What are ASC 606 new revenue recognition standards?
All US businesses, for-profit and nonprofit, were subject to new revenue recognition standards starting by 2019. These new standards are detailed in ASC 606 and impact all companies that contract with customers to transfer goods or services.
Is there a new revenue recognition standard for nonprofit organizations?
Luckily for us in the nonprofit industry, there is a second revenue recognition standard that will have an impact. FASB issued ASU 2018-08, Clarifying the Scope and Accounting Guidance for Contributions Received and Contributions Made (Topic 958-605).
How does ASU 2018-08 impact nonprofit accounting?
FASB issued ASU 2018-08, Clarifying the Scope and Accounting Guidance for Contributions Received and Contributions Made (Topic 958-605). For those nonprofits that are engaging in both contribution and exchange transactions, both standards will have an impact on how nonprofits recognize revenue.
How will the new accounting standards impact your nonprofit?
These new standards not only impact accounting; others in your nonprofit should be engaged as well. There are many other employees within an entity that receive grant agreements, contracts, etc. and they are crucial to determining the revenue recognition process.

Does revenue recognition apply to nonprofits?
The typical way most nonprofit organizations recognize revenue is to: Record income as cash. Invoice customers and donors and record that income as accounts receivable.
Who does ASC 606 apply to?
ASC 606 is a revenue recognition standard that applies to all business entities that enter into contracts to provide goods or services to customers; including non-profit, private, and public companies. Considering this, both private and public companies need to comply with ASC 606.
What accounting standards do nonprofits follow?
Both nonprofits and government agencies must follow GAAP, the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles. GAAP's main objective is to ensure that financial information is reported on effectively and efficiently.
Do nonprofits have to disclose financials?
Tax-exempt nonprofits are required to provide copies, upon request, of their three most recently filed annual information returns (IRS Form 990) and their application for tax-exemption.
Does ASC 606 apply to private companies?
ASC 606 applies to all public and private companies that follow generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
How is ASC 606 different?
ASC 606 defines flexible and robust guidance to accommodate the entire gamut of revenue recognition changes that would affect the financial statements of a company. Additionally, the new guidance would also improve the comparability of revenue recognition practices across different companies and industries.
How is accounting different for nonprofits?
The key difference in for-profit and nonprofit standards is the concept of fund accounting, which focuses on accountability rather than profitability. Whereas a profit entity would have a general ledger, which is a single self-balancing account, nonprofits typically have a number of general ledgers, or funds.
Do nonprofits use cash or accrual accounting?
Established nonprofits generally use the accrual method (aka “accrual basis”) for preparing and issuing financial statements. Smaller or startup organizations often choose the cash method (aka “cash basis”).
What are the financial reporting requirements for nonprofit accounting?
Nonprofits use four main financial reporting statements: balance sheet, income statement, statement of cash flows and statement of functional expenses. Three of these are similar to common for-profit company statements, with the functional expenses statement being unique.
What happens when non profit refuses to show documents?
If the organization fails to provide the documents at the agreed upon time, statutory penalties may be assessed.
How often should a nonprofit be audited?
§ 24:513(J)(1)(c) | A nonprofit that meets the definition of “quasi-public agency” will be required to conduct an annual independent audit if the nonprofit receives $500,000 or more in revenues in any one fiscal year; a financial review is required if annual revenue is $200,000 or more but less than $500,000; a ...
What financial statements are nonprofits required to issue?
5 financial documents for every US nonprofitStatement of financial position (SOP) The SOP is the nonprofit's equivalent of a for-profit company's balance sheet. ... Statement of activities. ... Statement of functional expenses. ... Statement of cash flows. ... Annual report.
What is the point of ASC 606?
ASC 606 is the new revenue recognition standard that affects all businesses that enter into contracts with customers to transfer goods or services – public, private and non-profit entities. Both public and privately held companies should be ASC 606 compliant now based on the 2017 and 2018 deadlines.
What is the purpose of ASC 606?
ASC 606 directs entities to recognize revenue when the promised goods or services are transferred to the customer. The amount of revenue recognized should equal the total consideration an entity expects to receive in return for the goods or services.
