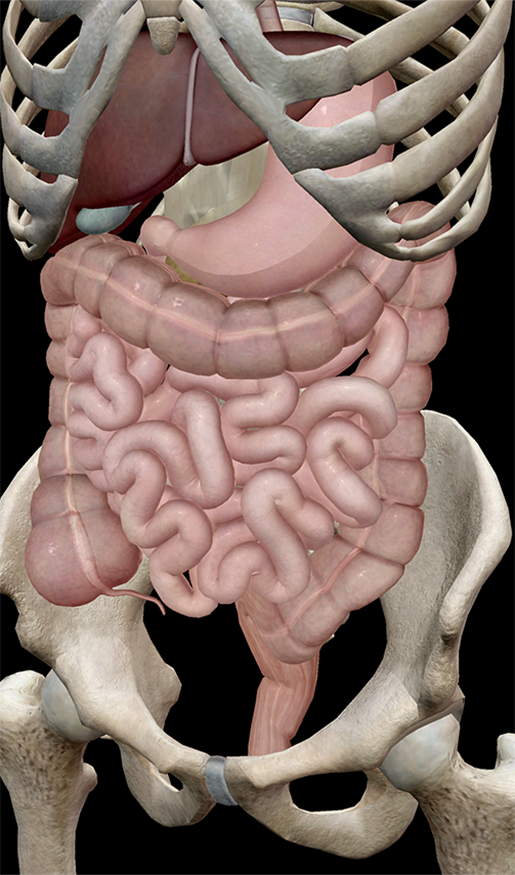
Gut or the intestine is the place where most of the nutrients and water being absorbed into the body through mesenteries. The small intestine and the large intestine are the two major parts of the gut, and the small intestine contains three major parts known as duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Full Answer
Is the large intestine part of the digestive system?
The large intestine is the last part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, the long, tube-like pathway that food travels through your digestive system. It follows from the small intestine and ends at the anal canal, where food waste leaves your body.
What is the function of the gut?
Gut or the intestine is the place where most of the nutrients and water being absorbed into the body through mesenteries. The small intestine and the large intestine are the two major parts of the gut, and the small intestine contains three major parts known as duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Where is the gut located?
Where is the gut found? The mouth is the first part of the gut (gastrointestinal tract). When we eat, food passes down the gullet (oesophagus), into the stomach, and then into the small intestine. The small intestine has three sections - the duodenum, jejunum and ileum.
What are the two major parts of the gut?
The small intestine and the large intestine are the two major parts of the gut, and the small intestine contains three major parts known as duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.

Is gut the same as intestine?
Your gut is quite literally your intestines, although the word is frequently used for any part of your digestive system, especially your stomach.
What is considered your gut?
These organs include the mouth, pharynx (throat), esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. The gastrointestinal tract is part of the digestive system.
Is gut and small intestine the same thing?
Where is the gut found? The mouth is the first part of the gut (gastrointestinal tract). When we eat, food passes down the gullet (oesophagus), into the stomach, and then into the small intestine. The small intestine has three sections - the duodenum, jejunum and ileum.
What is the large intestine called?
colonLarge intestine (colon)
What does gut mean in medical terms?
digestive tractMedical Definition of gut (Entry 1 of 2) 1a : digestive tract also : part of the digestive tract and especially the intestine or stomach the mix of bacteria making up the flora of the gut — W. E. Leary.
How do I heal my gut?
10 Steps To Heal Your Gut NaturallyPROBIOTICS WILL CHANGE YOUR LIFE. Probiotics are the live microorganisms (good bacteria) that reside in the gut. ... NOURISH YOUR BODY WITH PREBIOTICS. ... DRINK WATER + TEA. ... REMOVE INFLAMMATORY FOODS. ... FALL IN LOVE WITH KIWI FRUIT. ... NOURISH WITH COLLAGEN. ... ENJOY A GLASS OF GREEN JUICE. ... EXERCISE DAILY.More items...
What are the signs of a healthy gut?
These daily bowel movements should be free of symptoms like diarrhea, constipation, and loose stools. Other signs of a healthy gut include being free of rectal symptoms like hemorrhoids and abdominal symptoms such as gas, bloating, and abdominal pain. In other words, the gut just works.
