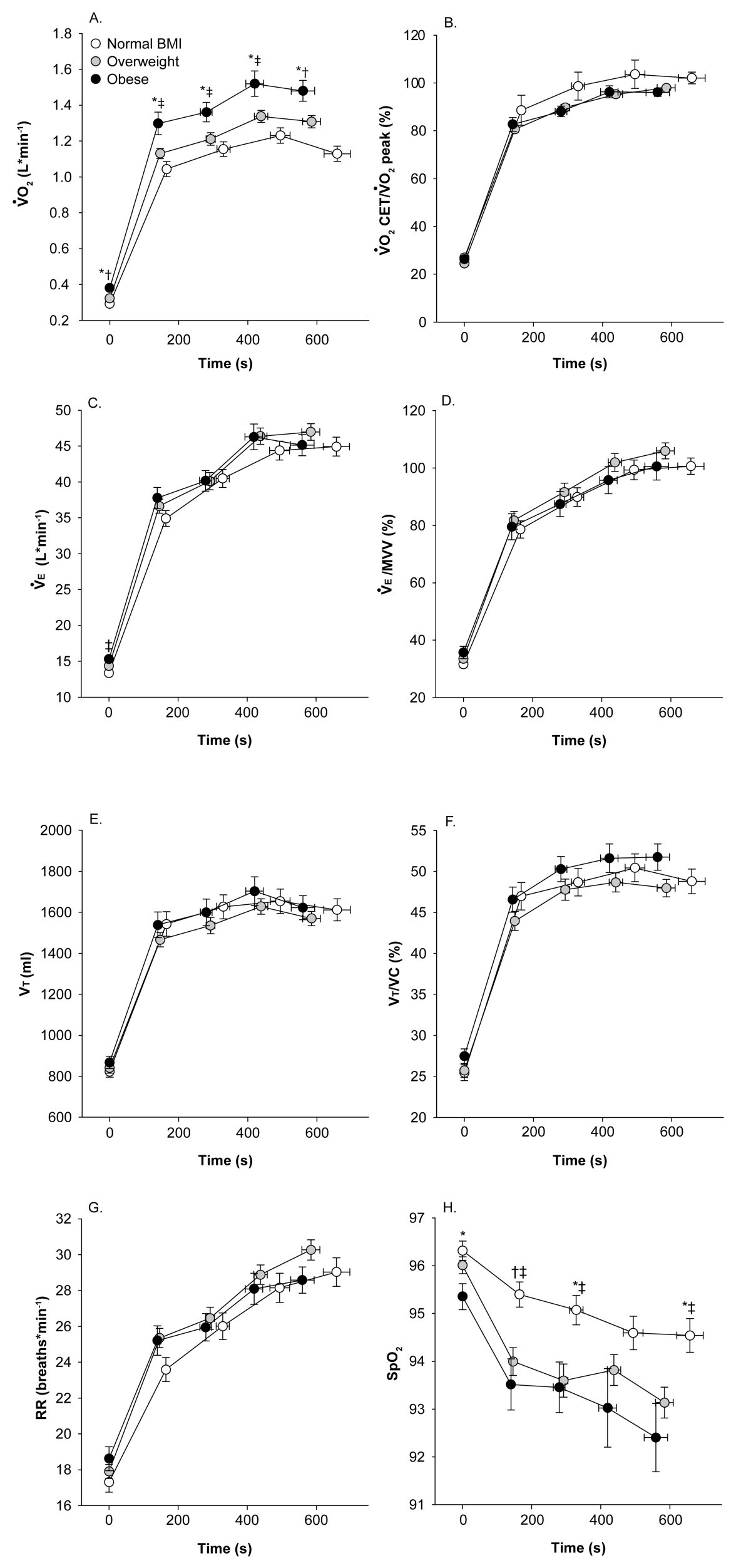
Why does expiratory reserve volume increase during exercise?
Exercise can raise your blood pressure when it is low. Conversely, exercise can lower your blood pressure when it is high. But that doesn’t mean exercise isn’t safe for people with low or high blood pressure. However, one should speak to their …
Why does the blood supply increase during exercise?
There is general agreement that the systolic blood pressure increase determined by isotonic exercise usually ranges from 50 to 70 mm Hg in both normotensive or hypertensive subjects. Diastolic blood pressure shows only minor changes in the normotensives, while in the hypertensives it tends to substantially increase because of their inability to adequately reduce …
What would experience a decreased blood flow during exercise?
