Bacillus subtilis
Bacillus subtilis
Bacillus subtilis, known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants and humans. A member of the genus Bacillus, B. subtilis is rod-shaped, and can form a tough, protective endospore, allowing it t…
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis usually means the cleavage of chemical bonds by the addition of water. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g. sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is termed saccharification. Generally, hydrolysis or …
Is Bacillus subtilis positive for starch hydrolysis?
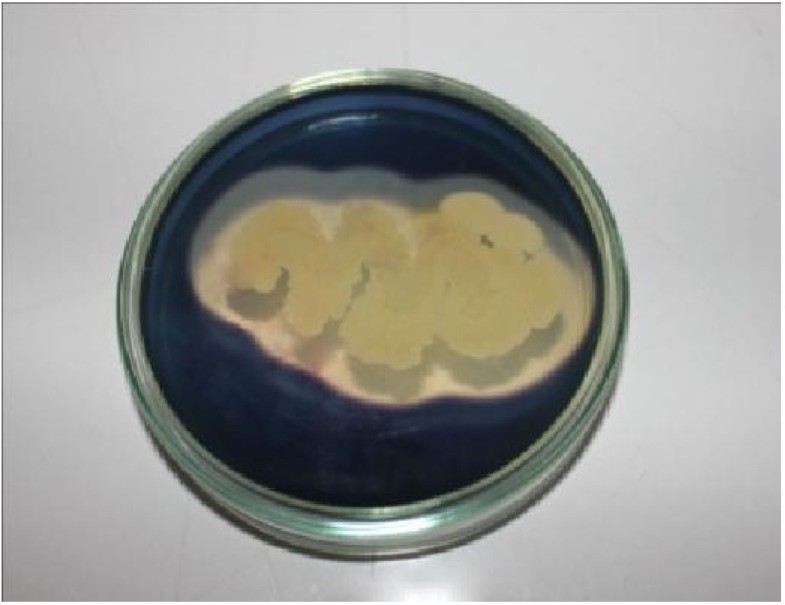
Bacillus subtilis is positive for starch hydrolysis (pictured below on the left). The organism shown on the right is negative for starch hydrolysis. Positive for starch hydrolysis
How does hydrolysis of starch affect bacterial growth?
Thus, hydrolysis of the starch will create a clear zone around the bacterial growth. Bacillus subtilis is positive for starch hydrolysis (pictured below on the left). The organism shown on the right is negative for starch hydrolysis. Positive for starch hydrolysis
What does a positive test for starch hydrolysis look like?
Bacillus subtilis is positive for starch hydrolysis (pictured below on the left). What does a positive test for amylase look like? Positive test (“+”): The medium will turn dark.
Does Bacillus subtilis produce α-amylase?
A moderately thermophilic Bacillus subtilis strain, isolated from fresh sheep’s milk, produced extracellular thermostable α-amylase. Maximum amylase production was obtained at 40 °C in a medium containing low starch concentrations.

Is Bacillus subtilis starch positive or negative?
Bacillus subtilis is a Gram positive, endospore forming bacteria that is a common soil inhabitant (Micrograph 1).
Which organisms can hydrolyze starch?
The major component of starch can be hydrolyzed by a-amylase, which is present in some bacteria while well known in case of fungi. The ability to degrade starch is used as a criterion for the determination of amylase production by a microbe.
Does Bacillus cereus hydrolyze starch?
Emetic toxin-producing B. cereus has been reported to neither produce diarrheal toxin nor hydrolyze starch (Ehling-Schulz et al., 2005; Pirhonen et al., 2005).
Does E coli hydrolyze starch?
To hydrolyze starch in the milieu and use its hydrolysis products for growth and/or metabolite synthesis, α-amylase must be expressed and secreted by E. coli.
Which bacteria is positive for starch hydrolysis test?
Bacillus subtilis is positive for starch hydrolysis (pictured below on the left).
Why do some bacterial species hydrolyze starch?
Starch molecules are too large to enter the bacterial cell, so some bacteria secrete exoenzymes to degrade starch into subunits that can then be utilized by the organism. Starch agar is a simple nutritive medium with starch added.
