genetic drift, also called genetic sampling error or Sewall Wright effect, a change in the gene pool of a small population that takes place strictly by chance. Genetic drift can result in genetic traits being lost from a population or becoming widespread in a population without respect to the survival or reproductive value of the alleles involved.
Full Answer
What are some real life examples of genetic drift?
Genetic drift can be understood well with the following examples:
- The American Bison was once hunted to such an extent that it became endangered. ...
- Let's take an example of a group of rabbits with brown fur and white fur, white fur being the dominant allele. ...
- It should be noted that a child will have blue or brown eyes if either of the parents has blue or brown eyes. ...
What are the effects of genetic drift?
DisplayTitle Population Genetics of Plant Pathogens Genetic Drift
- Measuring Genetic Drift. The magnitude of genetic drift depends on N e, the effective population size, for the population. ...
- Genetic Drift Decreases Gene Diversity and Leads to Population Subdivision. ...
- Genetic Drift in Pathogen Populations. ...
- Examples of Genetic Drift. ...
What is true about genetic drift?
genetic drift, also called genetic sampling error or Sewall Wright effect, a change in the gene pool of a small population that takes place strictly by chance. Genetic drift can result in genetic traits being lost from a population or becoming widespread in a population without respect to the survival or reproductive value of the alleles involved. A random statistical effect, genetic drift can occur only in small, isolated populations in which the gene pool is small enough that chance events ...
What causes genetic drift?
Genetic drift can be caused by a number of chance phenomena, such as differential number of offspring left by different members of a population so that certain genes increase or decrease in number over generations independent of selection, sudden immigration or emigration of individuals in a population changing gene
How does genetic drift impact survival?
Both inbreeding and drift reduce genetic diversity, which has been associated with an increased risk of population extinction, reduced population growth rate, reduced potential for response to environmental change, and decreased disease resistance, which impacts the ability of released individuals to survive and ...
How is genetic drift beneficial?
Genetic Drift in Evolution Genetic drifting is important in evolution since it determines the fate of a mutation, it determines whether it will disappear or becomes fixed in the population after a few generations. For nonideal populations Small in size), genetic drift is important even for the common genes.
Is genetic drift always advantageous to a population?
Every population experiences genetic drift, but small populations feel its effects more strongly. Genetic drift does not take into account an allele's adaptive value to a population, and it may result in loss of a beneficial allele or fixation (rise to 100% frequency) of a harmful allele in a population.
Why is genetic variation a survival advantage?
Genetic variations that alter gene activity or protein function can introduce different traits in an organism. If a trait is advantageous and helps the individual survive and reproduce, the genetic variation is more likely to be passed to the next generation (a process known as natural selection).
Is genetic drift better than natural selection?
Natural selection increases the frequency of the trait more adaptive to the environment, whereas genetic drift rarely results in more adaptive species to the environment. Natural selection increases genetic variation, whereas genetic drift does not increase genetic variation compared to natural selection.
Why is drift important?
The phenomenon of drifting occurs because the rear slip angle is greater than the front slip angle. Maneuvering a car while turning is quite simple. You simply rotate the car's steering wheel to your desired direction. Once you do this, physics will take over, and you will be left with limited control of your car.
Is genetic drift good for evolution?
In these cases, genetic drift can result in the loss of rare alleles and decrease the gene pool. Genetic drift can cause a new population to be genetically distinct from its original population, which has led to the hypothesis that genetic drift plays a role in the evolution of new species.
Which statement about genetic drift is correct?
Correct answer: Genetic drift occurs as a result of chance events causing changes in the allele frequency of a population. It doesn't favor the most fit individuals, but occurs at random.
Is genetic variation an advantage or disadvantage?
This variation permits flexibility and survival of a population in the face of changing environmental circumstances. Consequently, genetic variation is often considered an advantage, as it is a form of preparation for the unexpected.
How does variation affect their survival?
Genetic variation in a group of organisms enables some organisms to survive better than others in the environment in which they live. Organisms of even a small population can differ strikingly in terms of how well suited they are for life in a certain environment.
Why is variation beneficial to the species but not necessary for survival?
Solution : Variations are beneficial to the species than individual because sometime for a species, the environmental conditions change so drastically that their survival becomes difficult. During that period, only few variants that are resistant would be able to survive. Thus, variants help in survival of the species.
Is genetic drift good for evolution?
In these cases, genetic drift can result in the loss of rare alleles and decrease the gene pool. Genetic drift can cause a new population to be genetically distinct from its original population, which has led to the hypothesis that genetic drift plays a role in the evolution of new species.
