What are the 7 steps of DNA replication?
What are the 7 steps of DNA replication?
- Initiation. …
- Primer Synthesis. …
- Leading Strand Synthesis. …
- Lagging Strand Synthesis. …
- Primer Removal. …
- Ligation. …
- Termination.
What occurs during DNA replication?
- The first step in DNA replication is to unravel the double helix structure of the DNA molecule.
- An enzyme called helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds holding complementary bases of DNA together (A with T, C with G).
- When two single strands of DNA separate, they form a Y-shaped structure called a replication ‘fork’. ...
What is the second step of DNA replication?
What is the second step of DNA replication? On the lagging strand primase synthesises a short RNA primer in the 5'-3' direction. Primase leaves and DNA polymerase adds DNA nucleotides to the RNA primer in the 5'-3' direction.
Which molecules participate in DNA replication?
Note:
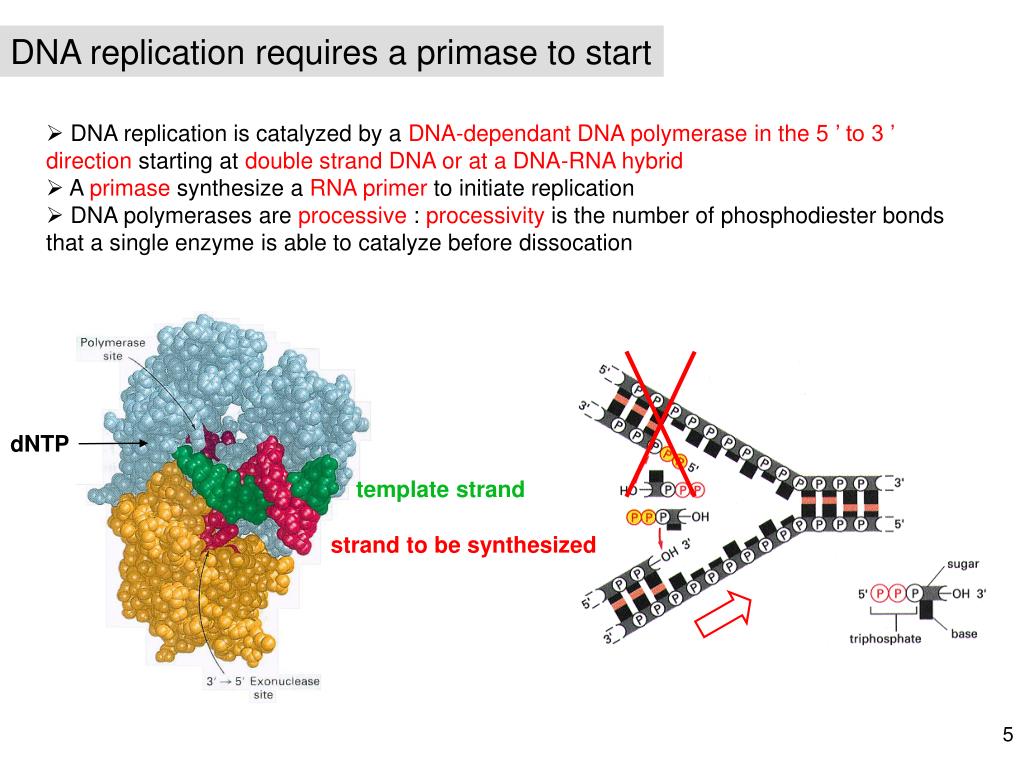
- DNA replication is semiconservative in the process. ...
- New DNA is made by participation of the enzymes called DNA polymerases, which require a template, a primer, and a synthesized DNA in the 5' to 3' direction.
- During the process of DNA replication, one new strand (that is leading strand) is made as a continuous piece. ...

Why are enzymes required for replication?
An enzyme is a molecule that speeds up a reaction. In the case of DNA reproduction, enzymes not only speed up the reaction, they are necessary for DNA reproduction. Recall that DNA is a long strand with a many repeating base pairs. In order for DNA to reproduce, the base pairs must be split apart.
What does DNA replication require?
Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or DNA, as the parent cell. The replication process relies on the fact that each strand of DNA can serve as a template for duplication.
What is not needed for DNA replication?
RNA polymerase is an enzyme that transcribes RNA from DNA; it is not essential for DNA replication.
What enzyme is used in DNA replication?
DNA polymeraseThe central enzyme involved is DNA polymerase, which catalyzes the joining of deoxyribonucleoside 5′-triphosphates (dNTPs) to form the growing DNA chain.