What is leaky gut?
Leaky gut syndrome is a theory that intestinal permeability is not only a symptom of gastrointestinal disease but an underlying cause that develops independently. If your intestinal barrier is impaired, it may be letting toxins into your bloodstream.
Why is a healthy gut important?
The gut microbiome plays a very important role in your health by helping control digestion and benefiting your immune system and many other aspects of health. An imbalance of unhealthy and healthy microbes in the intestines may contribute to weight gain, high blood sugar, high cholesterol and other disorders.
What are the 3 parts of large intestine?
The large intestine is one long tube, but slightly different things happen in different parts of it. Its three parts are the colon, the rectum and the anus.
Is the colon and large intestine the same?
The colon is also known as the large bowel or large intestine. It is an organ that is part of the digestive system (also called the digestive tract) in the human body.
What causes pain in the large intestine?
Causes. Pain that's located in the large intestine or colon may be caused by constipation, diarrhea, IBS, colitis, diverticular disease, or colorectal cancer.
Where does the gut begin and end?
The digestive tract begins at the mouth and ends at the anus. It is like a long muscular tube, up to 10 metres long, with digestive organs attached along the way. A large reservoir of microbes, such as bacteria, live within the large intestine and, to a lesser degree, in vthe rest of the digestive system.
What is the difference between the gut and the stomach?
The main difference between stomach and gut is that stomach is a part of the gastrointestinal tract (GI) whereas the gut is the entire gastrointestinal tract: from mouth to anus. The stomach and gut are two parts of the digestive system of an animal.
What are the symptoms of an unhealthy gut?
Here are 10 warning signs you may have an unhealthy gut.You have an upset stomach. ... You feel tired more often than not. ... You have trouble sleeping in general. ... You are intolerant to some foods. ... You have extreme food cravings, especially sugar. ... You have unintentional weight gain or loss. ... You have skin irritations.More items...•
What are the symptoms of gut problems?
The first sign of problems in the digestive tract often includes one or more of the following symptoms:Bleeding.Bloating.Constipation.Diarrhea.Heartburn.Incontinence.Nausea and vomiting.Pain in the belly.More items...•
What does the gut do?
The gut (gastrointestinal tract) processes food - from the time it is first eaten until it is either absorbed by the body or passed out as stools (faeces). The process of digestion begins in the mouth. Here your teeth and chemicals made by the body (enzymes) begin to break down food. Muscular contractions help to move food into the gullet (oesophagus) and on to the stomach. Chemicals produced by cells in the stomach begin the major work of digestion.
What is the first part of the large intestine called?
Following on from the ileum is the first part of the large intestine, called the caecum. Attached to the caecum is the appendix. The large intestine continues upwards from here and is known as the ascending colon. The next part of the gut is called the transverse colon because it crosses the body.
What is the first part of the digestive system?
The mouth is the first part of the gut (gastrointestinal tract). When we eat, food passes down the gullet (oesophagus), into the stomach, and then into the small intestine. The small intestine has three sections - the duodenum, jejunum and ileum. The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine and follows on from the stomach.
What organ is responsible for lubricating food?
The food passes into your oesophagus. The oesophagus releases mucus to lubricate food. Muscles push your meal downwards towards the stomach. The stomach is a j-shaped organ found between the oesophagus and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). When empty, it is about the same size as a large sausage.
How many sphincters does the stomach have?
Using its muscles, the stomach then pushes small amounts of food (now known as chyme) into the duodenum. The stomach has two sphincters, one at the bottom and one at the top. Sphincters are bands of muscles that form a ring. When they contract the opening, the control closes.
How does the stomach work after eating?
A few minutes after food enters the stomach the muscles within the stomach wall start to tighten (contract). This creates gentle waves in the stomach contents. This helps to mix the food with gastric juice. Using its muscles, the stomach then pushes small amounts of food (now known as chyme) into the duodenum.
What is the function of the stomach?
Its main function is to help digest the food you eat. The other main function of the stomach is to store food until the gastrointestinal tract (gut) is ready to receive it . You can eat a meal faster than your intestines can digest it. Digestion involves breaking food down into its most basic parts.
