than a medial meniscus tear? It is hard to differentiate what type of tear is worse if it is repairable. However, it is well known that if a lateral meniscus is taken out, the consequences are almost always worse than having a medial meniscus resected.
Can you bend knee with ACL tear?
Some people find that the knee joint feels looser than it should. Less range of motion. After you damage your ACL, it's very likely that you won't be able to bend and flex your knee like you normally would.
Can you walk with a torn ACL MCL and meniscus?
Can you walk with a torn ACL? The short answer is yes. After the pain and swelling subsides and if there is no other injury to your knee, you may be able to walk in straight lines, go up and down stairs and even potentially jog in a straight line.
How do I know if I tore my MCL or meniscus?
How Can I Tell If I Tore My MCL? Signs & Symptoms to Watch ForA popping sound when the injury is sustained.Pain (ranging from mild to severe depending on injury grade) on the inside of the knee.Instability, or feeling like the knee cannot bear weight and may give out.Knee stiffness.More items...•
What holds the meniscus in place?
The menisci are attached to each other via the transverse ligament. The horn attachments connect the tibial plateau to the meniscus.
What is the lateral meniscus attached to?
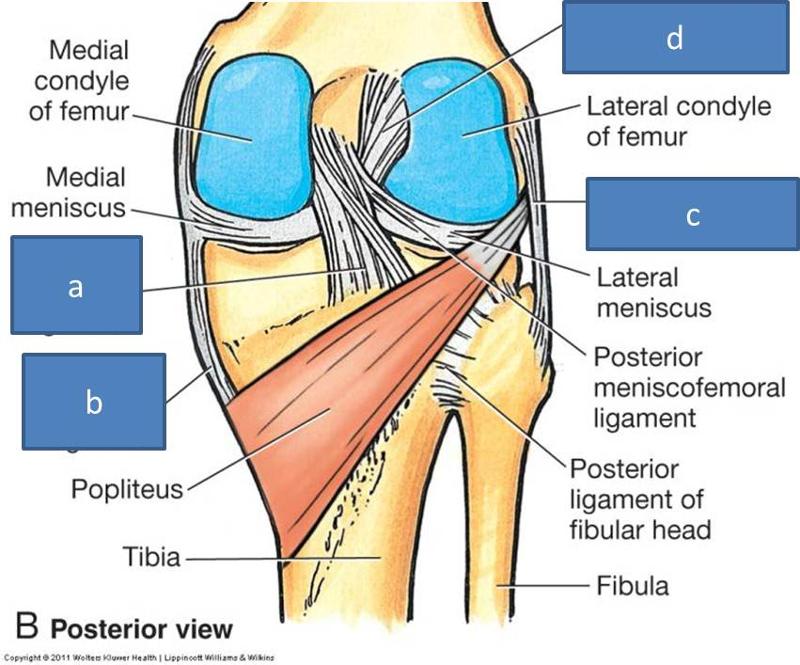
tibiaThe lateral meniscus has an intricate attachment to the tibia that includes the lateral menisco-tibial ligament (LMTL), the popliteo-fibular ligament (PFL) and the popliteo-meniscal ligament (PML).
What are clinical signs the medial meniscus is torn?
Swelling or stiffness. Pain, especially when twisting or rotating your knee. Difficulty straightening your knee fully. Feeling as though your knee is locked in place when you try to move it.
What attaches the meniscus to the tibia?
The meniscus attaches to the tibia via coronary ligaments.
What is the ACL?
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is a band of dense connective tissue which courses from the femur to the tibia. The ACL is a key structure in the knee joint, as it resists anterior tibial translation and rotational loads.
What is the ACL made of?
The ACL has a microstructure of collagen bundles of multiple types (mostly type I) and a matrix made of a network of proteins, glycoproteins, elastic systems, and glycosaminoglycans with multiple functional interactions.
What is the ACL reflex?
The ACL reflex is an essential part of normal knee function and is involved in the updating of muscle programs. This becomes even more obvious in patients with a ruptured ACL, where the loss of feedback from mechanoreceptors in the ACL leads to quadriceps femoris weakness.
Where does the ACL nerve fiber come from?
The ACL receives nerve fibers from the posterior articular branches of the tibial nerve. These fibers penetrate the posterior joint capsule and run along with the synovial and periligamentous vessels surrounding the ligament to reach as far anterior to the infrapatellar fat pad. Most of the fibers are associated with the endoligamentous vasculature and have a vasomotor function. The receptors of the nerve fibers mentioned are as follows:
Which bundle is tight in flexion?
The anteromedial bundle is tight in flexion and the posterolateral bundle is tight in extension. In extension both bundles are parallel; in flexion the femoral insertion site of the posterolateral bundle moves anteriorly, both bundles are crossed, the anteromedial bundle tightens and the posterolateral bundle loosens.
