Arrayed along the DNA strand are the genes, specific regions whose sequences carry the genetic code for making specific proteins. The genes of bacteria are tightly packed together; virtually all the DNA encodes proteins. It is estimated that only about five percent of human DNA encodes protein.
How do you convert DNA to protein?
How do you translate a DNA sequence? Basically, a gene is used to build a protein in a two-step process: Step 1: transcription! Here, the DNA sequence of a gene is “rewritten” in the form of RNA. Step 2: translation! In this stage, the mRNA is “decoded” to build a protein (or a chunk/subunit of a protein) that contains a specific series ...
Are there proteins in DNA?
Within chromosomes, DNA is held in complexes with structural proteins. These proteins organize the DNA into a compact structure called chromatin. In eukaryotes, this structure involves DNA binding to a complex of small basic proteins called histones. In prokaryotes, multiple types of proteins are involved.
How many proteins in DNA?
proteins 36. Nevertheless, TFBM over-representation has a value in predicting TF binding, because it does not depend on experimental difficulties such as antibody quality. Chromatin accessibilities at the DNA demethylated regions increased from 0 to 48 h ...
What is the process of DNA to protein?
What are the 9 steps of protein synthesis?
- DNA unravels, exposing code.
- mRNA comes in.
- transcription (copying genetic code from DNA)
- mRNA exits nucleus, goes to ribosome.
- translation (gives message to ribosome)
- tRNA brings in specific amino acids (anticodons)
- protein synthesis begins.
- peptides.
Does all DNA make proteins?
To carry out these functions, DNA sequences must be converted into messages that can be used to produce proteins, which are the complex molecules that do most of the work in our bodies. Each DNA sequence that contains instructions to make a protein is known as a gene.
Why does DNA not code for proteins directly?
Firstly, DNA is packed very tightly. Unwinding it every now and then to facilitate protein translation would consume too much energy. In addition to being energy inefficient, there is also a high risk of loss of genetic material. Secondly, protein translation occurs on ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
What are some examples of DNA that do not code for proteins?
Non-coding DNAHistorically referred to as 'junk DNA', these non-coding regions are now recognised to serve other important functions.Examples include satellite DNA, telomeres, introns, ncRNA genes and gene regulatory sequences.
Which strand of DNA does not code for protein?
Antisense is the non-coding DNA strand of a gene. In a cell, antisense DNA serves as the template for producing messenger RNA (mRNA), which directs the synthesis of a protein.
What is non-coding DNA called?
Non-coding DNA (ncDNA) sequences are components of an organism's DNA that do not encode protein sequences. Some non-coding DNA is transcribed into functional non-coding RNA molecules (e.g. transfer RNA, microRNA, piRNA, ribosomal RNA, and regulatory RNAs).
What are examples of non-coding DNA?
Transposable elements make up the major part of non-coding DNA. These include LINEs, SINEs, satellite DNA, and VNTRs. LINEs, or Long INterspersed Elements, are moderately repetitive, non-coding regions possibly derived from viruses.
Can any gene make any protein?
Overall Summary: The process of going from DNA, to RNA, to protein has many regulatory steps or checkpoints. A gene has other DNA sequence (that ultimately does not code for a protein product) that can regulate the expression of a gene. So, in general, the cell will not produce a protein product that it shouldn't.
What is the difference between coding and non-coding DNA?
Coding DNA refers to the DNA in the genome, containing for protein-coding genes while noncoding DNA refers to the other type of DNA, which does not code for proteins.
Why DNA is not a code?
The names guanine, adenine, thymine and cytosine are not codes: they are primary symbols. Primary symbols stand for real things and not for symbols. The real physical entities guanine, adenine, thymine and cytosine are not codes.
Do both DNA strands code for proteins?
So, yes, it is possible for a gene to be read in both directions (both strands) and code for different proteins.
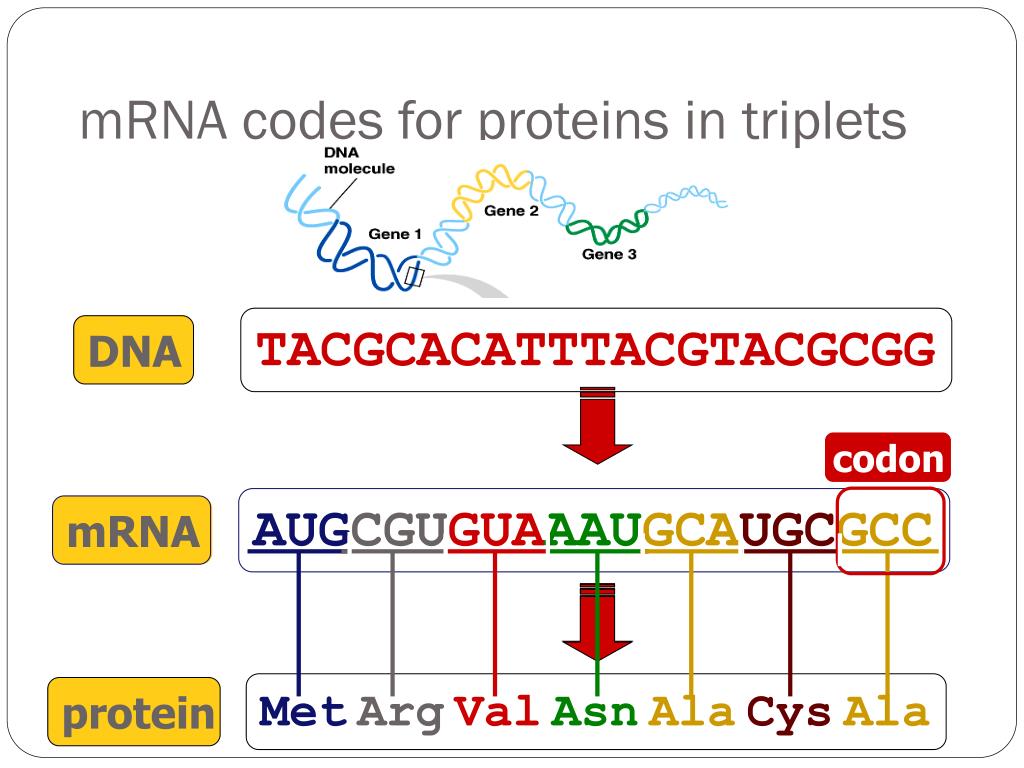
How does DNA code for proteins?
