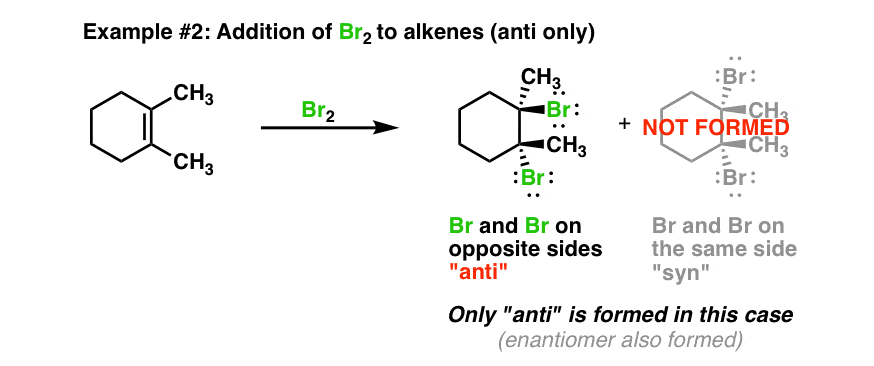
When Br2 reacts with an alkene, the molecule attaches across the double bond and the double bond becomes a single bond. So ethene would form 1,2-dibromoethane, propene becomes 1,2-dibromopropane, but-1-ene becomes 1,2-dibromobutane. However but-2-ene would make 2,3-dibromobutane.
Is alkene is more reactive than alkyne?
alkenes is more reactive than alkynes and alkynes are more reactive than alkanes .the reason is alkenes contain double bond and pi electrons so addition reactions can take place. Alkynes have 3 double bond so it does go under addition reaction but alkanes contain a strong single sigma bond only goes under substitution reaction in presence of light.
Is phenol reactive with Br2?
Phenol reacts with Br2 as follows ; + Br2 → Phenol is acidic in nature and the acidic nature of phenol is increased by the presence of - I (electron attracting) groups at o - and / or p - position of the - OH group .However benzoic acid is more acidic than nitro - phenol .
How does an alkene react with HBr?
HBr Addition Reaction: HBr adds to alkenes to create alkyl halides. A good way to think of the reaction is that the pi bond of the alkene acts as a weak nucleophile and reacts with the electrophilic proton of HBr. Alternatively, you can view the first step of the reaction as the protonation of the pi bond.
Does bromine react with alkanes?
Bromine will also react with aromatic compounds, such as phenol, but it can't react with alkanes as they contain only single bonds, and therefore there is no color change when these are mixed. Do saturated hydrocarbons react with bromine?
Do alkanes react with Br2?
The most commonly demonstrated halogenation reactions are brominations using bromine water, Br2, which is a red-brown colour. Alkanes and alkenes tend to be colourless. So, when bromine water is added to an alkane or alkene and mixed well, initially the mixture turns a red-brown colour due to the bromine.
Does Br2 react with alkynes?
Bromine reacts rapidly with alkenes and alkynes. This can be used as a visual test to distinguish between alkanes, which do not react rapidly with bromine, and alkenes and alkynes.
What functional groups does Br2 react with?
Bromine water, also called Bromide bromate solution or Bromine solution with the chemical formula Br2....The reaction between bromine water and different functional groups are as given below:Alkane. ... Alkene. ... Phenols. ... Aniline. ... Enol. ... Glucose. ... Ketones. ... Aldehydes.
Does alkene undergo bromination?
Bromination of Alkenes Gives anti Products It's a family of reactions which proceed through 1) attack of an alkene upon an acid, forming a free carbocation, and 2) attack of a nucleophile upon the carbocation.
Do alkanes or alkenes react with bromine?
Bromine water is an orange solution of bromine. It becomes colourless when it is shaken with an alkene. Alkenes can decolourise bromine water, but alkanes cannot.
What happens when Br2 reacts with?