What is DNA replication quizlet?
DNA replication definition. the process in which one DNA molecule produces two identical DNA molecules, occurs before the cell divides.
How does DNA replication works?
DNA replication is the production of identical DNA helices from a single double-stranded DNA molecule. Each molecule consists of a strand from the original molecule and a newly formed strand. Prior to replication, the DNA uncoils and strands separate.
Which statement about DNA replication is false?
The statement pertaining to DNA replication that is false is D: Okazaki fragments are synthesized as part of the leading strand.
Which of the following is not an enzyme involved in DNA replication?
So, the correct option is 'RNA polymerase'
Which of the following is not involved in the DNA replication process quizlet?
All of the following occur during DNA replication EXCEPT: synthesis of totally new double-stranded DNA molecules.
What enzymes are involved in DNA replication quizlet?
Terms in this set (6)DNA helicase. unwinds the DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen bond between the nucleotides to allow the resulting strand to be replicated.seperates the strand of the DNA double-helix in order for replication to happen.RNA primase. ... DNA polymerase III. ... DNA polymerase I. ... DNA ligase. ... Topoisomerase.
Which enzyme is required for this process?
Answer. Explanation: DNA polymerase enzyme adds deoxyribonucleotides to synthesize DNA using the base sequence of parental DNA strand by the process of DNA replication which makes option B incorrect.
What are the two enzymes that are related to DNA replication what are their roles?
Enzymes used in DNA replication:Primase (catalyze the synthesis of short RNA molecules used as primers for DNA polymerase)DNA polymerase I (for filling small DNA segments during replication and repair processes)DNA polymerase III (It is the main replicating enzyme)More items...
Why are primers needed for DNA replication?
The synthesis of a primer is necessary because the enzymes that synthesize DNA, which are called DNA polymerases, can only attach new DNA nucleotides to an existing strand of nucleotides. The primer therefore serves to prime and lay a foundation for DNA synthesis.
What is the first step that must occur in DNA replication?
The first step in DNA replication is the separation of the two DNA strands that make up the helix that is to be copied. DNA Helicase untwists the helix at locations called replication origins. The replication origin forms a Y shape, and is called a replication fork.
What are the 7 steps of DNA replication?
Steps in DNA ReplicationInitiation. DNA replication begins at specific site termed as origin of replication, which has a specific sequence that can be recognized by initiator proteins called DnaA. ... Primer Synthesis. ... Leading Strand Synthesis. ... Lagging Strand Synthesis. ... Primer Removal. ... Ligation. ... Termination.
What materials does DNA polymerase require in order to synthesize a complete strand of DNA?
In order for DNA polymerase to synthesize a complete new strand of DNA, it requires a template to determine the order of bases on the new strand, a 3'-OH end to add more nucleotides onto, and the full set of four kinds of nucleotides (A,C,T,G) if they are needed to complement the template strand.
Why are there so many enzymes involved in DNA replication?
There are many enzymes involved in DNA replication due to the complex nature of the whole process. Here are the main enzymes and their functions in eukaryotic cells, during cell division.
What is DNA replication?
DNA replication, the basis of biological inheritance, is made possible by certain enzymes present in cells. In this article, I talk about these prime replication enzymes and their functions. Home / Uncategorized / DNA Replication Enzymes.
What enzymes are needed to synthesize DNA?
These primers are synthesized by DNA primase enzymes, thus initiating the DNA replication process.
What is the name of the molecule that holds the DNA together?
DNA molecule has a double helix structure with two strands of nucleotides coiled together and held in place by a 2-deoxyribose sugar-Phosphate backbone. Each strand is made up of a series of nucleotides called Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C). These are the four letters, using which the entire genetic code is written. The order of nucleotides on both strands is complementary as Adenine only binds with Thymine and Cytosine only binds with Guanine.
How does DNA work?
For this genetic information to be transmitted from one generation to the other, it needs to be replicated during cell division, so that every new cell formed, carries its identical copy. This process is monitored and controlled by the DNA replication enzymes . Today DNA research has revealed intricate details of how the genetic code is copied or duplicated during cell division.
What is the name of the RNA segment that is synthesized by DNA primase enzymes?
After the DNA strands are separated, to begin the creation of new molecules, through addition of complementary bases to the templates, a short RNA segment, called a ‘primer ’ is required. These primers are synthesized by DNA primase enzymes, thus initiating the DNA replication process.
