
How does high blood pressure cause atherosclerosis?
Over time, this extra pressure can damage the arteries, making them more vulnerable to the narrowing and plaque buildup associated with atherosclerosis. The narrowed artery limits or blocks the flow of blood to the heart muscle, depriving the heart of oxygen.
What is atherosclerosis and why is it important?
What is atherosclerosis? Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis. The American Heart Association explains how atherosclerosis starts, how atherosclerosis is affected by high cholesterol levels, high blood pressure and smoking, blood clots and thickened artery walls.
What is the difference between atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis. The American Heart Association explains how atherosclerosis starts, how atherosclerosis is affected by high cholesterol levels, high blood pressure and smoking, blood clots and thickened artery walls. What is atherosclerosis? Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis.
How does atherosclerosis cause heart attacks and strokes?
Such blood clots are the cause of heart attacks and strokes. Atherosclerosis in coronary arteries leads to chest pain with physical activity or stress (angina). Blockages in the arteries that feed blood to the brain can cause a stroke.
How does atherosclerosis affect blood pressure?
How Does Atherosclerosis Relate to High Blood Pressure? Atherosclerosis is plaque buildup in the arteries. When it happens in the arteries that supply blood to the heart, doctors call it coronary artery disease, or CAD. High blood pressure can lead to CAD because it adds force to the artery walls.
Does atherosclerosis cause low BP?
Atherosclerosis — a condition in which fat (plaque) builds up in and on artery walls — can stiffen blood vessels and have the same effect on blood pressure. Thus, many older patients can have both a high systolic and a low diastolic blood pressure.
Do clogged arteries cause high or low blood pressure?
Blood pressure rises when the arteries are blocked and the blood can no longer flow freely. This is particularly pronounced during strenuous situations, as the heart must work even harder to supply the body with enough oxygen and nutrients.
Can coronary artery disease cause low blood pressure?
In patients with coronary disease (CAD), low diastolic blood pressure (DBP) is associated with increased risk of myocardial infarction, but its association with angina is unknown.
What causes sudden low blood pressure?
Orthostatic hypotension (postural hypotension). This is a sudden drop in blood pressure when standing from a sitting position or after lying down. Causes include dehydration, long-term bed rest, pregnancy, certain medical conditions and some medications. This type of low blood pressure is common in older adults.
What could cause low blood pressure?
What Causes a Sudden Drop in Blood Pressure?Loss of blood from bleeding.Low body temperature.High body temperature.Heart muscle disease causing heart failure.Sepsis, a severe blood infection.Severe dehydration from vomiting, diarrhea, or fever.A reaction to medication or alcohol.More items...•
What are the warning signs of clogged arteries?
Coronary artery disease signs and symptoms can include:Chest pain (angina). You may feel pressure or tightness in your chest. ... Shortness of breath. You may feel like you can't catch your breath.Fatigue. If the heart can't pump enough blood to meet your body's needs, you may feel unusually tired.Heart attack.
Can you have atherosclerosis with normal blood pressure?
And as shown in the study, even levels of blood pressure that are generally considered “normal” may indeed be high enough to foster the development of atherosclerotic heart disease by more than fourfold above the risk faced by people with systolic blood pressures that are physiologically ideal.
What is the lowest acceptable blood pressure?
Normal blood pressure in adults is less than 120/80 mmHg. Low blood pressure is a reading below 90/60 mmHg. Most forms of hypotension happen because your body can't bring blood pressure back to normal or can't do it fast enough. For some people, low blood pressure is normal.
Is 110/60 too low blood pressure?
A blood pressure reading of 110/60 mmHg is usually not considered a low blood pressure. Many people may have this reading without developing any signs and symptoms. The upper number (numerator) in the reading indicates the systolic pressure, whereas the lower number (denominator) represents the diastolic pressure.
What is the symptoms of atherosclerosis?
As arteriosclerosis progresses, clogged arteries can trigger a heart attack or stroke, with the following symptoms: Chest pain or pressure (angina) Sudden arm or leg weakness or numbness. Slurred speech or difficulty speaking.
Can you have atherosclerosis with normal blood pressure?
And as shown in the study, even levels of blood pressure that are generally considered “normal” may indeed be high enough to foster the development of atherosclerotic heart disease by more than fourfold above the risk faced by people with systolic blood pressures that are physiologically ideal.
Why do elderly people have wider blood pressure swings than normotensives?