Solution. When Br2 reacts with excess of F2, bromine trifluoride is formed.
Why alkane does not react with bromine?
Alkanes do not react with spontaneously bromine water due to their saturated nature. Bromine is non-polar and therefore dissolves more readily in a non-polar alkane than in polar water. Therefore, when alkanes come into contact with bromine water, they cause it to decolourise, while they adopt the colour.
What elements does bromine react with?
Potassium ignites in bromine vapor and explodes violently in contact with liquid bromine and rubidium ignites in bromine vapor. Aluminum, mercury, or titanium react violently with dry bromine. Warm germanium ignites in bromine vapor and antimony ignites in bromine vapor and reacts explosively with the liquid halogen.
How do alkenes react with bromine water?
Bromine water is an orange solution of bromine. It becomes colourless when it is shaken with an alkene. Alkenes can decolourise bromine water, but alkanes cannot.
Why is alkene and br2 called an addition reaction?
Explanation: Ethene and bromine are an addition reaction because ethene is an alkene - it has a double bond. It is easier for new atoms to open the double bond and react there than to remove the hydrogen already attached, and then bond to it, which would be a substitution reaction.
What is bromination of an alkene?
[Worth noting: bromination of alkenes is technically an oxidation reaction, because each carbon goes from being bound to another carbon (0) to bromine (–1). The oxidation state of each carbon in ethene is +2; the oxidation state of each carbon in dibromoethane is +1. ]
What type of reaction is bromination?
The bromination of benzene is an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. In this reaction, the electrophile (bromine) forms a sigma bond to the benzene ring, yielding an intermediate. Then, a proton is removed from the intermediate to form a substituted benzene ring.
What happens when Br2 is added to Ethyne?
During the reaction of ethyne with diatomic bromine, one of the 𝜋 bonds between the two carbon atoms along with the bond between the two bromine atoms will break, allowing for two new bonds to form between the carbon atoms and the bromine atoms. This produces 1,2-dibromoethene.
What happens when alkynes react with bromine water?
Addition of bromine to an alkene or alkynes results in the formation of vicinal dibromide which decolourises bromine water.
What are the reactions of alkynes?
The principal reaction of the alkynes is addition across the triple bond to form alkanes. These addition reactions are analogous to those of the alkenes. Hydrogenation. Alkynes undergo catalytic hydrogenation with the same catalysts used in alkene hydrogenation: platinum, palladium, nickel, and rhodium.
What does HBr do to alkynes?
The addition of one equivalent of hydrogen chloride or hydrogen bromide converts alkynes to haloalkenes. The addition of two or more equivalents of HCl or HBr converts alkynes to geminal dihalides through an haloalkene intermediate. These additions are regioselective and follow Markovnikov's rule.
What is the reaction of alkane and bromine?
The reaction of alkane with bromine involves a free-radical mechanism.
What is the reaction of halogen atoms?
When a compound reacts with a halogen atom, the chemical reaction is called halogenation. During this process, halogen atoms are inserted into the respective chemical compound. During halogenation reaction, the substitution of one or more than one halogen atom can happen, and these halogen atoms take the position of hydrogen atoms. Alkanes, being nonpolar compounds, are usually unreactive and lack attached functional groups at which reactions happen. Alkanes can be easily substituted by the halogen atoms using a well-known method called free radical halogenation .
What is the general notation for an alkane?
The general notation for an alkane is R-H. R represents an alkyl group. The addition of a hydrogen atom to an alkyl group results in the formation of a parent hydrocarbon chain of the alkyl group.
