
What should you do if your ear hurts?
- Ear infections are the most common cause of earaches, but there can be other causes as well. ...
- Depending on what’s causing your earache, your doctor might prescribe oral antibiotics, eardrops, or some other type of medication.
- If you think your baby or child has an earache, call their doctor for advice right away. ...
Why are ear tubes sometimes necessary?
- reduce the risk of future ear infection
- restore hearing loss caused by middle ear fluid
- improve speech problems and balance problems
- improve behavior and sleep problems caused by chronic ear infections
How long do ear tubes stay in for ear infections?
To allow air to enter your ear and to drain fluids, the surgeon inserts the tiny tube into the hole made by the incision. The surgeon may place short-term tubes, which are smaller and remain in the ear for 6 to 12 months before falling out on their own, or long-term tubes, which are larger and typically stay in place for a longer period of time.
How do ear tubes help for ear infections?
What are ear tubes and how are they placed?
- The (Eustachian) tube creates and allows an equalization of air pressure between the outer ear and the middle ear by replacing air that has leaked out into the surrounding tissue. ...
- There are two types of ear tubes:
- Short-term tubes are smaller and typically stay in place for six months to a year before falling out on their own.

Is getting ear tubes painful?
Most children have little pain after ear tube placement and usually recover quickly. Your child will feel tired for a day. But your child should be able to go back to school or daycare the day after surgery.
How long does it take to recover from ear tube surgery?
What is the recovery time? Your child will recover within a few days. There will be some drainage and slight pain, but this will go away in three to four days. There are some bathing and swimming restrictions because water in the ear can result in infection.
Are you awake when they put tubes in your ears?
Ear tube surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia. Adults may be placed under local anesthesia, depending on the situation.
How long does it take to put tubes in ears?
An ear tube procedure only takes 10 to 15 minutes to complete and is typically done in both ears. A pediatric ear, nose and throat surgeon, also known as an ENT or otolaryngologist, inserts a tiny metal or plastic tympanostomy tube, or ear tube, into the eardrum.
How serious is ear tube surgery?
Are There Any Risks From Ear Tube Surgery? This is a very common and safe procedure, although there are risks with any surgery, including infection, bleeding, and problems with anesthesia. Rarely, the hole in the eardrum does not close after the tube comes out, and might need to be fixed surgically.
Are ear tubes worth it?
While ear tubes are not medically necessary, they can help relieve the pain of middle ear infections and make those infections easier to manage. Your child's doctor may recommend ear tubes if your child has: Hearing loss due to fluid build-up or. More than 3 ear infections in 6 months or.
How do you prepare for ear tubes?
The night before surgery, you should not let your child eat or drink anything after midnight. If you've been instructed to give your child drugs, only let them take a small sip of water to wash them down. Be sure to arrive at the hospital on time. If your child is ill, you'll have to reschedule.
How long do ears bleed after tubes?
Ear Tube Pain and Drainage Your child may have a small amount of blood-tinged drainage from the ear for 1-2 days after the operation. If the drainage persists, there could be an infection.
Do ear tubes help immediately?
If you or your child suffered hearing loss related to a middle ear infection, your hearing might get better right away, but it usually takes about two weeks to notice a significant improvement. Also, hearing after ear tube surgery can be sensitive – avoiding loud noises for a few weeks can help your ears as they heal.
What not to do after getting tubes in ears?
Do not put anything (such as a cotton swab) into the ear, as these can cause damage to the eardrum. Water exposure/swimming: Your child can bathe or shower normally after ear tube placement, however, you may use earplugs to avoid soapy water entering the ears as an extra precaution to prevent infection.
How long after ear tubes can you shower?
Swimming/ bathing Try to avoid water from entering into the ear for up to 10 days. However, it is more of a problem if soap enters the ear through the tubes than if water does. For this reason, when washing hair or showering, use ear plugs.
Do you have to wear ear plugs after tubes?
