What is concrete floor radiant heat?
Quite simply, concrete floor radiant heat is a system of pex-tubes that carry hot water throughout a concrete floor or slab. Or... radiant heat can be an electrical heating element embedded into a very thin concrete overlay, then tiled, carpeted, or have wood flooring installed over it.
How does forced hot air heating work on concrete?
Due to it's density and low conductivity, concrete retains heat very well. When the concrete floor is heated the heat rises, warming everything in the room. Warm heat distributed with forced-hot-air systems is uneven. Most of the heat rises to the ceiling.
What happens when you heat a concrete slab?
When the thermal mass of the concrete is heated, the warm slab acts as a radiator distributing even heat throughout the structure. The picture above shows a concrete floor we're about to pour with radiant heating tubes installed.
Does concrete make heat while curing?
Does Concrete Make Heat While Curing? It is a little known fact that the process of curing concrete actually generates heat. This is because when you mix water with cement, the molecules in the cement begin a chemical reaction together. Sometimes they react with each other, and sometimes they react with the water, in a process called hydration.
Does concrete emit heat?
The heat produced by concrete during curing is called heat of hydration. This exothermic reaction occurs when water and cement react. The amount of heat produced during the reaction is largely related to the composition (Table 1) and fineness of the cement.
Does concrete raise the temperature?
In general, for every 100 pounds of cement used, concrete gains anywhere from 10 to 15 degrees Fahrenheit during curing. Controlling the temperature of concrete as it cures is very important to insure that it cures over a long enough period of time.
Why is concrete so hot?
This is because when you mix water with cement, the molecules in the cement begin a chemical reaction together. Sometimes they react with each other, and sometimes they react with the water, in a process called hydration. Heat is generated during some of these reactions, so they are called exothermic.
Does concrete release heat at night?
Concrete is a very dense material. When concrete gets heated, it retains the heat for a very long time. This heat is radiated into the rooms at night when the surroundings are getting cool. Due to the stillness of air below the roof, the air in the room also becomes hot.
Does concrete attract heat?
A very modern and efficient type of flooring is concrete. It has the ability to absorb heat from direct sunlight, store the heat and release it slowly. The ability of concrete to absorb and store heat energy is called "thermal mass".
How much hotter is concrete?
It recorded an average temperature just under 80°F, a couple degrees warmer than shaded grass. However, concrete that had been sitting in the sun almost all day was 55° warmer at 135°! That is very warm. Temperature of concrete in shade versus direct sunlight.
Do concrete homes stay cool?
The thermal mass of the walls and the tight seals at joints enable concrete homes to excel at keeping conditioned air in and extreme temperatures out. Temperature control. The tight building envelope also means concrete houses have fewer hot and cold zones and less draftiness.
How can I keep my concrete cool in the summer?
Here are some tips to keep in mind for cooling concrete in hot weather:Keep coarse aggregates cool by storing them in the shade or with mist,Use cold mixing water,Substitute some water with ice,Cool down the cement – cement is stocked in silos, and often retains high temperatures from the factory,More items...
Is concrete a natural insulator?
Concrete is a fantastic material that's been used for centuries to build homes around the world. It's very strong, durable, resistant to the elements and easy to work with. But for all it's strong points, concrete offers very low natural insulation levels.
How do you make a concrete cooler?
Changing color is the easiest way to make cool concrete. Concrete with a light color will reflect more sunlight and absorb less heat. This effect is measured using a figure called Solar Reflectance Index (SRI). This number is determined by the standards found in ASTM E1980.
Is concrete a thermal insulator?
Although concrete is not a particularly good insulator, heat loss or gain through a concrete slab is unlikely to be as significant as heat transmission through above-ground parts of your home, such as windows and doors, which are directly exposed to cold air and sunlight.
Is concrete a good insulator?
Concrete is a much better insulator, meaning it can significantly slow down electrical currents. Electrical conduction and insulation are measures of how easily electrons can move through a material. Concrete is made up of several different materials — namely aggregates, cement and water.
How does temperature affect concrete?