What is a good example of genetic drift?
Genetic Drift Example Consider a population of rabbits with brown fur and white fur, white fur being the dominant allele. Due to genetic drift, only the brown population might remain, with all the white ones eliminated.
What are two important examples of genetic drift?
There are two major types of genetic drift: population bottlenecks and the founder effect.
Why is genetic drift important to endangered?
We have shown that random genetic drift effects in threatened animals are widespread and lead to the erosion of neutral genetic diversity within species. This places many populations and species at a greater risk of extinction in a changing environment even if other threats can be obviated.
What happens when you drift over generations?
In extreme cases, drift over the generations can result in the complete loss of one allele in an allele pair; the remaining allele is then said to be fixed. In populations of finite size, the genetic structure of a new generation is not necessarily that of the previous one.
How do gene frequencies change?
Gene frequencies can change from one generation to another by a process of pure chance known as genetic drift. This occurs because the number of individuals in any population is finite, and thus the frequency of a gene may change in the following…
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...
Is the genetic structure of a new generation necessarily that of the previous generation?
In populations of finite size, the genetic structure of a new generation is not necessarily that of the previous one. The explanation lies in a sampling effect, based on the fact that a subsample from any large set is not always representative…
What is the importance of genetic diversity for a species?
Genetic diversity of plants, animals and other living organisms is what enables them to survive and thrive in this world. The capacity of species to adapt to new circumstances, whether this is resource scarcity, a changing environment or other disturbances to their natural environment, depends on genetic diversity.
How is genetic diversity measured?
Genetic diversity is measured by looking at how many different forms of genes exist across the genome* (the complete set of genes) among individuals in a population and how frequently they occur.
Why is genetic diversity important?
Genetic diversity helps maintain the health and vigor of a population to resist infectious diseases, pests and other stresses.
How does habitat fragmentation affect species?
Habitat fragmentation decreases genetic diversity of species. While there have always been alterations in the natural world that split populations, like rivers moving, mountains forming, and glaciations, species have continued to thrive.
Why did the Potato Famine happen?
The absence of genetic diversity was the reason behind one of history’s biggest famines. The causes of the Potato Famine in Ireland which took place in the 19th century can be traced back to the susceptibility of the new potato plant to a specific disease.
What is the cause of fungal mucormycosis?
The fungal mucormycosis is a disease caused by the fungus Mucor amphibiorum, which causes infection prone skin lesions and can be deadly to platypuses.
What is locus in biology?
Locus is like a physical address for a gene on a chromosome [2]. Genetic diversity of a species is high when there are many different allelic forms of all genes and when there are many different combinations expressed across the species.
How many simulations of random genetic drift of a single given allele with an initial frequency distribution of 0.5?
Ten simulations of random genetic drift of a single given allele with an initial frequency distribution 0.5 measured over the course of 50 generations, repeated in three reproductively synchronous populations of different sizes. In these simulations, alleles drift to loss or fixation (frequency of 0.0 or 1.0) only in the smallest population.
Why is genetic drift less likely than unequal numbers?
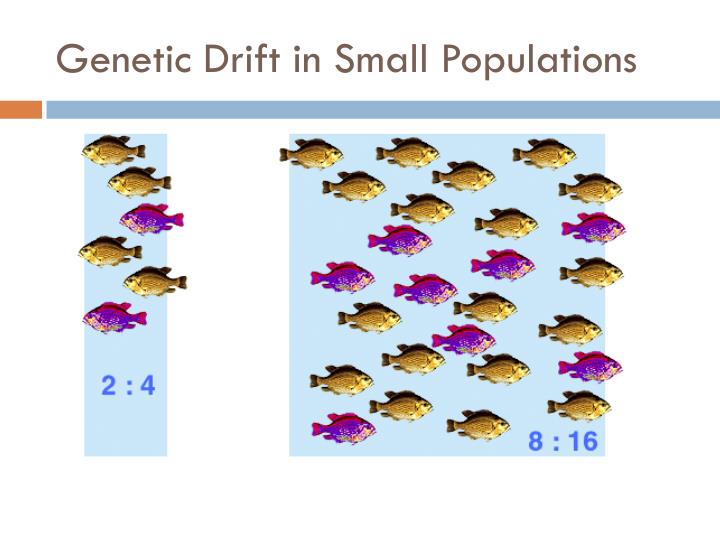
In the latter case, genetic drift has occurred because the population's allele frequencies have changed due to random sampling. In this example the population contracted to just four random survivors, a phenomenon known as population bottleneck .