Which artery is vascularized by the distal part of the cruciate ligament?
The distal part of both cruciate ligaments is vascularized by branches of the lateral and medial inferior geniculate artery. The ligament is surrounded by a synovial fold where the terminal branches of the middle and inferior arteries form a periligamentous network.
Where is the tibial attachment?
The tibial attachment is in a fossa in front of and lateral to anterior spine, a rather wide area from 11 mm in width to 17 mm in AP direction.
How was the ACL reconstruction taken down?
The former ACL reconstruction was taken down using a shaver, and a revision notchplasty was performed.
What is the physical exam for ACL reconstruction?
Physical exam should include observation of gait, standing limb alignment, Beighton score, and a complete ligamentous exam of the knee , with a focus on potential posterolateral corner (PLC) injuries missed at the time of initial injury. [7]
What is the best way to evaluate the ACL graft?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) should always be obtained to evaluate the status of the ACL graft and any additional ligamentous, meniscal, or chondral pathology. Tunnel position and size can also be evaluated on the MRI. A computed tomography (CT) scan should be obtained for a more detailed assessment if there is any concern about tunnel position (ie, posterior wall blowout) or significant tunnel widening. [8,9]
How much graft is in the femoral tunnel?
The graft was then advanced into the femoral tunnel, with about 20 mm of graft into the tunnel. We checked the graft for impingement and found none with the knee in flexion or in full extension in the notch (Figure 8).
What is included in a knee radiograph?
Imaging should include radiographs of the knee and standing full-length alignment films of the lower extremities. Radiographs of the knee can be evaluated for tunnel position and size, type of graft fixation, and posterior tibial slope. Coronal alignment of the knees should be evaluated on the standing full-length radiographs to determine if concomitant procedures, such as corrective osteotomies, may be needed.
How to harvest quadriceps tendon?
The quadriceps tendon was harvested using a 4-cm incision starting at the superior pole of the patella. A central slip of 1 cm of the quadriceps tendon, near full thickness in depth and about 80 mm in length, was taken from the superior pole of the patella. The tendon was first transected from the superior pole of the patella and traction was pulled distally to assure adequate length to the graft prior to proximal transection, with a goal length of 70 mm to 80 mm.
Is ACL reconstruction more predictable than primary reconstruction?
Outcomes after revision ACL reconstruction are less predictable than after primary ACL reconstruction, in part because concurrent meniscal and cartilage injuries are common in the setting of ACL graft rupture. [10-13] Return to sport can take longer after revision ACL reconstruction and only about 53% of patients who undergo revision ACL return to sport at their pre-injury level, despite relatively similar rates of return to activity between patients with revision ACL and primary ACL reconstruction. [12,14-18]
Why is the medial meniscus attached to the medial collateral ligament?
This is partly because the medial meniscus is attached to the medial collateral ligament, and partly because tackles are often directed towards the lateral side of the knee, causing external rotation of the tibia. Injury to the medial meniscus is about 5 times more common than injury to the lateral meniscus.
Where is the medial meniscus located?
Medial menisci are C shaped wedge fibrocartilagenous structure located between condyle of femur and tibia. It is somewhat more in C shape as compared to lateral menisci as it is medial meniscus are clear of the plateau anteriorly and posteriorly. Anteriorly, it is also attached to lateral menisci by transverse ligament and patella either directly or by patellomeniscal ligaments which are anterior capsular thickenings[1]. Its anterior portion is much narrower than the posterior portion and the narrower portion is less prone to injury also.
What causes a meniscus tear?
The most common mechanism of menisci injury is a twisting injury with the foot anchor on the ground, often by another player's body. A slow twisting force may also cause the tear.Damage to the meniscus is due to rotational forces directed to a flexed knee (as may occur with twisting sports) is the usual underlying mechanism of injury . The meniscal tear is of following types:
Why are my menisci rubbery?
The rubbery texture of the menisci is due to their fibrocartilagenous structure. Their shape is maintained by the collagens within them. One meniscus is on the inner side of your knee--the medial meniscus. The other meniscus is on the outer side of your knee--the lateral meniscus.
What is the pain in the medial joint line?
Pain in the area of the medial joint line during hyperflexion of the knee joint. Pain during external rotation of the foot and the lower leg when the knee is flexed at different angles around 70–90°. Weakened or hypotrophied quadriceps muscle.
How long is the medial meniscus?
The medial meniscus is approximately 1.4 in (3.5cm) in length. The anterior horn of the medial meniscus is attached to the anterior surface of the tibia well off the tibial plateau. The anterior fibers of the anterior cruciate attachment merge with the transverse ligament, which connects the anterior horns of the medial.
What is the role of menisci in the knee?