Elderly hypertensives have wider blood pressure swings than young normotensives. This is often attributed to hardening of the arteries. Although this explanation is correct, it is incomplete and of little practical use. A more complete explanation is that hardening of the arteries impairs stretch of the baroreceptors leading to diminished neural input to brain stem autonomic control centers and thereby to diminished autonomic output to the cardiovascular system (Figure). The consequence is a failure to return high or low blood pressure back to baseline. This more complete understanding of why atherosclerotic arteries are associated with postural hypotension and episodic hypertension has practical use. Patients with wide blood pressure swings should not be treated with drugs that further impair autonomic responses. Their blood pressure extremes are sometimes best treated with behavioral modifications that remove the stimulus to the blood pressure change. When patients experience excess blood pressure variability, a review of their heart rates and blood pressures can determine whether impaired baroreflexes are a likely cause. The presence of impaired baroreflexes should alert to the likelihood of postural hypotension, episodic hypertension, and vascular rigidity from diffuse atherosclerosis.
What is the site of atherosclerosis?
The carotid artery at the bifurcation ( A ). The common carotid (1) leads to the carotid sinus that extends from line (2) to line (3) leading to the internal carotid artery (4). The carotid sinus is the site of atherosclerosis shown in cross-section ( B) and lengthwise ( C ). The external elastic lamina is stained red; the internal lamina stained yellow. Atheromatous plaque internal to the laminae limits stretch of the baroreceptors in the wall of the carotid sinus. When atherosclerosis of the carotids impairs baroreflexes, postural hypotension and episodic blood pressure spikes follow. Histology insert reprinted from Suemoto et al 11 with permission. Copyright © 2009, The Authors.
How does postural hypotension affect blood pressure?
The baroreflex is the initial mechanism called into play to stabilize blood pressure. Blood pressure changes are sensed by the baroreceptors in the carotids and aortic arch and signaled to the brain stem, which initiates an increase in heart rate in a single heartbeat. Sympathetic nerves then lead to vasoconstriction so that blood pressure returns toward baseline levels in ≈20 seconds after standing. When this system fails, postural hypotension ensues. Postural hypotension is not just a risk for falls, it is also associated with an increased incidence of stroke and myocardial infarction. 2
How does Baroreflex affect blood pressure?
Baroreflex control of blood pressure slowly deteriorates with advancing age, diminishing both sympathetic 3 and parasympathetic 4 nervous responses to hypertension and hypotension. Loss of baroreflex function is accelerated in hypertension and atherosclerosis. Consequently, the incidence of postural hypotension and episodic hypertension also increases with age and vascular disease. The baroreflex is impaired in subjects with carotid plaque and coronary atherosclerosis. 5 Diminished heart rate variability is a sign of baroreflex loss and is associated with excess cardiovascular mortality and total mortality 6 and predicts coronary artery disease. After a myocardial infarction, depressed baroreflex sensitivity predicted a 280% increase in cardiac mortality. 7 Johansson et al 1 report that proteins associated with atherosclerosis are also associated with impaired blood pressure control. Why should this be so?
What is the mechanism that stabilizes blood pressure?
The baroreflex is the initial mechanism called into play to stabilize blood pressure. Blood pressure changes are sensed by the baroreceptors in the carotids and aortic arch and signaled to the brain stem, which initiates an increase in heart rate in a single heartbeat.
What are the symptoms of baroreceptor deficits?
Symptoms of hypotension, excess blood pressure variability, diminished heart rate variability and vascular rigidity are common with baroreceptor deficits. Two of the most vexing problems in the treatment of high blood pressure are symptomatic postural hypotension and episodes of excessively high blood pressure.
Which arteries are the strongest physiological correlate of a decreased baroreflex?
Rigid carotid arteries are the strongest physiological correlate of a decreased baroreflex. When baroreceptor input is diminished, the autonomic nervous system buffers blood pressure, poorly leading to both hypertension and hypotension. Figure. Atherosclerosis and the baroreflex.
What are the complications of atherosclerosis?
Plaque buildup inside the arteries reduces the blood flow. A heart attack may occur if the blood supply is reduced to the heart. A damaged heart muscle may not pump as well and can lead to heart failure. A stroke may occur if the blood supply is cut off to the brain. Severe pain and tissue death may occur if the blood supply is reduced to the arms and legs.
What is atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis thickening or hardening of the arteries. It is caused by a buildup of plaque in the inner lining of an artery.
How is atherosclerosis treated?
Treatment for atherosclerosis may include lifestyle changes, medicine, and surgery.
What are some medications that can be used to treat atherosclerosis?
Medicines that may be used to treat atherosclerosis include: Antiplatelet medicines. These are medicines used to decrease the ability of platelets in the blood to stick together and cause clots. Aspirin, clopidogrel, ticlopidine, and dipyridamole are examples of antiplatelet medicines. Anticoagulants.
How to prevent atherosclerosis?