Some children with ear tubes wear ear plugs when swimming. The ear plugs keep water out of the ear canal and out of the ear tube. However, water does not usually go through the tube during swimming. As a result, ear plugs are not necessary for most children.
How many days rest after ear surgery?
There are some limitations on activity until the incision behind the ear heals. Your child should limit activities for the first 7 to 10 days after surgery, avoiding exertion or active play.
Do and don'ts after ear surgery?
Avoid sudden head movements and bending over for the first 2 or 3 days after surgery. These actions may make you dizzy. Avoid strenuous activities, such as bicycle riding, jogging, weight lifting, or aerobic exercise, for about 2 to 4 weeks or until your doctor says it is okay.
Is ear surgery considered major surgery?
Otoplasty, as with any other type of major surgery, has risks, including the risk of bleeding, infection and an adverse reaction to anesthesia. Other risks associated with otoplasty include: Scarring. While scars are permanent, they'll likely be hidden behind your ears or within the creases of your ears.
What to expect after tubes put in ears in adults?
What to expect after surgery. Once the tubes are inserted, the patient may feel some popping, pulsation, or clicking in the ear. There will also be some minor pain, especially when burping, chewing, or yawning. The fluid will slowly run out as the days progress, and some patients see a clear discharge on the ear.
What is the purpose of an ear tube?
This opening enables drainage of the middle ear, allows air to flow into the middle ear and prevents the buildup of fluids behind the eardrum. An ear tube is usually made of metal or plastic.
How long does it take for an ear tube to fall out?
Even with ear tubes, your child may still get an occasional ear infection. Usually, an ear tube stays in the eardrum for four to 18 months and then falls out on its own. Sometimes, a tube doesn't fall out and needs to be surgically removed.
What are the conditions that can be treated with ear tubes?
Conditions that may be treated with ear tubes generally have two related features: Inflammation (otitis media) Buildup of fluids (effusion) Ear tubes may be an appropriate treatment for the following conditions: Middle ear infection (acute otitis media) is caused by a bacterium or virus.
What bones are in the middle ear?
Close. Middle ear. Middle ear. The middle ear includes three small bones — the hammer (malleus), anvil (incus) and stirrup (stapes). The middle ear is separated from your external ear by the eardrum and connected to the back of your nose and throat by a narrow passageway called the eustachian tube. The cochlea, a snail-shaped structure, is part ...
What is the eustachian tube?
In young children, the eustachian tube is short, floppy and mostly horizontal — factors that can lead to dysfunction or blockage of the tube.
Why do children need ear tubes?
Ear tubes are often recommended for children who have persistent fluid buildup behind the eardrum, especially if the condition causes hearing loss or affects speech development. Your child's doctor may also recommend ear tubes if your child gets frequent ear infections.
What is the cochlea?
The cochlea, a snail-shaped structure, is part of your inner ear. Ear tubes (tympanostomy tubes, ventilation tubes, pressure equalization tubes) are tiny cylinders, usually made of plastic or metal, that are surgically inserted into the eardrum.
Why do doctors insert ear tubes?
An ear tube insertion is when a doctor inserts tiny tubes, known as tympanostomy tubes or grommets, into the eardrum to reduce the occurrence of ear infections and allow drainage of excess fluids. The procedure is very common and poses minimal risks. An ear tube insertion is more common for children, who tend to suffer ear infections more often ...
Why do we need tubes for antibiotics?
Tubes also make it easier to use antibiotic drops in the ears to treat infections. The tubes function as a passageway, permitting the drops to travel directly into the ear. Because they make antibiotic drops easier to use, the tubes can eliminate the need for oral antibiotic treatment. Ear tube insertion, also called myringotomy ...
What is the procedure for ear tube insertion?
What’s the procedure for ear tube insertion? For the insertion, an otolaryngologist (ear, nose, and throat doctor) places tiny plastic or metal tubes in the eardrum. Once inside the ear, these tubes will: Reduce pressure. Ear infections and fluid buildup increase pressure inside the ear, which is what causes pain.
How to do ear surgery?