What is the large intestine?
What is the large bowel (large intestine)? The large bowel or large intestine is part of the digestive system. It includes the colon and rectum. The large intestine plays a vital role in removing waste from the body. Liquid food waste from the small intestine goes into the large intestine, where it turns solid.
What is a large bowel obstruction?
A large bowel obstruction is a medical emergency. It occurs when a tumor, scar tissue or something else blocks the large intestine. Gas and stool build up, and the intestine may rupture. Some bowel obstructions improve with minimal treatment in the hospital. Some people need surgery.
What happens if you have a blockage in your bowel?
A bowel blockage can stop blood flow, causing part of the intestine to die. As pressure builds up from the blockage, intestinal bacteria can leak into the bloodstream. You may develop peritonitis, an abdominal infection. You are also at risk for a life-threatening system-wide infection called sepsis.
What percentage of intestinal blockages are caused by large bowel obstruction?
Large bowel obstructions account for about 20% of all intestinal blockages. Small bowel obstructions are more common.
What happens when bowels block?
A bowel blockage can stop blood flow, causing part of the intestine to die. As pressure builds up from the blockage, intestinal bacteria can leak into the bloodstream.
Can a large intestine block a bowel?
An intestinal blockage can occur anywhere in the large intestine. The large bowel obstruction may block the bowel completely or partially. A blocked intestine may rupture, causing a life-threatening infection. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission.
Can a large bowel obstruction be surgically treated?
A large bowel obstruction is a serious medical emergency. Not all bowel blockages require surgery. But you still need to be in the hospital. There, your healthcare provider can treat dehydration and drain excess fluid. This care can prevent more serious problems. Most surgically treated bowel blockages improve, resulting in normal bowel function afterward.
How long is the large intestine?
Your large intestine is about five feet (or 1.5 meters) long. The large intestine is much broader than the small intestine and takes a much straighter path through your belly, or abdomen. The purpose of the large intestine is to absorb water and salts from the material that has not been digested as food, and get rid of any waste products left over. By the time food mixed with digestive juices reaches your large intestine, most digestion and absorption has already taken place.
What Is the Small Intestine?
The small intestine is made up of three segments, which form a passage from your stomach (the opening between your stomach and small intestine is called the pylorus) to your large intestine:
How much food does the small intestine absorb?
Each day, your small intestine receives between one and three gallons (or six to twelve liters) of this liquid . The small intestine carries out most of the digestive process, absorbing almost all of the nutrients you get from foods into your bloodstream. The walls of the small intestine make digestive juices, or enzymes, that work together with enzymes from the liver and pancreas to do this.
Which part of the large intestine absorbs salts?
It takes in digested liquid from the ileum and passes it on to the colon. Colon: This is the major section of the large intestine; you may have heard people talk about the colon on its own. The colon is also the principal place for water reabsorption, and absorbs salts when needed. The colon consists of four parts:
What are the three features of the small intestine?
The small intestine has three features which allow it to have such a huge absorptive surface area packed into a relatively small space: Mucosal folds: The inner surface of the small intestine is not flat, but thrown into circular folds. This not only increases the surface area, but helps regulate the flow of digested food through your intestine. ...
Which part of the small intestine is the longest?
Jejunum: The middle section of the small intestine carries food through rapidly, with wave-like muscle contractions, towards the ileum. Ileum: This last section is the longest part of your small intestine. The ileum is where most of the nutrients from your food are absorbed before emptying into the large intestine.
How big is the rectum?
Rectum: The final section of digestive tract measures from 1 to 1.6 inches (or 2.5 to 4 cm). Leftover waste collects there, expanding the rectum, until you go to the bathroom. At that time, it is ready to be emptied through your anus. Learn more about Intestine Transplant Disease States.
As nouns the difference between intestine and gut
is that intestine is (anatomy|often pluralized) the alimentary canal of an animal through which food passes after having passed all stomachs while gut is the alimentary canal, especially the intestine.
As adjectives the difference between intestine and gut
is that intestine is domestic; taking place within a given country or region while gut is made of gut, eg, a violin with gut strings .