You can prevent or delay atherosclerosis by reducing risk factors. This includes adopting a healthy lifestyle. A healthy diet, losing weight, being physically active, and not smoking can help reduce your risk of atherosclerosis. A healthy diet includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, skinless chicken, seafood, and fat-free or low-fat dairy products. A healthy diet also limits sodium, refined sugars and grains, and solid fats.
Why is blood pressure measured in the ankles and arms?
Blood pressure comparison. Comparing blood pressure measurements in the ankles and in the arms helps determine any constriction in blood flow. Significant differences may mean blood vessels are narrowed due to atherosclerosis.
Why does plaque build up on the inside of the artery?
However, a gradual buildup of plaque or thickening due to inflammation occurs on the inside of the walls of the artery. This reduces blood flow and oxygen supply to the vital body organs and extremities.
How to prevent atherosclerosis?
You can do this with lifestyle changes such as exercising every day; eating a heart-healthy diet; not smoking; and controlling high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and high blood sugar. Taking a low-dose aspirin every day is also important.
What is the difference between a healthy artery and an atherosclerotic artery?
A healthy artery is like a clean pipe: It has a smooth lining and is free of blockages that interfere with blood flow. Atherosclerosis is the buildup of cholesterol-filled deposits called plaque on the inner walls of arteries. Plaque narrows the vessels and slows down blood flow.
What are the first signs of damage to the artery wall?
The first signs of damage are fatty streaks called plaque in the artery wall. These fatty streaks begin early in life and even occur in young adults.
What happens to the white blood cells in the artery wall?
Cells from the wall of the artery gradually surround the mixture. The artery wall becomes inflamed; white blood cells become activated, race to the injured area, and try unsuccessfully to heal the damage. Over time, a fibrous cap forms over the fatty deposit.
Where does atherosclerosis occur?
Atherosclerosis can occur in any artery in the body, from those nourishing the heart (coronary arteries) to those supplying the brain, intestines, kidneys, and legs. Atherosclerosis begins as microscopic damage to the inner lining of an artery wall.
Can fibrous cap cause heart attacks?
Even under the cap, the deposit can grow, progressively blocking blood flow and ultimately causing chest pain (angina). If the fibrous cap ruptures, a blood clot can form. Such blood clots are the cause of heart attacks and strokes.
Does statin help with heart disease?
Taking a cholesterol-lowering statin can keep atherosclerosis from getting worse, and can also pull cholesterol out of artery-clogging plaque. Statins can also help stabilize atherosclerotic plaques and keep them from breaking open—the event that triggers most heart attacks and strokes.
What is atherosclerosis?
What is atherosclerosis? Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis. The American Heart Association explains how atherosclerosis starts, how atherosclerosis is affected by high cholesterol levels, high blood pressure and smoking, blood clots and thickened artery walls.
What are the causes of atherosclerosis in the aorta?
Elevated levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. High blood pressure. Cigarette smoking. Diabetes. Smoking plays a big role in the progression of atherosclerosis in the aorta (the body’s main artery), coronary arteries and arteries in the legs.
Why does plaque get worse as you age?
Atherosclerosis is a slow, lifelong progression of changes in the blood vessels that may start in childhood and get worse faster as you age. The cause of atherosclerosis isn’t completely known. Many scientists believe plaque begins when an artery’s inner lining (called the endothelium) becomes damaged.
What happens if a plaque is blocked?
In either case, the artery can be blocked, cutting off blood flow. If the blocked artery supplies the heart or brain, a heart attack or stroke occurs.
What is the pain of a chest that is reduced blood flow to the heart muscle?
Angina(ch est pain from reduced blood flow to the heart muscle)
Can a blocked artery cut off blood flow?
In either case, the artery can be blocked, cutting off blood flow.
What Is Atherosclerosis, and How Is It Related to High Blood Pressure?
One of the most serious health problems related to untreated high blood pressure is atherosclerosis, or plaque buildup in the arteries. When those blockages occur in the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle, the end result is called coronary artery disease.
How to treat atherosclerosis?
In general, the treatment for atherosclerosis includes making changes to diet, increasing exercise, and often using medications to reduce blood cholesterol levels. Other treatments may include angioplasty and stenting for severe blockages. In some cases, open heart (bypass) surgery may even be required.