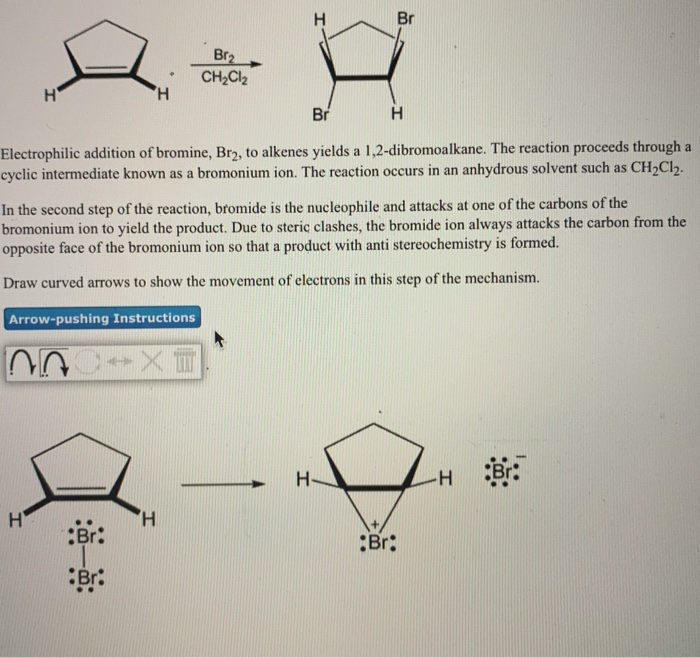
What happens when Br attacks the carbon of the intermediate?
In the second step, the nucleophilic bromide, Br – (generated in step 1), attacks the carbon of the cyclic intermediate. Since the bottom side of the intermediate is blocked by the ring, the Br – can only attack from the top side, that results in the anti position of the two Br in the product. The attack is similar to S N 2 reaction and cause the ring to open and the formation of vicinal dibromide. For the above example, the two carbons in the bromonium ion intermediate are in same chemical environment, so they both have the same chance to be attacked by Br –, as shown in blue and red arrows. The two attacks result in the same product, the meso compound ( 2R,3S )-2,3-dibromobutane, in this reaction.
Why does the C-Br bond break?
This is due to the difference between the two double bond carbons in the cyclic intermediate. When nucleophile water attacks, the C-Br bond start to breaking and the carbon atom has partial positive charges. The carbon atom with two substituents bears more positive charges and it resembles the more stable tertiary carbocation, and the other carbon atom with one substituent shows secondary carbocation character. As a result, the attack to the carbon with more tertiary carbocation character it is more preferably.
What is the difference between Z and E butene?
Starting from the two different diastereomers, (E)-2-butene and (Z)-2-butene, the addition reaction produces different stereoisomers. The addition of (E)-2-butene gives one product, the meso compound ( 2R,3S )-2,3-dibromobutane, while the addition of (Z)-2-butene produces the racemic mixture of two enantiomers, ( 2S,3S )-2,3-dibromobutane and ( 2R,3R )-2,3-dibromobutane. Such reaction, the one where a particular stereoisomer of the starting material yields a specific stereoisomer of the product is called stereospecific reaction. The anti addition of a halogen to an alkene is an example of a stereospecific reaction.
How are halogen atoms added to a double bond?
It turns out that the halogen atoms are added via anti addition to the double bond, as examples shown here: The mechanism that accounts for the anti addition of halogen involves the electron pairs transferred in a way that is different to what we are familiar with, and the formation of the cyclic halonium ion intermediate.
What happens when bromine is added to a sample?
When bromine is added to the sample, if the reddish color disappear, that means the sample does contain an alkene. The addition reaction occurs to get reddish bromine consumed and colorless product formed, so color fades off.
Does an alkene have a symmetric structure?
If the alkene is not in symmetric structure, it is observed that the addition shows the regioselectivity as well, specifically the halogen adds on the carbon atom with greater number of hydrogen atoms, and OH group ends up on the double bond carbon with less amount of hydrogen atoms.
Is bromine an electrophile or nucleophile?
The lone pair on the closer bromine atom then acts as nucleophile to attack the other sp 2 carbon. Thus, the same bromine atom is both electrophile and the nucleophile, and two single bonds are formed between ...