The total volume change in concrete is the sum of the volume changes of the cement paste and concrete.At high temperature ,the cement paste will shrink due to dehydration of calcium silicate hydrate(C-S-H), while the aggregate will expand. for normal aggregate concrete, there is net expansion.
What are temperature effects on fresh concrete?
An increase in ambient temperature generally results in a loss of workability of the concrete mixture. The reason for this phenomenon is both the acceleration of the cement setting process and the faster evaporation of the mixing water at higher temperatures.
How does heat affect concrete?
Hot weather accelerates the cement hydration reaction and increases the water demand and rate of slump loss of a given concrete mixture. As a result, it is often more difficult to properly adjust mixture proportions, deliver, place, consolidate, and finish concrete during hot weather.
What material is compatible with concrete?
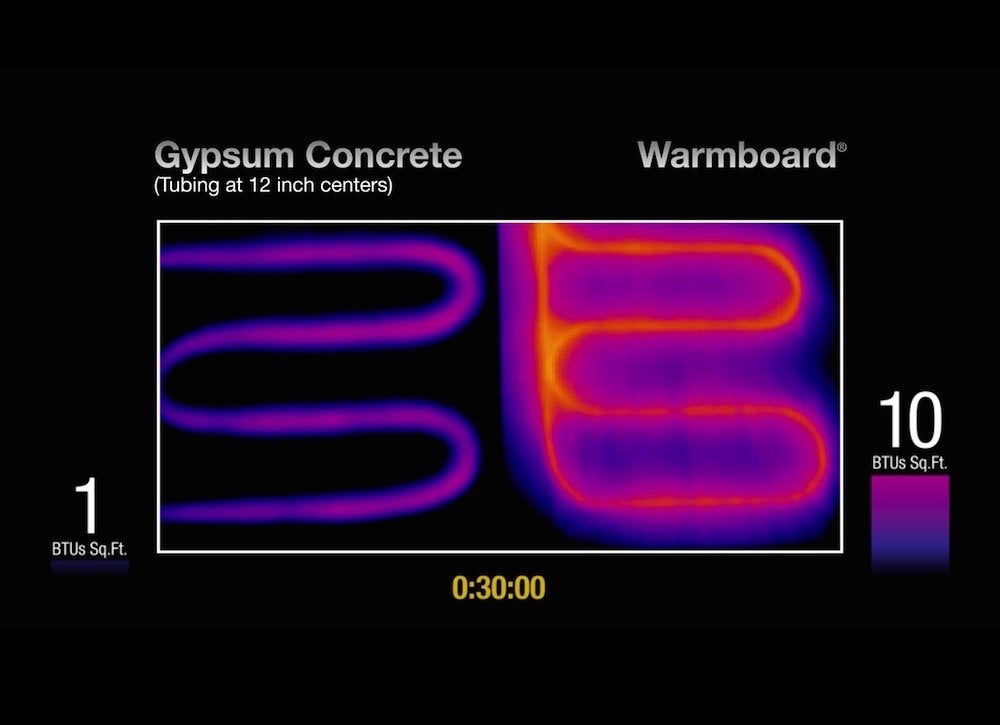
Although steel, copper, and rubberhave been used as tubing in radiantfloor heating systems, one material ismost compatible with concrete in theslab: cross-linked polyethylene orPEX. Unlike other plastic and metaltubing materials, PEX tubing cast inconcrete is capable of lasting the life ofthe structure.
What is the reaction that forms a gel that swells as it draws water from thesurrounding cement
The alkali-silica reaction forms a gelthat swells as it draws water from thesurrounding cement paste. Reactionproducts from ASR have a great affin-ity for moisture. In absorbing water,these gels can induce pressure, ex-pansion, and cracking of the aggre-gate and surrounding paste. The reac-tion can be visualized as a two-stepprocess:
Why is concrete radiant floor heating good?
Because of its energy efficiency and clean draft-free heat, concrete radiant floor heating offers numerous environmental benefits. Here are some of them: Less energy required to achieve better thermal comfort at a lower thermostat setting. Water has 3,500 times the energy transport capacity of air.
What are the benefits of a heated concrete floor?