How is DNA replication made possible?
DNA replication, the basis of biological inheritance, is made possible by certain enzymes present in cells. In this article, I talk about these prime replication enzymes and their functions. Continuity of life is made possible due to inheritance of genetic material by every new generation of organisms. Every family has certain traits inherited ...
Which enzyme needs to make a long enough chain to replicate the entire chromosome?
The replication enzyme needs to make a long enough chain to replicate the entire chromosome. The repair enzyme needs only to make a long enough strand to replace the damaged sequences in the chromosome. The best‐studied bacterium, E. coli, has three DNA polymerase types.
What is the difference between DNA polymerase and DNA repair enzyme?
A DNA polymerase used in replication is more processive than a repair enzyme. The replication enzyme needs to make a long enough chain to replicate the entire chromosome.
How do DNA polymerases copy DNA?
These enzymes copy DNA sequences by using one strand as a template . The reaction catalyzed by DNA polymerases is the addition of deoxyribonucleotides to a DNA chain by using dNTPs as substrates, as shown in Figure 2.
What enzyme removes RNA primers?
DNA polymerase I then uses its polymerizing and 5′ to 3′ exonuclease activities to remove the RNA primer and fill in this sequence with DNA. Because Pol I is not very processive, it falls off the lagging strand after a relatively short‐length synthesis. DNA polymerases can't seal up the nicks that result from the replacement of RNA primers with DNA. Instead, another enzyme, DNA ligase, seals off the nicks by using high energy phosphodiester bonds in ATP or NAD to join a free 3′ hydroxyl with an adjacent 5′ phosphate.
What enzyme is responsible for chain initiation?
Chain initiation occurs when a specialized RNA polymerase enzyme called primase makes a short RNA primer. DNA polymerase III extends this RNA primer on both strands. Because DNA polymerase synthesizes DNA only in one direction (5′ to 3′), only one strand is copied in each direction (left and rightward in the next figure). At the end of the initiation process, two replication forks exist, going in opposite directions from the “bubble” at the origin of replication, as shown in Figure 7.
How many phosphodiester bonds does DNA polymerase I make?
About 400 Pol I molecules exist in a single bacterium. DNA polymerase I only makes an average of 20 phosphodiester bonds before dissociating from the template.
What is the reaction of DNA polymerases?
The reaction of DNA polymerases is thus better understood as the addition of nucleotides to a primer to make a sequence complementary to a template. The requirement for template and primer are exactly what would be expected of a replication enzyme.
Which enzyme is required for DNA replication?
DNA polymerase: This enzyme is the main enzyme required for DNA replication. It can link free DNA nucleotides to form the complementary strand of DNA. It polymerises nucleotides in 5’→3’ direction only. It is also known as a DNA-dependent enzyme as it uses a DNA template for polymerisation of deoxynucleotides.
Why is DNA replication important?
The significance of DNA replication is as follows: To produce two identical copies of the parental DNA so that each daughter cell receives its own copy of DNA. To maintain the original chromosome number of an individual. Essential for the cell division process during the growth or repair of an individual.
How many strands does DNA replication have?
After the completion of the DNA replication, each DNA has one parental (or old) strand and one daughter (or new) strand.
Why is replication discontinuous on the other template?
But replication is discontinuous on the other template with polarity 5 ′ → 3 ′ because DNA polymerase enzymes can add nucleotides in 5 ′ → 3 ′ direction only.
What is DNA replication?
DNA Replication is a very unique and complex multistep biological process of producing two identical replicas from one original DNA molecule. It occurs in all living organisms (both prokaryotes and eukaryotes) because it forms an essential part of biological inheritance. It requires a number of enzymes, protein factors, ...
What phase of cell division does DNA replication take place?
It is because of the DNA Replication process that takes place during the S-phase (synthetic phase) of the cell division (mitosis or meiosis) in each and every cell. In DNA Replication, the DNA forms its own replica and doubles its quantity so that after the process of cell division, the original number of chromosomes is maintained for ...
Which direction does DNA replication occur?
Thus, replication over the two templates proceeds in opposite directions . One strand with polarity 3 ′ → 5 ′ forms its complementary strand continuously and is called the leading strand.
Why are enzymes important for DNA replication?
Enzymes are vital to DNA replication since they catalyze very important steps in the process. The overall DNA replication process is extremely important for both cell growth and reproduction in organisms. It is also vital in the cell repair process.
Why Replicate DNA?