At knee joint the menisci plays a major role in congurency of the joint. Menisci forms the concavity in which the femoral condyles sits. Menisci rests between the thigh bone femur and the tibia and there are two knee joint ligaments. They are a type of cartilage in the joint.
Who is the doctor who tore the meniscus and ACL?
I tore both the ACL and the Meniscus. Do I need multiple surgeries? — Dr. Bill Sterett
How does a meniscus tear happen?
So the knee must be compressed, and then rotated to cause this injury. The meniscus becomes trapped between the femur and the tibia bones, and the added twist causes the tear.
What is the Meniscus and Why Is It Important?
Now let's move on to the meniscus. While the ACL is a ligament, the meniscus is actually cartilage. It's the "cushion cartilage" of your knee, acting like a shock absorber. So you can see why this cartilage is so important. Without meniscus cartilage, the bone begins to rub together, causing arthritis.
What Does a Meniscus Tear Feel Like?
So how do you know if you have a meniscus tear? Well, the symptoms are what we call "mechanical". So, if you have a meniscus tear you will be dealing with
What Are The Symptoms of ACL Tears?
So you tore your ACL...what will it feel like after the injury? Well, for the first two days, you'll feel a lot of pain and swelling. If it swells up more in the first 1-2 hours after the injury, it's more commonly an ACL tear and less commonly a meniscus tear. Of course, we are talking about both injuries here, at once. But many people tear the ACL while damaging the meniscus, as well.
What happens when you twist your ACL?
What often happens is the ACL tears from twisting, and as the rotation of the knee continues, the meniscus tears next, often resulting in the cushion cartilage being “flipped” up into the wrong place, actually blocking or hindering the ability to fully straighten the knee. You may have heard of this referred to as a bucket handle tear, ...
How long does it take for an ACL tear to feel like it's tearing?
If it swells up more in the first 1-2 hours after the injury, it's more commonly an ACL tear and less commonly a meniscus tear.
What type of meniscus tear is most common in ACL reconstruction?
Lateral meniscus tears are the most common type of meniscus tears seen at ACL reconstruction. Most are asymptomatic and can be left in situ, says Dr. Shelbourne, based on data from patients at Shelbourne Knee Center.
What is the phone number for meniscus tears?
For more information about appropriate treatment for meniscus tears, please call 888-FIX-KNEE.
Can meniscus tears be treated?
Most of these meniscus tears are asymptomatic (2) and don’t require treatment. “Even most symptomatic meniscus tears will get better on their own,” says K. Donald Shelbourne, MD, orthopedic surgeon at Shelbourne Knee Center.
Is Shelbourne Knee Center a fellowship?
At the Shelbourne Knee Center, our pioneering efforts to focus only on the specialty of knee pain and injuries have given us unmatched insight into the options available to patients. Our team has tracked the outcomes of thousands of patients from non-surgical treatments to ACL reconstructions. And from this experience, our fellowship trained surgeons know when therapeutic options are more successful than surgery and how to minimize recovery time when surgery is necessary.
Can meniscus repair affect ACL?
Unnecessary meniscus repair can jeopardize ACL rehab by restricting weight-bearing and range of motion (ROM). It can also lead to possible complications:
Does weight bearing help meniscus?
Through the physical therapy between the first and second procedures, Dr. Shelbourne learned that weight-bearing as tolerated and working on ROM both helped the meniscus heal. “Our data show that almost all tears can heal with allowing full ROM and weight-bearing,” he says. This is now a routine part of physical therapy at Shelbourne Knee Center.
Can a firefighter with arthritis get back to helping people after knee replacement surgery?
Firefighter with severe arthritis gets back to helping people after knee replacement surgery.
Why is ACL reconstruction important?
Early ACL reconstruction is recommended also for the prevention of secondary meniscal tear. The incidence of meniscal tear associated with ACL injury is higher in chronic cases; the number of medial meniscal tears is particularly high, many of which require meniscectomy. Early ACL reconstruction is recommended also for the prevention ...
How many knees are meniscal tears?
Regarding the locations of meniscal tears, in acute group (186 knees), medial meniscal tear only was found in 20 knees (10.8 %), lateral meniscal tear only in 129 knees (69.4 %), and bilateral (including medial and lateral) meniscal tears in 37 knees (19.9 %).
What is the incidence of meniscal tears?
Meniscal tears associated with anterior cruciate ligament injury. The incidence of meniscal tear associated with ACL injury is higher in chronic cases; the number of medial meniscal tears is particularly high, many of which require meniscectomy.
Which ligaments transport blood from the meniscus to the meniscus?
The coronary liga ments attached to the meniscus, transport the blood from the perimeniscal plexus (network of blood vessels) into the peripheral of the menisci. The anterior and posterior horns of the menisci also receive a good amount of blood as they are covered by a vascular synovium.
What ligaments attach the menisci to the knee?