Nov 05, 2018 · It’s normal for blood pressure to rise during exercise. However, extreme spikes or drops in blood pressure can be a sign of a medical condition, such …
Why does your rate of breathing increase during exercise?
Aug 13, 2021 · Normally during exercise, blood pressure increases to push the flow of oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. However, in some individuals, the response to exercise is exaggerated. Instead of reaching a systolic (upper number) blood pressure of around 200 mmHg at maximal exercise, they spike at 250 mmHg or higher.

Does exercise affect blood pressure?
There are no conclusive data on the effect of training on blood pressure response to exercise. The majority of the published studies report small exertional pressure reductions after conditioning, which would merely reflect the reduction in resting blood pressure.
Is aerobic exercise good for hypertension?
Aerobic exercise is currently being recommended in addition to pharmacological therapy for lowering blood pressure levels in hypertensive patients, i.e. in subjects whose resting blood pressure levels exceed 145/90 mm Hg. On the other hand competitive sports are generally contraindicated in hypertensives, who are thought to be at increased risk ...
Is isotonic exercise good for blood pressure?
The results of several studies indicate that the blood pressure response to isotonic exercise is a marker for detection of hypertension earlier in the course of the disease, while resting blood pressure is still normal.
How long after exercise can you get high blood pressure?
In general, though, high blood pressure after a resting period of up to two hours following exercise includes any reading greater than 140/90 mm Hg. Low blood pressure after exercise includes any reading lower than 90/60 mm Hg.
How to lower blood pressure with exercise?
If you’re at risk for or have hypertension, speak to your doctor about the safest way to exercise. This may involve: 1 using medication to lower your blood pressure 2 choosing moderate activities 3 working up to daily exercise
What is systolic blood pressure?
Systolic blood pressure is a measure of blood vessel pressure when your heart beats. Diastolic blood pressure is a measure of the pressure in the blood vessels between heartbeats. It shouldn’t change significantly during exercise. If it does, consult your doctor.
What is the diastolic pressure after exercise?
Your diastolic pressure (bottom number) changes significantly during exercise. Your blood pressure reading surpasses 180/120 mm Hg during or after exercise. In general, if you’re worried about your blood pressure, make an appointment with your doctor.
What does it mean when your blood pressure is high?
Unmonitored blood pressure in this range can be a sign of a heart attack or stroke.
How long does it take for blood pressure to go down after exercise?
In general, your blood pressure should return to normal within several hours of a workout. Even then, you might notice that your blood pressure doesn’t return to exactly what it was before exercise. That’s because it’s normal for blood pressure to drop slightly within a few hours of exercise.
How to treat low blood pressure?
Exercise for people with low blood pressure. Also check with your doctor before starting a new exercise program if you have low blood pressure (hypotension). Exercise — especially exercise that involves sudden changes in posture — can trigger symptoms, including dizziness, blurred vision, and nausea.
Does BP increase during exercise?
Normally during exercise, blood pressure increases to push the flow of oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. However, in some individuals, the response to exercise is exaggerated. Instead of reaching a systolic (upper number) blood pressure of around 200 mmHg at maximal exercise, they spike at 250 mmHg or higher.
Why does blood pressure increase during exercise Google Scholar?
Systolic blood pressure (BP) normally rises with exercise as cardiac output increases during exercise in responses to the increased demand of oxygen from working muscles via increased sympathetic tone. However, some individuals present with abnormally exaggerated rise in systolic BP during exercise.
Should your blood pressure go up during a stress test?
The study found that if you have a high blood pressure during a stress test, it could actually indicate you are more fit, and that the problem with current guidelines for interpreting these blood pressure levels is that workload or “exercise intensity” is not being taken into account, said Hedman who now works as a Oct 7, 2019
How long should you wait to take your blood pressure after walking?
Exercise – Great to do, just wait until after you check your blood pressure. Avoid exercise for thirty minutes prior to blood pressure readings. Medication – For an accurate reading, you should have as little medication in your blood as possible.
How long after exercise should I take my blood pressure?
How to Take & Record Blood Pressure. Wait for at least 30 minutes after drinking alcohol or caffeine, smoking or exercise before you take a reading. Rest for at least 5 minutes before you take a reading.
What is a normal blood pressure after exercise?
It’s normal for systolic blood pressure to rise to between 160 and 220 mm Hg during exercise. Unless you’ve cleared it with your doctor, stop exercising if your systolic blood pressure surpasses 200 mm Hg. Beyond 220 mm Hg, your risk of a heart problem increases.
Does walking decrease blood pressure?