DNA, found within the nucleus, must be replicated in order to ensure that each new cell receives the correct number of chromosomes. The process of DNA duplication is called DNA replication. Replication follows several steps that involve multiple proteins called replication enzymes and RNA. In eukaryotic cells, such as animal cells and plant cells, DNA replication occurs in the S phase of interphase during the cell cycle. The process of DNA replication is vital for cell growth, repair, and reproduction in organisms.
What are the steps of DNA replication?
DNA replication would not occur without enzymes that catalyze various steps in the process. Enzymes that participate in the eukaryotic DNA replication process include: 1 DNA helicase - unwinds and separates double stranded DNA as it moves along the DNA. It forms the replication fork by breaking hydrogen bonds between nucleotide pairs in DNA. 2 DNA primase - a type of RNA polymerase that generates RNA primers. Primers are short RNA molecules that act as templates for the starting point of DNA replication. 3 DNA polymerases - synthesize new DNA molecules by adding nucleotides to leading and lagging DNA strands. 4 Topoisomerase or DNA Gyrase - unwinds and rewinds DNA strands to prevent the DNA from becoming tangled or supercoiled. 5 Exonucleases - group of enzymes that remove nucleotide bases from the end of a DNA chain. 6 DNA ligase - joins DNA fragments together by forming phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides.
How does lagging DNA work?
The lagging strand begins replication by binding with multiple primers. Each primer is only several bases apart. DNA polymerase then adds pieces of DNA, called Okazaki fragments, to the strand between primers. This process of replication is discontinuous as the newly created fragments are disjointed.
How many bases are needed for DNA replication?
Before DNA can be replicated, the double stranded molecule must be “unzipped” into two single strands. DNA has four bases called adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G) that form pairs between the two strands. Adenine only pairs with thymine and cytosine only binds with guanine. In order to unwind DNA, these interactions between base pairs must be broken. This is performed by an enzyme known as DNA helicase. DNA helicase disrupts the hydrogen bonding between base pairs to separate the strands into a Y shape known as the replication fork. This area will be the template for replication to begin.
What phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur?
In eukaryotic cells, such as animal cells and plant cells, DNA replication occurs in the S phase of interphase during the cell cycle. The process of DNA replication is vital for cell growth, repair, and reproduction in organisms.
What is DNA made of?
It consists of a 5-carbon deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base. Double-stranded DNA consists of two spiral nucleic acid chains that are twisted into a double helix shape. This twisting allows DNA to be more compact.
What enzyme is responsible for DNA replication?
DNA polymerase III enzyme is responsible for DNA replication in vivo. It has 5’→ 3′ polymerase and 3’→ 5′ exonuclease activities. It catalyzes DNA synthesis at very high rates, e.g., 15,000 bases/min at 37°C. It is composed of several subunits. A DNA polymerase molecule has the following 4 functional sites involved in polymerase activity (Fig. 28.15).
What is the name of the enzyme that can initiate replication in vitro?
DNA polymerase I is encoded by gene polA, has a single polypeptide, and can initiate replication in vitro at a nick in a DNA duplex. It can be cleaved by proteolytic treatments into a large and a small fragments.
What enzyme seals the nicks remaining in a DNA strand?
Enzyme # 3. Polynucleotide Ligase: ADVERTISEMENTS: DNA ligase or polynucleotide ligase catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester linkage between two immediate neighbour nucleotides of a DNA strand. Thus it seals the nicks remaining in a DNA strand either following DNA replication or DNA repair.
What is the function of DNA polymerase I in E. coli?
DNA polymerase I enzyme provides the major part of activity in E. coli. It is chiefly a DNA repair enzyme, and is used for in vitro DNA replication.
What are the requirements for DNA polymerases?
All DNA polymerases require the following: ADVERTISEMENTS: (1) A template DNA strand, (2) A short primer (either RNA or DNA), and. (3) A free 3′ -OH in the primer. They add one nucleotide at a time to the free 3′ -OH of the primer, and extend the primer chain in 5′ → 3′ direction. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What is the function of DnaG in eukaryotes?
In E. coli, DnaG functions as primase. But in eukaryotes, DNA polymerase α provides this function. There are, however, several other ways in which primers are produced, e.g., the 3′-OH generated by a nick in the template DNA molecule. Enzyme # 3.
What enzyme is used to repair DNA?
DNA polymerase II enzyme functions in DNA-repair. It has 5′ → 3′ polymerase and 3′ → 5′ exonuclease activities, and uses as template only such DNA duplexes that have short gaps.