
How can you make electricity using geothermal energy?
Three different types of geothermal power plants exist:
- Dry steam plants. Hot steam is piped directly from geothermal reservoirs into generators in the power plant. ...
- Flash steam plants. Water that's between 300 and 700 degrees Fahrenheit (148 and 371 degrees Celsius) is brought up through a well. ...
- Binary cycle plants. ...
What are the positive effects of geothermal energy?
What are the Disadvantages of Geothermal Energy?
- Location Restricted. The largest single disadvantage of geothermal energy is that it is location specific. ...
- Environmental Side Effects. Although geothermal energy does not typically release greenhouse gases, there are many of these gases stored under the Earth’s surface which are released into the atmosphere ...
- Earthquakes. ...
- High Costs. ...
- Sustainability. ...
How much does it cost to use geothermal energy?
Geothermal System Cost Comparison vs. Peer HVAC Systems System Type Average Cost Operating Cost Geothermal $24,000 $1,000 Mini split air source $12,250 $1,380 Standard air source $8,600 $1,840 Your annual costs will vary based on the efficiency of the system you choose, the size and condition of your home and local climate factors.
How can geothermal energy replace fossil fuel?
Geothermal energy is clean because it can be generated without burning fossil fuels. Geothermal plants release a fraction of the carbon dioxide produced by fossil fuel plants, and they create very little nitrous oxide or sulfur gases [source: U.S. Department of Energy].
Does geothermal increase electric bill?
Your electric usage will increase with geothermal, but that additional cost won't be divided equally throughout the year. Your electric bill will likely be lower in the summer than you paid previously. You'll be spending less money overall than when heating with oil or propane – even with an increased electric bill.
How much electricity does geothermal energy use?
In conclusion, a 6-ton SEER 30 geothermal heat pump uses 4.6kWh of power. An airconditioning unit of the same size would use roughly 7kWh. Similarly, a 3-ton SEER 30 geothermal heat pump would use 2.3kWh, while a 3-ton AC unit would use 3.5kWh.
Is geothermal electricity expensive?
The initial cost for the field and power plant is around $2500 per installed kW in the U.S., probably $3000 to $5000/kWe for a small (<1Mwe) power plant. Operating and maintenance costs range from $0.01 to $0.03 per kWh.
What are 3 disadvantages of geothermal energy?
What are the Disadvantages of Geothermal Energy?Location Restricted. The largest single disadvantage of geothermal energy is that it is location specific. ... Environmental Side Effects. ... Earthquakes. ... High Costs. ... Sustainability.
Is geothermal energy cheaper?
Unlike solar and wind energy, geothermal energy is always available, 365 days a year. It's also relatively inexpensive; savings from direct use can be as much as 80 percent over fossil fuels.
Will geothermal save me money?
Numbers from US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) show that homeowners using geothermal systems may realize savings of 30-70% on heating costs and 20-50% on cooling costs, compared to other conventional systems. That can translate to savings of $1,500 annually.
How much does it cost to heat a house with geothermal?
between $18,000 to $30,000On average, a homeowner can expect total expenses to reach between $18,000 to $30,000 on geothermal heating and cooling cost. This cost would cover a complete geothermal installation. The price can range from $30,000 to $45,000 with high-end ground-source heat pump systems for large homes.
Is geothermal cheaper than natural gas?
Geothermal Heating Costs vs Gas A geothermal heat pump uses electricity. In a lot of areas around the country, natural gas costs are very low. It is much cheaper to operate a natural gas furnace than to rely on an electric furnace. Of course, geothermal heat pumps operate very differently than electric furnace units.
How much does geothermal cost per year?
Geothermal System Cost Comparison vs. Peer HVAC SystemsSystem TypeAverage CostOperating CostGeothermal$24,000$1,000Mini split air source$12,250$1,380Standard air source$8,600$1,840Your annual costs will vary based on the efficiency of the system you choose, the size and condition of your home and local climate factors.
Why is geothermal bad?
Geothermal plants can release small amounts of greenhouse gases such as hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide. Water that flows through underground reservoirs can pick up trace amounts of toxic elements such as arsenic, mercury, and selenium.
What can go wrong with geothermal?
4 Common Geothermal Heat Pump Problems You Should Know AboutLeaks. The refrigerant or water can leak from the underground or underwater pipes in geothermal heat pumps. ... Water Contamination. Pipes leaking refrigerant in a closed loop of pipes could harm plants and contaminate your local water. ... Corrosion. ... Ductwork Issues.
How long do geothermal systems last?
Geothermal heat pumps last significantly longer than conventional equipment. They typically last 20-25 years. In contrast, conventional furnaces generally last anywhere between 15 and 20 years, and central air conditioners last 10 to 15 years.
How much does geothermal energy cost a year?
Table of Comparison: Geothermal Energy vs. Fossil FuelVariableGeothermal Heat PumpFossil Fuel (Furnace)Installation$10,000 to $80,000$2,500 to $6,500Electricity per kWh$0.05 to $0.09$0.030 to $0.036Maintenance$150 to $350$80 to $120/yearHeat SourceFreeVaries and changes1 more row•Feb 24, 2022
Why is geothermal energy so expensive?
The cost of developing a geothermal power plant is often comparable to a conventional fuel plant. The cost of a geothermal plant is largely in the construction of the plant and the scouting of the site. On the other hand, it requires little upkeep to produce electricity efficiently.
Is geothermal cheaper than natural gas?
Geothermal heat pumps are more costly than natural gas systems, coming in at $20,000 to $25,000 compared to the cost of a natural gas furnace, which is between $2,600 to $6,400. For homeowners who cannot pay the upfront costs, natural gas may be a much more affordable option than geothermal heat.