Can B subtilis ferment glucose?
subtilis cannot ferment either glucose or pyruvate efficiently (unlike E. coli) and why pyruvate enhances glucose fermentation are unknown. NMR analysis showed that fermentation products in B. subtilis include acetate, acetoin, ethanol, lactate, succinate and 2,3-butanediol, indicating a mixed acid fermentation [10].
How can you tell the difference between Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus cereus?
The key difference between Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus cereus is that Bacillus subtilis is fermenting mannitol, but it lacks the ability to produce enzyme lecithinase while Bacillus cereus is not fermenting mannitol, but it produces enzyme lecithinase. Bacillus is a genus of gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria.
Does Bacillus subtilis ferment mannitol?
Bacillus subtilis is not able to ferment mannitol and yet the Mannitol test yielded a positive result. The conclusion drawn from this is human error during the inoculating process. It is believed that there must have been a mannitol fermenting bacterium somewhere along the length of the inoculating loop.
Does Staphylococcus aureus hydrolyze starch?
From this study, it was observed that 100% S. aureus isolates showed positive results in gelatin, urea and galactose hydrolysis test, 50% isolates were positive in starch hydrolysis test, 35% in protein hydrolysis test, 100% isolates in lactose fermenting test, but no isolate was positive in sucrose fermenting test.
Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa positive or negative for starch hydrolysis?
Biochemical Test of Pseudomonas aeruginosaBasic CharacteristicsProperties (Pseudomonas aeruginosa)RibosePositive (+ve)SorbitolNegative (-ve)StarchNegative (-ve)SucroseNegative (-ve)55 more rows•May 23, 2022
Which of the following enzyme is used in the hydrolysis of starch?
Pancreatic α-amylase is secreted into the small intestine from the pancreatic duct and completes the hydrolysis of the starch.
Does Staphylococcus aureus hydrolyze starch?
From this study, it was observed that 100% S. aureus isolates showed positive results in gelatin, urea and galactose hydrolysis test, 50% isolates were positive in starch hydrolysis test, 35% in protein hydrolysis test, 100% isolates in lactose fermenting test, but no isolate was positive in sucrose fermenting test.
What class of enzymes are those that hydrolyze starch?
AmylasesAmylases are generally referred to as a class of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of starch into glucose and maltose.
Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa positive or negative for starch hydrolysis?
Biochemical Test of Pseudomonas aeruginosaBasic CharacteristicsProperties (Pseudomonas aeruginosa)RibosePositive (+ve)SorbitolNegative (-ve)StarchNegative (-ve)SucroseNegative (-ve)55 more rows•May 23, 2022
Does amylase break down starch?
Amylases digest starch into smaller molecules, ultimately yielding maltose, which in turn is cleaved into two glucose molecules by maltase. Starch comprises a significant portion of the typical human diet for most nationalities.
Abstract
Bacillus subtilis T41a, an amylase-producing bacterium, was isolated from wheat phylosphere. The optimum catalytic activity and affinity toward different starch types hydrolysis were studied. Response surface methodology was applied to investigate the optimum catalytic conditions.
1. Introduction
The α-amylase constitutes one of the three largest groups of industrial enzymes. This class accounts for about 30% of the world's enzyme production ( Alkando & Ibrahim, 2011 ). All amylases act as a glycoside hydrolysers and hydrolyze α-1,4 glycosidic bonds ( Tiwari, Shukla, Mishra, & Gaur, 2014 ).
2. Material and methods
Bacillus sp. T41a was isolated from wheat phylosphere and preserved in the ABRII culture collection. Organism refreshment was done by culturing on Nutrient Broth at 28 °C for 24 h.
3. Results and discussions
The 16S rDNA sequencing result, with the accession No. JX274661, titled Bacillus subtilis T41a was deposited in the NCBI database. Phylogenetic analysis and the alignment of available sequences in the NCBI GenBank with partial 16S rDNA showed the close relation of the isolated strain with other B.
4. Conclusion
A thermo-stable amylase-producing strain was identified as B. subtilis T41a. The RSM optimization of the amylase performance resulted in a considerable increase in catalytic activity. The enzyme complex displayed broad pH (5.0–10.0) stability. Moreover, the temperature stability test showed that the amylase activity was stable at 40 °C for 48 h.