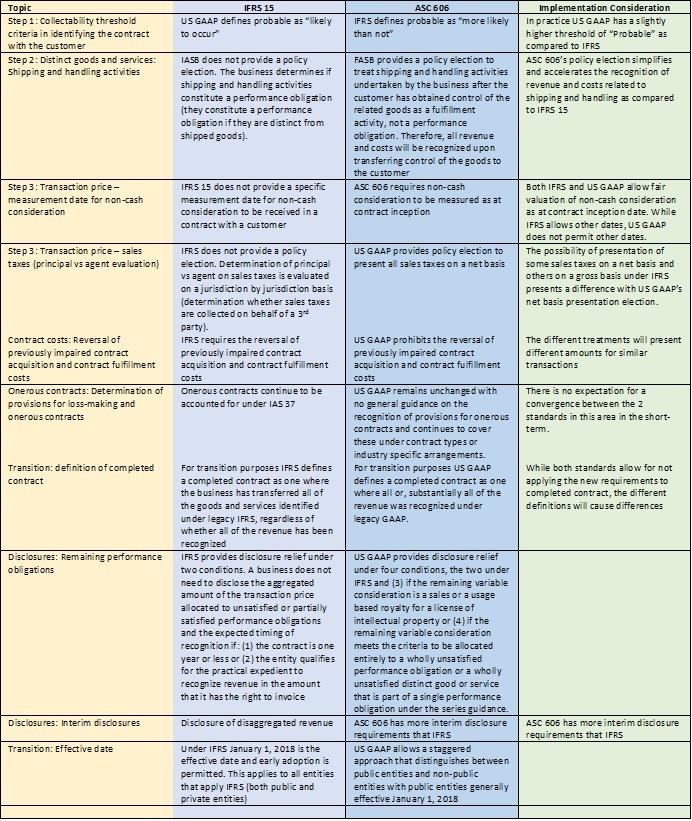
What is the difference between IFRS 15 and ASC 606?
Completed Contracts at Transition A completed contract under ASC 606 is defined as a contract in which all, or substantially all, the revenue has been recognized. Under IFRS 15, a completed contract is one in which the entity has transferred all goods or services.
When was ASC 606 effective for private companies?
The amendments in this Update are effective for a private company for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2020, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2021.
What is ASC 606?
ASC 606 instructs the entity to recognize revenue for the transfer of goods or services in an amount that reflects the consideration which the entity expects it is entitled to receive from customers in exchange for those goods or services. Customers are defined as a party that has contracted with an entity to obtain goods or services in the ordinary course of business in exchange for consideration. The following steps should be applied:
When is ASC 606 effective?
The new revenue recognition framework is effective for non-public entities, including not for profit entities (NFPs), for periods beginning after December 15, 2018, and interim periods within annual periods beginning after December 15, 2019.
How to determine revenue in ASC 606?
ASC 606 instructs the entity to recognize revenue for the transfer of goods or services in an amount that reflects the consideration which the entity expects it is entitled to receive from customers in exchange for those goods or services. Customers are defined as a party that has contracted with an entity to obtain goods or services in the ordinary course of business in exchange for consideration. The following steps should be applied: 1 Identify the contract (s) with a customer. 2 Identify the performance obligations in the contract. 3 Determine the transaction price. 4 Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract. 5 Recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation.
How to contact Selden Fox?
For additional information please call us at 630.954.1400, or click here to contact us. We look forward to serving you soon.
What is the performance obligation of the annual conference?
The first performance obligation, admission to the annual conference and corresponding meal, is satisfied once the annual conference has occurred. The second performance obligation, delivery of the quarterly magazine, is satisfied over time and based on when the member receives the magazine.
What is contract asset?
A contract asset is an entity’s right to consideration in exchange for goods or services that the entity has transferred to a customer. These assets arise when goods or services have been transferred to a customer but customer payment is contingent on a future event.
When to recognize revenue?
Recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation.
What is ASC 606?
ASC 606 applies to all public and private companies that follow generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). Suppose you have no legal obligation to follow GAAP. In that case, you might not have to follow these principles. But it remains good practice to create a consistent accounting system!
How to assign a cost to each sub-obligation?
Divide the total price to assign a cost to each sub-obligation. Each performance obligation should now have its own expense that adds up to the total transaction price.
Does ASC 606 change revenue?
Over the years, the small resulting tax differences should level out. ASC 606 presents primarily a change in your accounting, not your actual revenue .
How is revenue recognized under the new standard?
Revenue is recognized under the new standard as performance obligations are satisfied, specifically as goods and services are transferred to the member. For dues revenue, this transfer occurs evenly throughout the one-year membership period.
When will revenue recognition become effective?
FASB’s new revenue recognition standard will become effective for most not-for-profit (NFP) entities in 2019. Although this date may seem distant, the new standard will require a considerable transition effort in advance. The author focuses on the key accounting and auditing concerns that NFPs must address under the new standard, including a hypothetical example that illustrates some of the unique complexities the standard presents for the NFP environment and a discussion of significant challenges the new requirements are likely to pose for NFP auditors.