A heated concrete floor offers these benefits: Your feet are always toasty warm. The temperature is consistent and easy to control. You won't feel the drafts or hear the noise of blowing air. No dust or allergens get circulated within your home through air vents.
How does radiant heating work?
The sun radiates its energy towards the earth. The radiant energy is absorbed by the earth and is released as heat. A radiant floor heating system simply radiates heat upward from the floor to provide optimum comfort and many other benefits.
What are the benefits of radiant floor heating?
Because of its energy efficiency and clean draft-free heat, concrete radiant floor heating offers numerous environmental benefits. Here are some of them: 1 Less energy required to achieve better thermal comfort at a lower thermostat setting. 2 Water has 3,500 times the energy transport capacity of air. 3 Adaptable to various energy-efficient heat sources, such as solar and geothermal. 4 Improved indoor air quality. 5 Radiant systems that use PEX tubing vs. copper pipe expedite hot water delivery and reduce water waste. The walls of PEX tubing provide better insulation than copper. 6 Reduces building materials required for concealing ductwork and compensating ceiling heights. 7 Provides more usable area, which allows for smaller spaces without sacrificing livability.
What are the components of a radiant floor heating system?
Components of a Radiant Floor Heating System. Here are the components required for a radiant floor heating system: Heating Source - this can be electricity, solar, natural gas, propane, oil, wood, or any other heating source. Boiler - houses the water to be heated.
Why does my coffee cup feel hot?
That is why you can feel the heat of the coffee cup when you place your hand to the side of it. Radiant energy transfer is caused by a warm surface giving up its heat to a cooler surface. Consider how the sun (10,000° F) heats the earth (61° F ). The sun radiates its energy towards the earth.
How many volts does a radiant floor system use?
However, low-voltage systems are available that can operate on as little as 24 volts, using a transformer to reduce the line voltage, according to RPA. Some electric radiant systems are intended only for warming floors in specific rooms; others are designed for use as whole-house primary heating.
How much heat does cement produce?
How Much Heat is Generated? As a general rule, the Portland Cement Association estimates that for every 100 pounds of cement, the concrete gains anywhere from 10 to 15 degrees Fahrenheit in temperature.
Why is it important to control the temperature of concrete?
As a result, controlling the temperature of the concrete is very important to insure that it cures over a long enough period of time. The factors that affect curing are both this internally generated heat and the external temperature.
What temperature should concrete be poured?
Ideally, concrete should be poured and cured at an internal temperature of 50 to 90 degrees Fahrenheit. On a cold day, this may mean that your concrete contractor needs to heat or insulate the concrete.
What is the role of cement mixers?
In this way, the cement mixer also plays a role in guaranteeing a solid final product, based on the size of the job and the state of the weather.
Why is cement called exothermic?
Sometimes they react with each other, and sometimes they react with the water, in a process called hydration. Heat is generated during some of these reactions, so they are called exothermic.
What is epoxy coating on concrete?
After all this work, knowledge and expertise have been invested in a well-made concrete slab, it would be a shame not to take good care of it! Epoxy coatings protect the concrete, lending it additional strength against abrasion damage and permeability. Plus, a colorful coating or colored concrete stain adds beauty to a product that is otherwise rather bland. To protect your investment in concrete, clients in Sacramento and Northern California can talk to California Custom Concrete, available for free consultations on the phone or online.
Does concrete affect heat?
Besides using external methods like evaporative cooling when it is hot or insulation and additional heating when it is cold, the heat generated by hydration can also be affected by the mix of the concrete.
Why Does Concrete Get Hot?
Concrete gets hot due to its contents: water, cement, and aggregate (sand, stones, and/or gravel). When sunlight shines on the surface, this combination of ingredients goes through a chemical reaction that generates a thermal mass, absorbing the heat given off by the sun.
How Concrete is Made
Concrete needs to set and harden before reaching its optimal state of function that we see as our everyday sidewalks. As mentioned above, a chemical reaction occurs in the making of concrete, when Portland cement and water are mixed. The cement is added to water, and then hydroxyl ions are released from the dissolving cement.