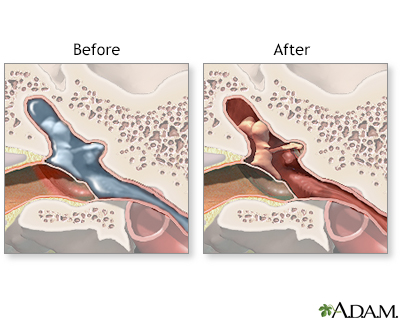
The actual surgery takes only about 10 to 15 minutes. During this time, the surgeon performs the following steps: 1 Makes an incision. The surgeon makes a tiny incision in the eardrum with a small scalpel or laser. If left alone, this incision would close and heal within a few days. 2 Removes fluid. Using a tiny vacuum, the surgeon suctions out any excess fluids from the middle ear, cleaning out the area. This is called aspiration of the middle ear. Your doctor will determine if this step is necessary. 3 Inserts the tube. To allow air to enter your ear and to drain fluids, the surgeon inserts the tiny tube into the hole made by the incision. The surgeon may place short-term tubes, which are smaller and remain in the ear for 6 to 12 months before falling out on their own, or long-term tubes, which are larger and typically stay in place for a longer period of time.
Why do children need ear tubes?
Individuals who suffer from severe ear infections that spread to nearby tissues and bones, or experience a pressure injury from flying or deep sea diving may also require an ear tube insertion.
Why do children have ear tubes inserted?
The procedure is usually performed because of bacteria that travel from the nasal cavity into the ear during a cold or other respiratory ailment. This influx of bacteria stimulates inflammation ...
What is ear tube placement?
Ear tube insertion, also called myringotomy and tympanostomy tube placement, is a very common procedure performed under general anesthesia. During the procedure, the patient is asleep and breathing on their own. The surgical team monitors heart rate, blood pressure, and blood oxygen throughout the surgery.
Who needs ear tubes?
Middle ear infections and fluid are thought to result from problems with a child’s eustachian tube — the tube that connects the open space behind the nose (the nasopharynx) to the middle ear space. The eustachian tube permits air to ventilate the middle ear and allows the drainage of normal ear fluid into the nasopharynx.
How is the surgery performed?
A surgeon who specializes in ear, nose and throat conditions will perform your child’s ear tube placement procedure. In most cases, this is an outpatient surgery, which means your child will have surgery and go home the same day.
What happens if a tube falls out of a child's ear?
They may fall out and leave a hole in the ear drum. This is typically the result of the ear drum being in poor condition and not having sufficient healing capacity to close the small incision site in the ear drum (the myringotomy site) after the tube has fallen out. Extremely thin drums or drums with a lot of scar tissue (known as myringosclerosis) have a harder time healing. If this occurs, your child’s doctor will wait to see if the perforation will spontaneously close. If it fails to close, another operation to repair the hole (paper patch, myringoplasty or tympanoplasty) is typically recommended.
What is the tube in the middle of a child's ear called?
Ear tubes may also be called tympanostomy tubes, myringotomy tubes or ventilation tubes.
How to treat ear infection in children?
Even if your child develops an ear infection with tubes in place, many of these infections can be treated by putting antibiotic drops in the affected ear rather than having to resort to oral antibiotics. Improve hearing or correct hearing problems caused by the presence of either fluid or negative pressure. Improve speech development.
How long does it take for ear tubes to fall out?
Ear tubes are generally extruded (forced out naturally as the child’s ear grows) from the ear drum anywhere from six to 18 months after insertion. If the tubes fall out and your child still has frequent ear infections, continues to accumulate fluid, or his eardrum collapses again, he may need to have the tubes reinserted.
What is the purpose of the eustachian tube?
The eustachian tube permits air to ventilate the middle ear and allows the drainage of normal ear fluid into the nasopharynx. A child’s eustachian tube is narrower, shorter and more horizontally positioned than an adult’s.
What Is Ear Tube Placement Surgery?