Why are there opportunities for auditors?
These opportunities are not without risk, however, because they may put auditors in danger of impairing their independence . Like their small business counterparts, smaller NFPs in particular may have greater need for help in implementing the new standard and so may look to their auditors for assistance. Professional standards permit auditors to advise their attest clients provided they are careful not to assume the role of management. As previously mentioned, discussions with clients about the many aspects of implementation will occur frequently, and auditors will need to avoid making any comments that could cross this line.
Why do auditors need to understand NFPs?
As a potential starting point, auditors will want to take a fresh look at how and where NFPs obtain their resources. Facing the financial pressure of a changing and often turbulent economy , NFPs continue to seek new sources of funding and alternative forms of revenue as a way to supplement the support they receive from donors. Therefore, GAAS’s requirement to understand the entity’s industry and its operating environment will take on much greater importance.
Why should auditors look beyond revenue?
Auditors should look beyond revenue, however, because the new standard affects the completeness of other financial statement elements as well, particularly assets and liabilities in the statement of financial position. For example, certain contract costs expensed under current GAAP will be capitalized.
When is revenue recognized?
Specifically, revenue is to be recognized when a performance obligation is satisfied through the transfer of a promised good or service , and such transfer is deemed to have occurred when the customer obtains control of same (ASC 606-10-25-23). In the example here, at the point of payment the member receives the right of admission and controls the determination of when to exercise it. Thus, the museum might conclude that immediate recognition of the $9 in admissions revenue is appropriate.
When to recognize revenue?
Recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation.
How Should Nonprofits Begin Implementation?
The first steps in implementing these standards are to review current practices, which includes reviewing current policies and accounting procedures.
What is ASU 2018-08?
ASU 2018-08 provides a variety of indicators of barriers and right of returns to be aware of. A stipulation that is unrelated to the purpose of the agreement (trivial or administrative conditions) is not indicative of a barrier. Examples of trivial or administrative conditions would be items such as a requirement to provide an annual report, submit a budget or budget to actual reporting.
Do non profit organizations have to re-examine their contracts with customers?
Nonprofits will need to re-examine their contracts with customers to be sure they recognize the related revenues in accordance with this new standard. All program-related products or services for which a fee is charged, and all other sales of any goods or services, whether program-related or not, are subject to the new standard.
Do nonprofits have to have both contribution and exchange?
For those nonprofits that are engaging in both contribution and exchange transactions, both standards will have an impact on how nonprofits recognize revenue.
Is a federal grant a conditional contribution?
Many federal awards currently are treated as exchange transactions, and under the new standard, most federal award contracts will be treated as conditional contributions. The result of how the revenue is recognized may not change. Donors and donees will need to consider whether stipulations in grant agreements, such as objectives and milestones, are measurable performance barriers or simply guidelines and mutually agreed-upon goals. For a right of return to exist, it must be evident from the gift agreement or another document referred to in the gift agreement; its existence cannot simply be implied.
When are Topic 606 and Topic 958 effective?
The effective date of Topic 606 is for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2019 (see related article related to recent extension ). This means the standard would be applicable to calendar year nonprofits for their December 31, 2020 year-end and fiscal year nonprofits for their fiscal year 2021 year-end. Early adoption is permitted.
How can a nonprofit earn revenue and have customers?
Many nonprofit entities have contracts with government agencies that request the performance of specific services and are paid by the government for those services. Often time these transactions occur when government agencies elect to outsource certain services. These arrangements may be in the form of fee-for-service contracts. Nonprofit entities will now be required to review the terms of all their contracts to determine whether they need to apply the new revenue recognition standard.
Is a government agency's advance payment a contribution?
Recording a contribution from government agencies may appear unusual. However, Topic 958 clarifies what meets the definition of a nonexchange transaction (i.e., a contribution). In which case, the advance payment from the government agency may be recorded immediately as a contribution in the year the funds are received, if there are no conditions or barriers. It is partly due to the need to clarify these conditions and barriers that ASU 2018-08 was issued.
When to recognize revenue?
Recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation.
Is a fee for service contract automatically covered by Topic 606?
However, it is important to note that you cannot assume a fee-for-service contract will automatically fall under Topic 606. You must perform an analysis by reviewing the contract terms to make this determination.
Is this all that a nonprofit must do to determine how to record revenue?
The answer is, not exactly. Due to the unique aspects of the nonprofit industry, there was a need for additional revenue recognition clarification as a result of Topic 606. FASB’s answer came in the ASU 2018-08, Not-for-Profit Entities (Topic 958) that provides clarifying scope and accounting guidance for contributions received and contributions made.