Ten minutes of brisk or moderate walking three times a day Exercise lowers blood pressure by reducing blood vessel stiffness so blood can flow more easily. The effects of exercise are most noticeable during and immediately after a workout.
Effect Of Aerobic Exercise On Systolic Blood Pressure
In this experiment, 13 subjects were required to perform a modified version of jumping jacks at different intensity levels. The exercise was performed in cycles where increased cycles of jumping jacks will increase the intensity of the exercise.
How Does Exercise Affect Your Heart
Why does heart rate increase during exercise? Now you know that the heat rate increases because your heart needs to supply more oxygen to your muscles. But what else will exercise do to your heart?
Why Does Heart Rate Increase During Exercise
If youve ever wondered why your heart rate increases during exercise, then you should know that while you exercise, or carry out any vigorous physical activity, your muscles require a large amount of energy.
Building Activity Into Your Day
If the idea of doing exercise isnt for you, being more active in your day-to-day life can make a difference too.
Knowing Why Does Blood Pressure Increase With Exercise
So far we have understood how exercise affects blood pressure. But its time to find out why does blood pressure increase with exercise. Our muscles require a bit of extra oxygen when we do exercises. This requirement is more than what we need while lying on a bed. So, this process leads us to breathe much faster than we do in regular life.
Why You Should Take Your Own Blood Pressure At Home Or On The Go
Because of regular fluctuations in blood pressure, white-coat syndrome, and masked hypertension, doctors; may recommend self-monitoring for people with HBP. There are; many benefits to taking your own BP:
Ask The Doctor: Are My Blood Pressure And Heart Rate Changing Normally During Exercise
Q. Sometimes I take a walk while wearing my blood pressure cuff. For the first few minutes, as I walk at a modest pace, my systolic blood pressure rises from 115 to 130 or so, while my heart rate hardly changes from its usual 60-something beats per minute.
Why does blood flow increase during exercise?
During exercise, blood flow increases to provide more oxygen to the working muscles. This increased cardiac output is associated with a rise in heart rate and systolic blood pressure which both increase along with exercise intensity. In people with normal resting blood pressure, the systolic pressure could be expected to increase up ...
What is the blood pressure reading?
Blood pressure is a common vital sign which is typically measured when the body is at rest. A blood pressure reading consists 2 numbers. The top number, or systolic, is the pressure against the artery walls when the heart contracts, and the diastolic is the pressure in between heart beats. Although regular physical activity helps lower resting ...
Does exercise lower blood pressure?
In people with normal blood pressure, diastolic pressure runs below 80 mm Hg. During exercise, the diastolic blood pressure stays about the same or falls slightly. This is because exercise dilates or expands blood vessels, improves blood flow and decreases the resistance to blood flow within the arteries. Blood pressure changes during exercise vary person to person, and are related to the type, intensity and length of exercise, as well as a person's fitness level, health status and usual blood pressure ranges.
Can exercise cause shortness of breath?
If exercise causes pain, dizziness, weakness or severe shortness of breath, see your doctor right away.
Can exercise cause high blood pressure?
Exercise Hypertension. In some people, blood pressure rises too much during exercise, even if they don't have high blood pressure, or hypertension. This exercise hypertension occurs when systolic blood pressure runs higher than 210 mm Hg in men or above 190 mm Hg in women, or when diastolic blood pressure readings during exercise are higher ...
How does the release of hormones affect blood pressure?
The release of these hormones leads to increased blood pressure through increased volume of blood pumped by the heart in a single heartbeat, increased heart rate, blood vessel constriction, and reduced renal sodium excretion.
Why does the heart pump with increased force?
To meet this need, the heart must pump with increased force to deliver more oxygenated blood with each contraction. As the heart’s workload increases during exercise, systolic blood pressure increases.
What is the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure?
Systolic blood pressure is the top blood pressure reading and measures the force against artery walls when the heart pumps. It is normal for systolic blood pressure to range between 160 and 220 during exercise. The diastolic blood pressure, or the bottom number, typically does not change during exercise. Diastolic pressure measures the force ...
What is the normal blood pressure?
While your ideal average blood pressure is below 120/80 mm Hg, blood pressure fluctuates throughout the day depending on what you are doing. Every time your blood pressure spikes does not necessarily equal a medical emergency.
Can stress cause blood pressure to spike?
Once the stressful situation resolves, your blood pressure should return to normal. However, if temporary blood pressure spikes due to stress occur frequently enough, it can damage blood vessels, the heart, and kidneys.
Is it normal to have a cool down period after exercise?