How to Reduce Heat in Concrete
Depending on the building design or structure type being created with concrete, there may be different steps when it comes to heat regulation. With normal-sized structures, like sidewalks, the concern may not be too great, as heat can dissipate through the soil or air.
Why Hot Weather Can Cause Problems for Cement
When it comes to setting concrete, hot weather causes water evaporation. It is, therefore, necessary to mix in more water in order to enable the cement to react with it to create ample, sturdy, and durable concrete.
Ways to Cool Down Concrete for Construction
According to this article on the USDA website, here are some ways that construction workers can use to reduce concrete temperatures that “decrease water demand, slow slump loss, increase setting time, and reduce the chance of plastic shrinkage cracking”:
Building Designs Made of Concrete
There are a number of different types of buildings and structures around the world that are made from concrete. Some of these include:
Shrinkage and Cracks in Concrete
The next time you take a walk down a street made of concrete, take a look closer look at it. You might see quite a few cracks–some larger, some smaller.
How does concrete help us?
Concrete gives us the power to dam enormous rivers, erect buildings of Olympian height, and travel from place to place with an ease that would astonish our ancestors. Concrete hospitals and schools can be built and repaired far more quickly than their counterparts of adobe, wood, or steel.
What is concrete made of?
Concrete is essentially just sand and gravel glued together with cement. To feed the construction industry’s needs, tens of billions of tons of sand are dug out of the earth each year, enough to blanket the entire state of California. Much of it is dredged from river beds, lake bottoms, and beaches.
Why are concrete roads important?
Concrete roads help farmers get their crops to market, students to get to school, and sick people to get to hospitals in all weathers. It’s an almost supernaturally cheap, easy way to quickly create sturdy housing for huge numbers of people.
What causes concrete to fail?
Concrete fails and fractures in dozens of ways. Heat, cold, chemicals, salt, and moisture all attack that seemingly solid artificial stone, working to weaken and shatter it from within. If it’s not monitored and maintained, most concrete slowly disintegrates.
How much of the world's population lives in concrete?
An estimated 70% of the world’s population now lives in structures made at least partly out of concrete. For all its blessings, however, concrete incurs serious costs to people and the planet—including boosting the potency of heat waves.
What invention made the heat in July worse?
The scorching temperatures across Europe and the U.S. in July were made worse by one of humanity’s most widely used but least-loved inventions: concrete. To most people, concrete is just the ugly stuff used to pave paradise and put up a parking lot. But concrete is an invention as transformative to humanity as fire or electricity.
What is the cement industry?
The cement industry produces somewhere between 5-10% of all carbon-dioxide emissions worldwide, making it the third-largest source of global-warming, behind only coal-fueled power plants and combustion-engine vehicles. Concrete is essentially just sand and gravel glued together with cement.
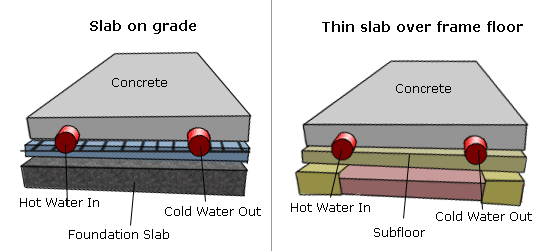
How deep should tubing be in concrete?
Typically the maximum depth that tubing should be placed in a concrete floor slab is 2" down from the finished floor surface. Supervise: If you cannot be present at the job site at critical stages in construction, find someone knowledgeable who can inspect for you before the work continues.
What are the effects of putting tubing deep into a slab?
The effects of putting the tubing deep into the slab created a problem of heat transfer losses to the ground, not just a matter of longer response time to warm the building. Even if money had been no object, the system simply could not heat the building to an acceptable temperature.
Can you run radiant heat under a refrigerator?
Normally you would not bother to run radiant heat under cabinets and IMO even more important, not under a refrigerator, but if it does run there it's not a catastrophe.
Is the rate of heat loss through the floor slab slower at the center of the floor than at the building perimeter?
Although the rate of heat loss through the floor slab is slower at the center of the floor than at the building perimeter (of an installation that is not insulated), in cold climates the heat loss through the floor will be continuous will be significantly greater at an uninsulated slab.