What is the difference between a stomach and a gut?
What is the difference between Gut and Stomach? • Both are hollow structures, but the stomach is J-shaped with a large cavity, and the hollow is not very long, whereas the gut is the longest organ of the body and it is not broad. • Stomach performs many functions, but digestion is the main responsibility.
What is the meaning of the word "intestine"?
Despite the colloquial meaning of the gut being the entire alimentary tract , the intestine is the main meaning of the term. This article reviews the characteristics of both gut and stomach separately and then presents a comparison between those for a better understanding.
What is the function of the small intestine?
The small intestine absorbs mainly the nutrients of the digested food while the large intestine mainly absorbs water from food. Small intestine is the longest organ of the body, which is usually three times as the height of the particular person. The microstructure of the gut is extremely adapted for the absorption of food with the presence of villi and mirovilli. These microstructures are small projections towards to inner lumen of the intestine, so that the surface area is large and that facilitates more absorption of nutrients from digested food. The networks of capillaries absorb the nutrients through four main processes known as Active transport, Passive diffusion, Endocytosis, and Facilitative diffusion. The duodenum performs two main functions including chemical digestion and absorption, but jejunum and ileum are mainly responsible for absorption. The vitamins, lipids, Irons, sugars, amino acids, and water are mainly absorbed in the gut.
What is the function of the stomach?
The overall structure of the stomach is large, muscular, and hollow. The main functions of the stomach are chemical and mechanical digestion of food, in addition to absorption of nutrients from the digested food. What is the difference between Gut and Stomach?
How does the stomach help with enzymatic digestion?
It performs both mechanical and chemical digestion respectively via peristalsis and secretion of protein digesting enzymes. Stomach secretes strong acids as well , which helps for enzymatic digestion. The strong layer of muscles around the stomach helps the mechanical digestion of food through producing peristaltic movements.
Which organ is responsible for absorption of nutrients?
The duodenum performs two main functions including chemical digestion and absorption, but jejunum and ileum are mainly responsible for absorption. The vitamins, lipids, Irons, sugars, amino acids, and water are mainly absorbed in the gut.
What is the shape of the stomach?
Usually, the stomach is a J-shaped organ, but the shape varies drastically within species. The structure in ruminants is a great variation from all other species, as the rumen has four distinct chambers. However, the relative location of the stomach is the same in most of the animals.
What is the pain in the large intestine?
Pain in the large intestine is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the abdomen, stomach region or belly. Acute abdominal pain has many potential underlying causes, ranging from benign, self-limited conditions to life-threatening surgical emergencies.
What does it mean when you feel pain in your stomach?
Other ways to describe pain in your abdomen include: Generalized pain: This means that you feel it in more than half of your belly. This type of pain is more typical for a stomach virus, indigestion, or gas. If the pain becomes more severe, it may be caused by a blockage of the intestines.
Why does my gallbladder hurt after eating?
Gallbladder pain may develop after meals as can pain from the pancreas and intestinal obstruction. The irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal problem which typically is associated with gaseous or crampy pain after meals along with a sensation of bloating.
Where is the gallbladder pain located?
Pain from the gallbladder and an inflamed liver will more often be located toward the right side of the upper abdomen. Gallbladder pain may also radiate through the right shoulder blade. Pain from an ulcer or irritation of the pancreas may radiate through to the back.
How long does diarrhea last?
It is likely to be due to gas and bloating, and is often followed by diarrhea. More worrisome signs include pain that occurs more often, lasts than 24 hours, or occurs with a fever. Colicky pain: This type of pain comes in waves. It very often starts and ends suddenly, and is often severe.
Why does my belly hurt?
It very often starts and ends suddenly, and is often severe. Kidney stones and gallstones are common causes of this type of belly pain. Constant pain. There may be some variation in the intensity but, overall, this type of pain is distinctively steady.
Where does pain come from in the belly?
Pain arising from the large intestine pain may localize to either the right, left, or middle of the abdomen below the belly button. Pain developing from inside the pelvis will often be experienced as a pressure-like discomfort in the rectal area.
What is the procedure to remove a small intestine?