Genetic Code Each gene's code uses the four nucleotide bases of DNA: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T) — in various ways to spell out three-letter “codons” that specify which amino acid is needed at each position within a protein.
How many non-coding genes do humans have?
RefSeq, a database run by the US National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), lists 20,203 protein-coding genes and 17,871 non-coding genes.
Does DNA make proteins directly?
The flow of information from DNA to RNA to proteins is one of the fundamental principles of molecular biology. It is so important that it is sometimes called the “central dogma.” Through the processes of transcription and translation, information from genes is used to make proteins.
Why is DNA not directly translated into A polypeptide chain?
Justifies reasons why a polypeptide chain is not directly translated from the DNA strand: Ribosomes are used to make polypeptide chains and are not found in the nucleus. Ribosomes are capable of translating only single stranded mRNA.
How does DNA code for proteins?
Genetic Code Each gene's code uses the four nucleotide bases of DNA: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T) — in various ways to spell out three-letter “codons” that specify which amino acid is needed at each position within a protein.
Why is it advantageous to use RNA as opposed to translating proteins directly from DNA?
Using RNA as a template for protein synthesis instead of translating proteins directly from the DNA is advantageous for the cell because a. RNA is much more stable than DNA. b. RNA acts as an expendable copy of the genetic material, allowing the DNA to serve as a permanent, pristine repository of the genetic material.
Why is DNA a computer code?
Because DNA has a quaternary (base 4) numeral system, DNA sequences that create “words” and “sentences”, has behavior similar to functions, and even displays a form of polymorphism, DNA operates very similar to computer code.
How many base pairs are encoding proteins?
Of the three billion base pairs in the human genome, only about 1–2% is encoding proteins. The rest is known as “non-coding DNA.”
Why do we transcribe DNA into RNA?
Remember, we transcribed the DNA into RNA. It’s just recopying (transcription), because DNA and RNA are just different dialects of the same nucleotide language. Now, though, we’re going to translate our nucleotide language into a different language - the language of amino acids.
What is the DNA sequence of phenylalanine?
For example, phenylalanine corresponds to TTT. DNA consists in a sequence of nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of one base (cytosine (C), guanine (G), adenine (A), and thymine (T)), a sugar (deoxyribose), and a phosphate group [ 1].
What is the direction of a strand of DNA?
Let’s look at an example - a 6-nucleotide strand that goes ACCTGA. DNA has a direction - the beginning of a strand is marked by a 5′, and the end of a strand is marked by a 3′, so our example strand is formally 5′ACCTGA3′. A strand of DNA is made up of a series of molecules called (among other things) “nucleotides”.
How many triplet codons are in DNA?
So, looking at our original DNA, it looks like we have 2 triplet codons: ACC and TGA (or UGA if we use the RNA). What are our amino acids from this?
How does RNA work?
Computers work with (uses) the code stored in their electronic memory devices. RNA structures work with (uses) the code stored in DNA memory devices. So, if anything should be called a “computer,” it is the many RNA structures, working together, that performs the “computing” (but only in a loosely analoguous way).
How many amino acids are in a protein?
Originally Answered: A protein contains 51 amino acids. How many nucleotides does the DNA that encodes it contain?
What is the function of DNA?
DNA can act as a binding region for transcription factors and other DNA binding proteins to trigger the biological function. DNA requires all these regulatory region such as promoter, operator, to physically form a protein with the coding sequence (refer the epigenetic modification of DNA that cause switch on/off to a gene).
What is the role of short non-coding RNA in RNA interference?
2) Short non-coding RNA involved in RNA interference or RNAi. There are at least several classes of these depending on their precise mechanisms, but their overarching function is gene regulation by inhibiting mRNA from being translated into its "intended" protein. They have also been adapted in the molecular biology lab to "knockdown" expression of specific proteins, which is an important way of knowing how they function in life.
What is the name of the RNA that is transcribed from DNA?
There are two other (old school) forms of RNA transcribed from DNA as well: transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA ( rRNA), neither of which code for proteins, but assist in its production. tRNA transports each individual amino acid (AA) const
What is the intermediary for DNA?
First of all, DNA only indirectly codes for polypeptides and proteins via an intermediary called messenger RNA or mRNA. Thus DNA transcription > mRNA translation > polypeptide/protein is the cell's basic paradigm of information flow resulting in "protein expression." Ultimately proteins are what build cells and the enzymes that permit them to function.
How many adenines are in a poly A-tail?
This Poly A-tail is a mere 150–200 string of Adenines at the 3′ end. Making this is where this modification gets complex, however.
How many splices are there in mRNA?
They are the enzymes that splice the mRNA at the splice site. Those are just the sequence where the mRNA spliced. On every strand of mRNA, there are 2 splice sites a start and an end one.