How does genetic drift work?
Once an allele becomes fixed, genetic drift comes to a halt, and the allele frequency cannot change unless a new allele is introduced in the population via mutation or gene flow. Thus even while genetic drift is a random, directionless process, it acts to eliminate genetic variation over time.
What is the effect of genetic drift?
Genetic drift ( allelic drift or the Sewall Wright effect) is the change in the frequency of an existing gene variant ( allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms. The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form.
What causes genetic variation to disappear?
Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation. It can also cause initially rare alleles to become much more frequent and even fixed.
Why does random sampling drive genetic drift?
Because random sampling can remove, but not replace, an allele, and because random declines or increases in allele frequency influence expected allele distributions for the next generation, genetic drift drives a population towards genetic uniformity over time.
How to explain genetic drift?
The process of genetic drift can be illustrated using 20 marbles in a jar to represent 20 organisms in a population. Consider this jar of marbles as the starting population. Half of the marbles in the jar are red and half are blue, with each colour corresponding to a different allele of one gene in the population. In each new generation the organisms reproduce at random. To represent this reproduction, randomly select a marble from the original jar and deposit a new marble with the same colour into a new jar. This is the "offspring" of the original marble, meaning that the original marble remains in its jar. Repeat this process until there are 20 new marbles in the second jar. The second jar will now contain 20 "offspring", or marbles of various colours. Unless the second jar contains exactly 10 red marbles and 10 blue marbles, a random shift has occurred in the allele frequencies.
What Causes Genetic Drift?
Genetic drift is much more likely in smaller populations of organisms, as seen in the image found in this article. The individual lines in the graph track the frequency of alleles in a given population. When the population is small and many alleles exist (see the first graph), any of the alleles can quickly become fixed or extinct in the population. When there are many organisms in the population (see the last graph), there is less of a chance of losing an entire allele, because many organisms carry the allele and it is less likely they will all be wiped out.
What is gene flow?
Populations of organisms exhibit gene flow when individuals from one population migrate and breed with a new population. Gene flow does not analyze the allele frequency of genes. Rather, it is a concept which describes the movement of genes between populations. By contrast, genetic drift describes the random selection of genes within a population, ...
How does genetic drift affect the allele frequency?
The difference is whether or not the allele is actively participating in the change in allele frequencies. If the allele affects an organism in a way that causes more reproduction of the DNA, the allele will increase in frequency. If it causes harm, it will decrease.
How does genetic drift happen?
These mutations get passed on if the organism reproduces, and do not get passed on if the organism does not survive. Although genetic drift used to be thought of in only small populations, even large populations experience genetic drift of certain alleles. This happens because a small number of individuals carry the alleles. Whether or not these alleles are duplicated is not a function of natural selection, but of chance. Many alleles come or go in populations without affecting great change.
Why is genetic drift important?
Although variations of genes (also known as alleles) can be selected for because they help or hinder an organism, other mutations can have no effect. When the allele itself is not responsible for the change in its frequency in a population, genetic drift is acting on the allele.
What happens when an allele is increased or decreased?
This is natural selection. When the allele is increased or decreased simply because it was present in the random organisms that survived, this is genetic drift.
What is a population bottleneck?
Population Bottleneck. A population bottleneck is a type of genetic drift in which a population’s size severely decreases. Competition, disease, or predation leads to these massive decreases in population size. The allele pool is now determined by the organisms which did not die.

Does Genetic Diversity Increase Biodiversity?
What Is The Importance of Genetic Diversity For A Species?
- Genetic diversity of plants, animals and other living organisms is what enables them to survive and thrive in this world. The capacity of species to adapt to new circumstances, whether this is resource scarcity, a changing environment or other disturbances to their natural environment, depends on genetic diversity. The greater the variation in gene...
Examples of Species with Low Genetic Diversity and Consequences
- Large populations tend to have high levels of genetic diversity. However, as populations shrink, they lose much of their diversity. The result is that the remaining individuals are more genetically similar to one another. This becomes a problem if survival traits have been lost and if genetic combinations causing diseases are expressed with marked frequency. The potato famine The a…
Examples of Species with High Genetic Diversity
- The most genetically diverse species of the eukaryotes, organisms with DNA in their chromosomes within the nucleus of their cells, including plants, animals and fungi, is a mushroom that lives on decaying wood. The split gill mushroom. The split gill mushroom can have a nucleotide diversity of twenty percent. This means that two different mushrooms can have differ…