Sometimes, a piece of the intestine will need removal. The removal of a portion of either the small or large intestine may result in a colostomy or ileostomy, which allows intestinal contents to drain or empty into a bag attached to your abdominal wall.
What is a hole in the gallbladder?
A hole in your gastrointestinal system or gallbladder can lead to peritonitis. Peritonitis is inflammation of the membrane that lines the abdominal cavity. It occurs when any of the following enters the abdominal cavity: GP is a medical emergency that requires immediate medical care. The condition is life-threatening.
How to fix peritonitis?
fix the cause of peritonitis. remove any foreign material in the abdominal cavity that might cause problems, such as feces, bile, and food. In rare cases, your doctor may forgo surgery and prescribe antibiotics alone if the hole closed on its own. Sometimes, a piece of the intestine will need removal.
Why does my gallbladder get perforated?
It can be due to a number of different diseases , including appendicitis and diverticulitis. It can also be the result of trauma, such as a knife wound or gunshot wound. A perforation may also occur in the gallbladder. This can have symptoms that are similar to the symptoms of a gastrointestinal perforation.
Does peritonitis hurt when lying down?
Pain often worsens when someone touches or palpates the area or when the patient moves. Pain is generally better when lying still. The abdomen may stick outward farther than normal and feel hard. In addition to the general symptoms of perforation, symptoms of peritonitis may include: fatigue.
How Can Intestinal Infections Be Prevented?
Preventing intestinal infections is much easier said than done, because microbes and bacteria are everywhere and cover virtually every surface: they’re in the air, in the water, on the ground, and on the walls, and people are covered in them. And because bacteria are microscopic, you can’t see them, so they easily become an afterthought; that’s just human nature. But that said, there are a few easy steps you can take that can go a long way toward lowering your chances of getting an intestinal infection, including:
What is the test for bacterial infection?
A common test for a bacterial or a parasitic intestinal infection is a stool sample . If there is an outbreak of a certain infection, it’s usually localized, so with enough information, doctors can more easily pin down what’s happening to you, since it’s happening to many people.
Are Intestinal Infections Contagious?
Intestinal infections are contagious and can be spread in a number of ways, including:
Can intestinal infections cause nausea?
Intestinal infection symptoms can be extremely painful. Intestinal pain caused by bacterial infections can result in diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dehydration, headaches and a number of other uncomfortable conditions. These intestinal infections are contagious, and nearly 200 million Americans are infected every year.
Is it safe to eat meat when you have an intestinal infection?
Although eating meat isn’t the best thing for your stomach when treating intestinal infections—because it’s relatively difficult to break down and your digestive system is already taxed—you want to make sure it’s cooked properly. When meat is cooked thoroughly, infection-causing bacteria are killed. This is essential when you’re trying to recover so that you don’t feed more bad bacteria in your system. There are different cooking temperatures for different meats, so here are some guidelines:
Can you get a bacterial infection from ingestion?
You can get a bacterial infection from ingestion. Often these infections are asymptomatic, or if symptoms are present, they pass within a few days. But sometimes these infections lead to more severe complications. Here are some common infections and how they might affect you. 1.
Is Intestinal Infection Linked to Other Health Conditions?
Yes and no. Although some populations—infants, the elderly, and people with autoimmune diseases—may be more prone to and face complications from intestinal bacterial infections, the bulk of the population likely won’t develop severe long-term health conditions. However, if an infection lasts long enough or is very aggressive, it may contribute to (or be reinforced by):

Where Is The Gut Found?
What Does The Gut do?
- The gut (gastrointestinal tract) processes food - from the time it is first eaten until it is either absorbed by the body or passed out as stools (faeces). The process of digestion begins in the mouth. Here your teeth and chemicals made by the body (enzymes) begin to break down food. Muscular contractions help to move food into the gullet (oesophag...
How Does It Work?
- The mouth contains salivary glands which release saliva. When food enters your mouth the amount of saliva increases. Saliva helps to lubricate food and contains chemicals (enzymes) that start chemically digesting your meal. Teeth break down large chunks into smaller bites. This gives a greater surface area for the body's enzymes to work on. Saliva also contains special chemical…
Some Disorders of The Gut