The surgical placement of ear tubes is a relatively simple procedure that involves making a small hole in the tympanic membrane (eardrum) with a scalpel or laser—a procedure called a myringotomy —and then inserting a synthetic tube.
What is the procedure to implant a synthetic ear tube?
Ear tube placement surgery is a procedure to implant synthetic ear tubes inside of the auditory tube, also known as the eustachian tube. In adults, it may be done for people who are having trouble hearing because of a buildup of fluid in the middle ear or have experienced barotrauma due to extreme air pressure changes.
What is an artificial ear tube?
In adults, artificial ear tubes are used to ventilate and drain the middle ear and treat certain conditions after first-line treatment has failed. Conditions that may require a myringotomy with ear tube insertion include:
How long do synthetic ear tubes last?
The type of tube used will depend on your condition and how your inner ear is shaped. Short-term tubes, commonly used in children, last 6 to 18 months and typically fall out on their own.
What is the tube called that holds the auditory tube open?
The tubes, also called pressure equalization tubes, ventilation tubes, ear grommets , or tympanostomy tubes, are used to temporarily hold the auditory tube open and to allow proper ventilation and drainage of the middle ear. Verywell / JR Bee.
What causes ear infections that do not resolve?
Ear infections that are frequent or do not resolve with other treatments. Retracted eardrums. Auditory tube dysfunction (a condition often caused by chronic allergies in adults) Barotrauma due to air pressure changes, such as during air travel or scuba diving.
How long does it take to drive home after ear tube placement?
You will be given instructions for aftercare and to schedule a follow-up visit in two to four weeks. Most people are able to drive themselves home after having ear tubes placed in-office.
What is the respiratory system that wakes you up with a stuffy nose and sore throat?
Have you ever woken up with sinus pressure, a stuffy nose and sore throat? That’s your sinuses reacting to an irritant. Here are a few tips from Dr. Dean to keep your respiratory system healthy: 1. Proper Hygiene Much like…
What are the different types of sinuses?
Everyone has 4 different types of sinuses: maxillary (cheekbones), frontal (forehead), ethmoid (between the eyes), and sphenoid sinuses (behind the nose). Together, they make up an interconnected web of hollow cavities. Sinuses are lightly lined with mucus and help to…
How much mucus does your nose produce?
Your nose is almost constantly producing mucus. In fact, it makes approximately a quart of it each day. Mucus performs necessary functions including trapping bacteria and moistening the airways, but overproduction can lead to some annoying side effects. Most of…
What happens when the weather turns cold?
When the weather turns cold, many people experience pain or discomfort in their ears, nose and throat. People often confuse symptoms caused by cold weather with illness or infection (or vice versa). It is important to know how cooler weather can affect your respiratory…. read more.
How many people get headaches a year?
It is estimated that approximately 45 million Americans complain of headaches each year, which comes to nearly 17% of the population. While some can be minor and go away quickly, others can become serious, and require daily treatment of some sort. The big question is,…
How long should you use ear tubes for a child?
Some doctors jump the gun with ear tubes. They should only be used if a child has at least four ear infections within a six month period. Ear Tubes can improve hearing for children.
What drains fluid from the ears?
Tubes drain the fluid that sits in the ears, resulting in less pressure.
How long does it take for ear drainage to stop?
Chronic Ear Drainage. Normally, after the tube has been inserted, it takes two days maximum in order for any excess fluid to be drained. However, sometimes, as a complication from the surgery, the patient can deal with chronic ear drainage that lasts more than four days. 3. An Ear Infection.
Why do people have ear tubes removed?
Frequent ear infections, fluid build-up in the ear, auditory tube dysfunction, and retracted eardrums are the most common reasons for an ear tube surgery to be performed within adults. As a part of the procedure, the adenoids, which are the glands that are located above the roof of the mouth and behind your nose, can be removed as well.
Why does my hearing get muffled after ear tube surgery?
Muffled Hearing After The Ear Tube Surgery. The muffled hearing is a common side-effect of the middle ear infection itself. The hearing is muffled because there is fluid build-up due to either inflammation or swelling of the middle ear and eardrum. It might take a few days for the inserted ear tube to drain the fluid so ...