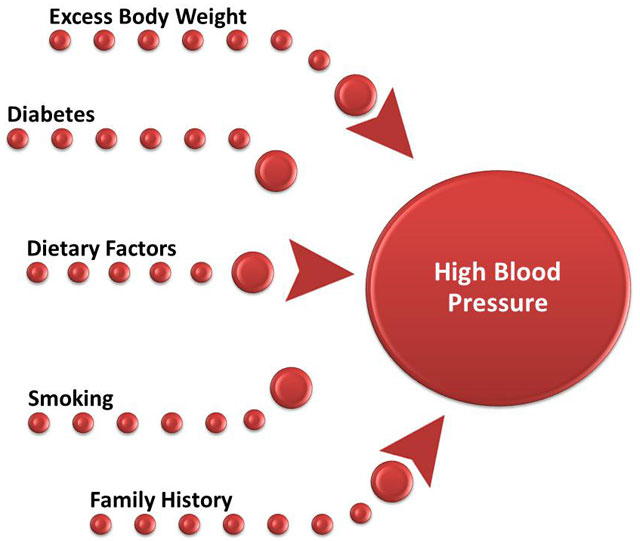
What Else Puts You at Risk for Atherosclerosis?
High blood pressure alone raises the risk of atherosclerosis, but it's especially dangerous if you also have conditions or make lifestyle choices like:
How Is Atherosclerosis Diagnosed?
Atherosclerosis isn't usually diagnosed until a person complains of chest pain. At this point, the doctor may conduct tests to evaluate your risk for heart disease. These tests include:
What is the most serious health problem that can be caused by high blood pressure?
One of the most serious health problems related to untreated high blood pressure is atherosclerosis, or plaque build-up in the arteries. When those blockages occur in the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle, the end result is called coronary artery disease. People with high blood pressure are more likely to develop coronary artery ...
How does a narrowed artery affect the heart?
The narrowed artery limits or blocks the flow of blood to the heart muscle, depriving the heart of oxygen.
What is the procedure called when a cardiologist opens a clogged artery?
During a cardiac catheterization, a cardiologist may also be able to open up any clogged arteries detected with a procedure called an angioplasty. This may also involve expanding a small tube, called a stent, inside the blood vessel to better prop the artery open.
Why is my diastolic blood pressure low?
The condition may be associated with severe hypotension, or it could be caused by profoundly stiff arteries that occur due to aging, diabetes or fatty buildup in the arteries (atherosclerosis).
What causes a sudden drop in blood pressure?
Other conditions, including dehydration, blood loss, significant infection and a severe allergic reaction may cause severe hypotension. But these disorders usually cause a sudden, dramatic and temporary drop in blood pressure, rather than a sustained low blood pressure reading over time.
Why are my arteries so stiff?
Arteries may also become stiff due to the effects of diabetes. Many people with diabetes have high blood pressure as a result. In some cases, the systolic blood pressure may be high while the diastolic reading is low. Atherosclerosis — a condition in which fat (plaque) builds up in and on artery walls — can stiffen blood vessels and have the same effect on blood pressure.
What is the blood pressure reading?
A blood pressure reading, given in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg), has two numbers. The first, or upper, number measures the pressure in arteries when the heart beats (systolic pressure). The second, or lower, number measures the pressure in arteries between beats (diastolic pressure).
Is 90 mm Hg a good blood pressure?
A systolic blood pressure reading of 90 mm Hg or less or a diastolic reading of 60 mm Hg or less is generally considered low blood pressure (hypotension). Normal blood pressure varies from person to person, though. If your diastolic blood pressure is consistently below 60, and you aren't experiencing problems as a result, treatment might not be required. If low blood pressure is causing noticeable symptoms — such as dizziness, light-headedness or fainting — more investigation may be required to uncover the possible cause and provide appropriate treatment.
What is the name of the condition where blood pressure is low?
Hypotension . Hypotension , also called low blood pressure, is blood pressure low enough that the flow of blood to the organs of the body is deficient. Symptoms may include: unsteadiness; dizziness; blurred vision; confusion; fainting heartbeats that suddenly become more noticeable; nausea.
How many people have high blood pressure?
An estimated 75 million American adults have high blood pressure. Around 54 percent of these people have their hypertension under control. About 1 in 3 adults in the United States has prehypertension – blood pressure numbers which are higher than normal – but not yet in the high blood pressure range.
What is the term for the hardening of the arteries?
Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis, also known as hardening of the arteries, can also slowly narrow the arteries throughout the body. Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood to your heart and other parts of your body. Atherosclerosis generally does not cause symptoms until it severely narrows an artery.
What are the symptoms of hypotension?
Extreme hypotension can result in this life-threatening condition. Symptoms include: 1 weak and rapid pulse; 2 rapid, shallow breathing; 3 cold, clammy, pale skin; 4 confusion, particularly in seniors.
What is the optimum blood pressure?
Optimal blood pressure is less than 120/80 (systolic/diastolic).
Does atherosclerosis cause symptoms?
Atherosclerosis generally does not cause symptoms until it severely narrows an artery.
Does smoking cause heart disease?
Smoking increases both the chance of developing hardening of the arteries and the chance of dying from cardiovascular disease.