It is normal for blood pressure during exercise to increase. It should return to normal post exercise. Consistent physical activity will strengthen your heart and promote lower blood pressure levels.
Does diastolic blood pressure change during exercise?
The diastolic blood pressure, or the bottom number, typically does not change during exercise. Diastolic pressure measures the force against artery walls in between contractions. If your diastolic blood pressure increases during exercise by more than 20 mm Hg or becomes greater than 100 mm Hg, stop exercising and consult your doctor.
Does BP increase or decrease during exercise?
Normally during exercise, blood pressure increases to push the flow of oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. However, in some individuals, the response to exercise is exaggerated. Instead of reaching a systolic (upper number) blood pressure of around 200 mmHg at maximal exercise, they spike at 250 mmHg or higher.
What happens to diastolic blood pressure during exercise?
During upright exercise, the normal blood pressure response is to observe a progressive increase in systolic blood pressure with no change or even a slight decrease in diastolic blood pressure. The slight decrease in diastolic blood pressure is due primarily to the vasodilation of the arteries from the exercise bout.
Does running reduce blood pressure?
Cardiovascular, or aerobic, exercise can help lower your blood pressure and make your heart stronger. Examples include walking, jogging, jumping rope, bicycling (stationary or outdoor), cross-country skiing, skating, rowing, high- or low-impact aerobics, swimming, and water aerobics.
Why does blood pressure increase after exercise?
It’s normal for your systolic blood pressure (the higher of your two readings, taken when your heart is pumping blood through your body) to increase when you take vigorous exercise. This is because your muscles need more oxygen, so your heart has to work harder to deliver it.
Does walking decrease blood pressure?
Ten minutes of brisk or moderate walking three times a day Exercise lowers blood pressure by reducing blood vessel stiffness so blood can flow more easily. The effects of exercise are most noticeable during and immediately after a workout. Lowered blood pressure can be most significant right after you work out.
What happens to your heart rate during exercise?
During exercise, your heart typically beats faster so that more blood gets out to your body. Your heart can also increase its stroke volume by pumping more forcefully or increasing the amount of blood that fills the left ventricle before it pumps.
Does systolic blood pressure increase during exercise?
Factors such as anxiety, caffeine consumption, and performing resistance and cardiovascular exercises, cause immediate, temporary increases in systolic pressure. During cardiovascular exercise, for example, systolic pressure can increase to values close to and over 200 with higher levels of effort.
Why is the blood vessel stiffer?
Because stiff blood vessels do not absorb any of the pressure behind the blood flow, the faster the blood travels, the more stiff the vessel is . They compared these readings with blood pressure measures taken at rest and while the participants walked to maximal effort on a treadmill.
Is exercise a risk factor for heart disease?
It also is associated with aging, menopause, high cholesterol, smoking and diabetes, and may be a common process for developing heart disease among all of these risk factors. "It's too early to recommend that people have exercise tests just to measure their blood pressures," Stewart says.
Does exercise raise blood pressure?
Normally during exercise, blood pressure increases to push the flow of oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. However, in some individuals, the response to exercise is exaggerated. Instead of reaching a systolic (upper number) blood pressure of around 200 mmHg at maximal exercise, they spike at 250 mmHg or higher.
Is exercise hypertension a risk factor?
So-called "exercise hypertension," an ab normally high spike in blood pressure experienced by generally healthy people during a workout, is a known risk factor for permanent and serious high blood pressure at rest. But who gets it, and why, has been largely unknown.
Does exercise cause blood vessel expansion?
In their analysis, researchers found that higher blood pressures in response to exercise were associated with poorer blood vessel expansion in the arm following the cuff test, suggesting that the endothelial cells failed to dilate enough to handle the extra blood flow.
What is exercise stress testing?
Exercise stress testing is routinely used to identify individuals who potentially have obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD) and information regarding aerobic functional capacity also is obtained. 1 As a result of the increase in cardiac output that occurs with exercise, systolic arterial blood pressure is expected to rise 20 mm Hg per metabolic equivalent of task. 2 Reductions in systolic blood pressure during exercise stress testing are associated with left ventricular systolic dysfunction and the presence of severe obstructive CAD. 3, 4
Does exercise stress increase risk of death?
In this analysis from the FIT Project, we have shown that an increased risk of adverse outcomes (eg, death and MI) exists in individuals who have lower systolic blood pressure responses during exercise stress testing, and the risk for these outcomes is highest among those with exercise‐induced hypotension. A differential association was observed between systolic blood pressure response and all‐cause death by age, with the association being stronger for younger compared with older patients.