How long does it take for a muffled ear to go away?
It might take a few days for the inserted ear tube to drain the fluid so that the muffled hearing would finally go away. Even if you did not struggle with a muffled hearing before the surgery itself, it is very common to deal with it when it is done. 2. Chronic Ear Drainage.
How to protect your ears after ear surgery?
Do keep a small piece of cotton inside the ear to absorb any discharge, bloody or yellow colored that might happen after the surgery.
Can ear infections continue?
Unfortunately, sometimes even when the ear tubes have been properly inserted, ear infections can continue to occur. However, this is a complication that is more commonly noticed to develop within children rather than adults, since it is the children’s eat tubes that need to be replaced from time to time. That is usually when ear infections develop the most.
Is it safe to have an ear tube removed?
The ear tube surgery is considered to be generally safe, posing minimal risks only. This is an outpatient procedure, which means that after the procedure has been successfully completed, patients are free to go home.
What does it mean when your ear hurts?
Doctors call this type of pain that starts in one area but is felt in another “referred pain.”. If your earache comes with a severe sore throat, it could be an infection like tonsillitis or pharyngitis. In fact, ear pain is often the worst symptom of one of these conditions. Learn more about sore throat symptoms.
How to treat ear wax?
You can treat mildly impacted ears at home with over-the-counter ear drops that soften the wax so it can naturally drain. Or go see your doctor if the wax has hardened. She can get the wax out without damaging the eardrum. Learn more about earwax.
How to stop jaw pain from grinding teeth?
The ache in your ears or face comes after you chew, talk, or yawn. To treat it, take over-the-counter pain medicine and put warm compresses on your jaw. Try not to clench your teeth. You may benefit from using a mouth guard when you sleep. This can help ease the tension that causes ear pain. Eating soft foods will help, too. Learn more about causes of jaw pain.
What happens if you don't treat ear infection?
Let her know if your pain doesn’t improve or returns. If it isn’t treated, a middle ear infection can spread or cause hearing loss. Learn more about ear infection treatments. You may feel pain in your ears even when the source is somewhere else in your body, like a toothache.
Why does my middle ear hurt?
Middle Ear Infection. A cold, allergies, or a sinus infection can block the tubes in your middle ear. When fluid builds up and gets infected, your doctor will call it otitis media. This is the most common cause of ear pain. If your doctor thinks the cause is a bacteria, she may prescribe antibiotics.
What does it mean when your ear pops when you swallow?
Air Pressure. Most of the time, your ear does a great job of keeping pressure equal on both sides of your eardrum. That little pop you feel when you swallow is part of the process. But quick changes, like when you’re on an airplane or in an elevator, can throw off the balance.
How to avoid eustachian tube dysfunction?
To avoid problems on a plane: Chew gum, suck on hard candy, or yawn and swallow during takeoff and landing. Stay awake while the plane descends.
Overview
Surgical procedure to drain out the excess fluid built up in the ear and placing tube so as to drain any left fluid.
Treatment for: Acute Otitis Media · Cholesteatoma · Eardrum Rupture
Type of procedure: Invasive
Recovery time: Can take several days
Duration: About 15-20 minutes
Hospital stay: Typically a few hours
Risks
How You Prepare
What You Can Expect
Results
- Ear tube placement is a relatively safe procedure with a low risk of serious complications. Possible risks include: 1. Bleeding and infection 2. Persistent fluid drainage 3. Blocked tubes from blood, mucus or other secretions 4. Scarring or weakening of the eardrum 5. Tubes falling out too early or staying in too long 6. Failure of the eardrum to close after the tube falls out or is removed
Clinical Trials
- You'll receive instructions from the hospital on how to prepare your child for surgery to place ear tubes. Information to providemay include: 1. All medications your child takes regularly 2. Your child's history or family history of adverse reactions to anesthesia 3. Known allergy or other negative reactions to medications, such as antibiotics Questions to askyour doctor or the hospit…