The menisci also attach to leg muscles which help the menisci maintain their position during movement. The semimembranosus and quadriceps attach to both menisci. The lateral meniscus attaches to the popliteus below the knee and the femur via the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). On the inner part of the knee, the ends of the medial meniscus (known as the anterior and posterior horns) are attached to the tibia and joint capsule and along the exterior edge of the meniscus by the coronary ligaments. This means that the medial meniscus is attached at three points compared to the lateral meniscus which is only attached at two points. Coronary ligaments are loose which allow the menisci to pivot freely. However, because the medial meniscus is anchored by a third point, it does not move as freely in the joint as the lateral meniscus and as a result is torn more frequently.
What Happens When the Meniscus is Injured?
Menisci tend to get injured during movements that forcefully twist your knee while bearing weight. As we age the meniscal tissue degenerates - getting thinner and becoming weaker overall. A degenerated meniscus, as you can probably infer, is more likely to tear as a result of minor injuries or movements.
How does the menisci help the knee?
Your menisci act much like a wedge to help naturally prevent over-rotation in the joint, but just as important, the menisci are the true shock absorbers in the knee joint. When walking, jumping or running, there are heavy forces exerted on the knees; your meniscus absorbs and disperses much of the forces instead of the ends of the bones (where the upper leg and lower leg meet in the knee joint) . If the ends of these bones absorb too much force, they will become damaged. It is also worth knowing that the amount of force exerted on the knee joint grows exponentially as speed of movement increases (ie. from walking to running) 1. If you are already suffering from some meniscus damage, it goes without saying that you want to minimize load on the knee joint when you are upright, so take care to avoid running and/or jumping as load forces multiply quite quickly with faster movements.
What is the cartilage in the knee?
As well as providing stability, the tendons, ligaments, articular cartilage and menisci in the joint provide cushioning and protect the upper and lower leg bones where they meet at the knee joint. A type of slick, hard yet flexible tissue known as articular cartilage covers the surface ends of the tibia and femur at your knee joint, allowing them to move easily against one another. The articular cartilage in the knee is generally 1/8 to 1/4 inch thick. A thick, stringy, egg-like fluid, called synovial fluid - found inside the knee capsule - lubricates your knee joint and, along with the meniscus and articular cartilage help reduce friction.
How does the meniscus work?
They work like shock absorbers, supporting the load by compressing and spreading the weight evenly within the knee. Even while walking, the pressure put on the knee joints can be 2 - 4 times your own body weight; when you run these forces increase up to 6 - 8 times your body weight and are even higher when landing from a jump. By increasing the area of contact inside the joint by nearly 3 times, the menisci reduce the load significantly (dispersing between 30 and 55% of the load).
Why does my meniscus tear?
A degenerated meniscus, as you can probably infer, is more likely to tear as a result of minor injuries or movements. Regardless of how the meniscus was damaged, once your meniscus is damaged and/or torn, it starts to move abnormally inside the joint.
Introduction
Attachments
- Origin
Arises from the posteromedial corner of medial aspect of lateral femoral condyle in the intercondylar notch. This femoral attachment of ACL is on posterior part of medial surface of lateral condyle well posterior to longitudinal axis of the femoral shaft. The attachment is actuall… - Orientation
It runs inferiorly, medially and anteriorly.
Nerve Supply
- The ACL receives nerve fibers from the posterior articular branches of the tibial nerve. These fibers penetrate the posterior joint capsule and run along with the synovial and periligamentous vessels surrounding the ligament to reach as far anterior to the infrapatellar fat pad. Most of the fibers are associated with the endoligamentous vasculature and have a vasomotor function. Th…
Vascular Supply
- The major blood supply of the cruciate ligaments arises from the middle geniculate artery. The distal part of both cruciate ligaments is vascularized by branches of the lateral and medial inferior geniculate artery. The ligament is surrounded by a synovial fold where the terminal branches of the middle and inferior arteries form a periligamentous network. From the synovial sheath bloo…
Composition
- The ACL has a microstructure of collagen bundles of multiple types (mostly type I) and a matrix made of a network of proteins, glycoproteins, elastic systems, and glycosaminoglycans with multiple functional interactions.
Bundles
- There are two components of the ACL, the smaller anteromedial bundle (AMB) and the larger posterolateral bundle (PLB), named according to where the bundles insert into the tibial plateau. The anteromedial bundle is tight in flexion and the posterolateral bundle is tight in extension. In extension both bundles are parallel; in flexion the femoral insertion site of the posterolateral bun…
Function
- The ACL provides approximately 85% of total restraining force of anterior translation. It also prevents excessive tibial medial and lateral rotation, as well as varus and valgus stresses. To a lesser degree, the ACL checks extension and hyperextension. Together with the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), the ACL guides the instantaneous center of rotation of the knee, therefore contr…