What is geothermal energy?
Geothermal energy—energy derived from the heat of the earth—can be harnessed both as a source of renewable electricity as well as directly for heating and cooling applications. The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) funds geothermal research and development ...
Where is geothermal energy available?
Traditionally, geothermal resources are most accessible in the western states, from Colorado and New Mexico up to Utah, Nevada, Idaho and Oregon. However, with the development of enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) technologies and additional research in deep direct-use (DDU) capabilities, geothermal energy will potentially be accessible across ...
Where was the first geothermal system developed?
In fact, the first modern geothermal district heating plant was developed in 1892 in Boise, Idaho. DOE supports direct-use efforts, striving to heat more homes and reduce more energy bills. 4.
When was the first geothermal plant built?
Over 100 years of geothermally sourced energy: The first ever geothermal plant was set up in Larderello, Italy, in 1904. Steam from that geothermal source was used to turn a small turbine which powered five light bulbs.
What is geothermal energy used for?
Geothermal energy is also used to directly heat individual buildings and to heat multiple buildings with district heating systems. Hot water near the earth's surface is piped into buildings for heat. A district heating system provides heat for most of the buildings in Reykjavik, Iceland.
How much electricity does the United States generate from geothermal energy?
International geothermal electricity generation. In 2018, 27 countries, including the United States, generated a total of about 83 billion kWh of electricity from geothermal energy.
What are the different types of geothermal energy?
Some applications of geothermal energy use the earth's temperatures near the surface, while others require drilling miles into the earth. There are three main types of geothermal energy systems: 1 Direct use and district heating systems 2 Geothermal power plants 3 Geothermal heat pumps
How hot does geothermal energy get?
Geothermal electricity generation requires water or steam at high temperatures (300° to 700°F). Geothermal power plants are generally built where geothermal reservoirs are located, within a mile or two of the earth's surface.
How does a geothermal heat pump work?
Geothermal heat pumps use the constant temperatures near the surface of the earth to heat and cool buildings. Geothermal heat pumps transfer heat from the ground (or water) into buildings during the winter and reverse the process in the summer.
Can we run out of geothermal energy?
Myth: We could run out of geothermal energy. Geothermal energy is a renewable energy and will never deplete. Abundant geothermal energy will be available for as long as the Earth exists.
Is geothermal energy safe?
Geothermal energy#N#(link is external)#N#is safe, reliable, and resides just beneath our feet. It can help meet U.S. energy demands by supplying power to our electric grid and can even be used to heat and cool homes and businesses.
Do geothermal plants take up space?
Myth: Geothermal power plants take up a lot of space. Geothermal energy has the smallest land footprint of any comparable energy source in the world. They are compact and use less land per gigawatt hours (404 m 2) than coal (3642 m 2 ), wind (1335 m 2 ), or solar photovoltaics plants (3237 m 2 ).
How Much Electricity Does A Geothermal Heat Pump use?
Why Do Geothermal Heat Pumps Use Such Little Electricity?
- The answer to this is quite simple. Instead of using electricity to generate heat, it transfersheat from one source to another. So, what does a geothermal heat pump’s electricity usage go towards? A geothermal heat pump uses electricityfor its compressor, fan, and circulation pumps. Only 1/4 units of electrical energy are used to create an output o...
Is Geothermal Energy Efficient?
- Geothermal heat pumps are efficient in many ways. Due to their efficiency, they use less electricity than conventional furnaces and air heat pumps. According to the EPA, GHPs use 72% less energy than a traditional furnace.
Final Thoughts
- To summarise, a geothermal heat pump is an efficient way to heat and cool your home. It’s 72% more efficient than conventional heating methods and 44% more efficient than AHPs. The calculation to determine your geothermal heat pump electrical usage is easy: 1. Firstly,you need to know the area of the space you’d like to heat and the SEER of your heat pump. 2. Secondly, use t…
Direct Use and District Heating Systems
- Direct use and district heating systems use hot water from springs or reservoirs located near the surface of the earth. Ancient Roman, Chinese, and Native American cultures used hot mineral springs for bathing, cooking, and heating. Today, many hot springs are still used for bathing, and many people believe the hot, mineral-rich waters have health benefits. Geothermal energy is als…
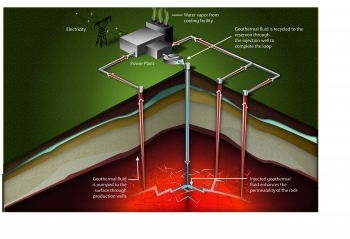
Geothermal Electricity Generation
- Geothermal electricity generation requires water or steam at high temperatures (300° to 700°F). Geothermal power plants are generally built where geothermal reservoirs are located, within a mile or two of the earth's surface. The United States leads the world in the amount of geothermal electricity generation. In 2021, there were geothermal power p...
International Geothermal Electricity Generation
- In 2019, 27 countries, including the United States, generated a total of about 88 billion kWh of electricity from geothermal energy. Indonesia was the second-largest geothermal electricity producer after the United States, at nearly 14 billion kWh of electricity, which was equal to about 5% of Indonesia’s total electricity generation. Kenya was the eighth-largest geothermal electricit…
Geothermal Heat Pumps
- Geothermal heat pumpsuse the constant temperatures near the surface of the earth to heat and cool buildings. Geothermal heat pumps transfer heat from the ground (or water) into buildings during the winter and reverse the process in the summer. Last updated: March 18, 2022 with preliminary data for the United States from the Electric Power Monthly, February 2022.