
Rearrangement occurs during meiosis when the chromosomes line up in homologous pairs during metaphase I
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsᵻs/ is a specialized type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multicellular eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the l…
How is independent assortment related to meiosis?
The mechanics of meiosis are the foundation of independent assortment. Homologous chromosomes pair up and align in the cell’s midplane in meiosis I, so each chromosome in a pair will be found on the same side of the midplane as the other. Along the plane, all of the homologous pairs appear at random.
Does law of independent assortment occur during prophase I or metaphase I?
Does law of Independent Assortment occur during Prophase I or Metaphase I? My thinking is that it happens in Prophase I as the rest of crossing over is happening but sources say that the Law of IA happens during Metaphase I. Someone please clear this up before I go crazy. I would say Anaphase I is most relevant.
What happens during anaphase I of meiosis?
During Anaphase I of meiosis, it is most noticeable when non-homologous chromosomes are randomly distributed as sister chromatids are connected. Meiosis I assures unique gametes by separate genes that are present on other chromosomes or, in other words, genes that carry other features.
Is it true that independent assortment occurs after crossing over?
The independent assortment will be made first during meiosis, followed by cross-over. No, after crossing over, there is no independent assortment. Is it true that crossing over occurs in prophase I, while independent assortment occurs in metaphase I and anaphase I?
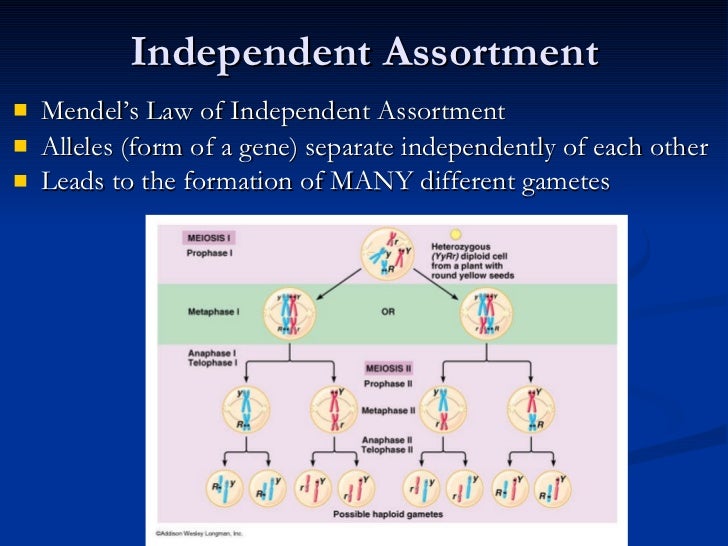
Does independent assortment occur in anaphase?
It results in new combinations of genes on each chromosome. When cells divide during meiosis, homologous chromosomes are randomly distributed during anaphase I, separating and segregating independently of each other. This is called independent assortment.
Does independent assortment occur in metaphase 1 or anaphase 1?
Answer and Explanation: The stage of meiosis where independent assortment occurs is metaphase I.
During which process does independent assortment?
meiosisWe now know that this independent assortment of genes occurs during meiosis in eukaryotes. Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in a parent cell by half to produce four reproductive cells called gametes.
What stage is independent assortment in mitosis?
metaphase IIndependent Assortment and Random Fertilization During metaphase I, the tetrads move to the metaphase plate with kinetochores facing opposite poles. The homologous pairs orient themselves randomly at the equator. This event is the second mechanism that introduces variation into the gametes or spores.
During which phase of meiosis are you most likely to observe Independent Assortment?
The independent assortment of chromosomes occurs during meiosis I. First, during prophase I, the homologous chromosomes exchange genes during a process called 'crossing over'.
In what phase of meiosis does random assortment occur?
The physical basis for the law of independent assortment lies in meiosis I of gamete formation, when homologous pairs line up in random orientations at the middle of the cell as they prepare to separate.
How and at what stage do chromosomes undergo independent assortment?
Independent assortment of chromosomes is the random distribution of one chromosome per homologous chromosomal pair to each daughter cell during anaphase I. Chromosomal crossover, which begins in prophase I, results in genetic recombination between each tetrad (homologous chromosomes).
Does Independent Assortment happen in mitosis?
When Does Independent Assortment Occur? Independent assortment occurs during the process of meiosis. Meiosis is similar to mitosis, only the final product is gamete cells. Gamete cells have half the DNA of regular, diploid cells and are considered haploid.
What is independent assortment in meiosis?
Independent assortment is the process where the chromosomes move randomly to separate poles during meiosis. A gamete will end up with 23 chromosomes after meiosis, but independent assortment means that each gamete will have 1 of many different combinations of chromosomes.
What is Independent Assortment in metaphase?
Metaphase I For example, if the two homologous members of chromosome 1 are labeled a and b, then the chromosomes could line up a-b, or b-a. This is important in determining the genes carried by a gamete, as each will only receive one of the two homologous chromosomes. This is called Independent Assortment.
Does independent assortment occur in meiosis 2?
Homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis I. Sister chromatids separate in meiosis II. Independent assortment of genes is due to the random orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I.
How does independent assortment during metaphase I help to produce diverse gametes?
The law of independent assortment states that the random orientation of homologous chromosome pairs during metaphase I allow for the production of gametes with many different assortments of homologous chromosomes.
What happens to chromosomes during anaphase 1?
During anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes are pulled toward opposite poles of the cell. During anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes are pulled toward opposite poles of the cell.
What happens during metaphase 1 of meiosis?
In metaphase I, the homologous pairs of chromosomes align on either side of the equatorial plate. Then, in anaphase I, the spindle fibers contract and pull the homologous pairs, each with two chromatids, away from each other and toward each pole of the cell.
Does independent assortment occur in mitosis?
When Does Independent Assortment Occur? Independent assortment occurs during the process of meiosis. Meiosis is similar to mitosis, only the final product is gamete cells.
What occurs during independent assortment in meiosis?
Independent assortment is the process where the chromosomes move randomly to separate poles during meiosis. A gamete will end up with 23 chromosomes after meiosis, but independent assortment means that each gamete will have 1 of many different combinations of chromosomes.